Science
How to Protect Endangered Species

Introduction
The rapid loss of biodiversity is one of the biggest challenges our planet faces today. Every year, thousands of species are pushed closer to extinction due to habitat destruction, climate change, poaching, and pollution. Protecting endangered species is not just about saving individual animals; it’s about preserving ecosystems and maintaining the delicate balance of nature.
But what can we do to stop this crisis? The good news is that conservation efforts, strong environmental policies, and public awareness can make a significant difference. In this article, we will explore how to protect endangered species, the causes of their decline, and the steps individuals and organizations can take to ensure their survival.
What Are Endangered Species?

Image by: Yandex.com
Endangered species are animals, plants, or organisms that are at risk of becoming extinct due to various environmental or human-related factors. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), species are classified into different categories based on their risk level, such as critically endangered, endangered, and vulnerable.
The loss of these species disrupts ecosystems, affecting food chains and biodiversity. If left unchecked, their extinction can have severe consequences on natural habitats, agriculture, and even human survival.
Why Are Endangered Species Important?
Endangered species play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance. Each species contributes to its habitat in a unique way, and their extinction can create a ripple effect, leading to unexpected consequences.
- Ecosystem Stability: Many species help in pollination, seed dispersal, and regulating pest populations.
- Medical and Scientific Research: Several medicinal discoveries come from plants and animals found in nature.
- Cultural and Economic Value: Many communities rely on wildlife for tourism, food, and traditional practices.
- Climate Regulation: Forests, marine life, and wildlife all contribute to absorbing carbon and reducing climate change.
By protecting endangered species, we protect our environment, future resources, and global biodiversity.
What Are the Main Causes of Endangered Species?

Image by: Yandex.com
Understanding the causes of species extinction is the first step in finding solutions. Some of the leading threats include:
1. Habitat Destruction
Deforestation, urban expansion, and industrial development destroy natural habitats, leaving animals and plants without food or shelter.
2. Climate Change
Rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and extreme events like wildfires and floods have devastating effects on wildlife populations.
3. Illegal Wildlife Trade
Poaching and illegal hunting for fur, ivory, and medicinal purposes drive many species toward extinction.
4. Pollution and Plastic Waste
Chemicals, plastics, and industrial waste contaminate water bodies and soil, affecting both land and marine species.
5. Overfishing and Overhunting
The excessive exploitation of certain species disrupts natural food chains and decreases population numbers.
The combined effect of these threats accelerates the loss of biodiversity, making conservation efforts more urgent than ever.
How Can We Protect Endangered Species?

Image by: Yandex.com
While the situation is critical, there are several effective ways to protect endangered species and restore their populations.
1. Protect and Restore Natural Habitats
One of the most effective ways to conserve species is by preserving their habitats. Governments and conservation organizations can:
- Establish protected areas such as national parks and wildlife reserves.
- Implement reforestation projects to restore lost forests.
- Support marine conservation zones to protect oceans and aquatic life.
Restoring habitats ensures that wildlife has a safe environment to thrive.
2. Strengthen Laws Against Poaching and Illegal Trade
Illegal wildlife trade is a billion-dollar industry that drives species to extinction. To combat this, governments and organizations should:
- Enforce strict anti-poaching laws with severe penalties.
- Ban the sale of endangered species products like ivory and exotic pets.
- Increase wildlife protection patrols in conservation areas.
Raising awareness about sustainable wildlife trade also helps reduce consumer demand for endangered species products.
3. Combat Climate Change
Since climate change directly affects wildlife, efforts to reduce carbon footprints can help protect species. Individuals and businesses can:
- Reduce deforestation by using recycled paper and supporting sustainable products.
- Lower carbon emissions by using renewable energy and reducing waste.
- Advocate for stronger climate policies to limit industrial pollution.
Taking action on climate change mitigation indirectly supports biodiversity conservation.
4. Reduce Pollution and Plastic Waste
Plastic pollution is a significant threat to marine life and ecosystems. To minimize its impact:
- Reduce single-use plastics and switch to reusable alternatives.
- Participate in beach and river clean-up drives.
- Support eco-friendly brands that prioritize sustainability.
Clean environments allow endangered species to thrive without the threat of toxic waste.
5. Support Conservation Programs and Organizations
Many organizations work tirelessly to protect endangered species. You can help by:
- Donating to reputable conservation groups.
- Volunteering for wildlife rescue and rehabilitation programs.
- Adopting sustainable habits to reduce environmental impact.
Supporting wildlife conservation efforts ensures long-term protection for species at risk.
6. Educate and Raise Awareness
Public awareness plays a vital role in wildlife conservation. Educating communities about the importance of biodiversity can:
- Encourage responsible tourism that does not harm wildlife.
- Promote school programs that teach children about endangered species.
- Inspire people to participate in citizen science projects to monitor species populations.
Knowledge leads to action, and collective efforts can make a significant impact.
The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity means the variety of life on Earth, from tiny insects to large mammals. It’s important because each species plays a role in keeping ecosystems balanced. When one species disappears, it can affect many others. For example, bees help pollinate plants, which helps produce food. If bees were to disappear, many plants and animals could also be at risk. Protecting biodiversity means protecting all the plants, animals, and insects that make up our world.
How Local Communities Can Help
Local communities play an important role in protecting endangered species. People who live near wildlife can help by spreading awareness and supporting conservation efforts. They can also help reduce threats to wildlife, like poaching or illegal logging, by working with conservation groups. When communities get involved, they can create a safe environment for animals while also benefiting from eco-tourism or sustainable farming practices.
The Role of Governments in Wildlife Protection

Image by: Yandex.com
Governments have a crucial role in protecting endangered species. They can create laws to stop poaching and illegal trade, as well as set up national parks and wildlife reserves. Governments can also provide funding for conservation projects and support research on how to save species. By making strong policies, governments can protect both the animals and the natural environments that they depend on.
How Technology Helps Conservation Efforts
Technology is playing a bigger role in wildlife conservation. Tools like drones, camera traps, and GPS tracking are used to monitor animals in the wild. These technologies help conservationists keep an eye on species without disturbing them. They can track migration patterns, identify threats, and even help with habitat restoration. Technology is making it easier to protect endangered species in ways that were not possible before.
The Challenges of Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife conservation faces many challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is funding conservation projects often require a lot of money to succeed. Another challenge is habitat loss, as human activity continues to destroy natural spaces. Additionally, poaching and illegal wildlife trade still threaten many species around the world.
The Future of Wildlife Conservation

Image by: Yandex.com
The future of wildlife conservation looks promising, but it will require continued effort. Advances in technology, like drones and camera traps, are helping conservationists monitor wildlife more effectively. There’s also a growing movement towards sustainable living, which will help protect natural habitats. With more awareness and action, the future holds hope for many endangered species.
Analysis Table: Simple Actions to Protect Endangered Species
| Action | Impact |
|---|---|
| Reduce plastic use | Prevents pollution in oceans and wildlife habitats |
| Support sustainable brands | Reduces deforestation and harmful industries |
| Donate to conservation groups | Funds research and wildlife protection projects |
| Participate in tree-planting activities | Restores forests and animal habitats |
| Follow ethical tourism practices | Prevents exploitation of wildlife |
Comparing Conservation Efforts in Different Countries
| Country | Conservation Efforts | Species Protected | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | National parks and reserves | Grizzly bears, wolves | Habitat loss, poaching |
| Kenya | Anti-poaching laws, community programs | Elephants, rhinos | Poaching, human-wildlife conflict |
| Australia | Marine reserves, habitat restoration | Koalas, reef species | Habitat destruction, climate change |
| Brazil | Amazon protection, wildlife corridors | Jaguars, manatees | Deforestation, illegal logging |
Conclusion
The fight to protect endangered species is one that requires global effort and individual responsibility. Every action, no matter how small, contributes to preserving biodiversity and ensuring a healthy planet for future generations.
By supporting wildlife conservation efforts, reducing pollution, and advocating for stronger environmental policies, we can help save thousands of species from extinction.
Call-to-Action (CTA)
Join the movement today! Support conservation organizations, make eco-friendly choices, and spread awareness about protecting endangered species. Every effort counts in creating a sustainable future for all life on Earth.
Care
Transform Your Smile with Dental Implants in Dubai
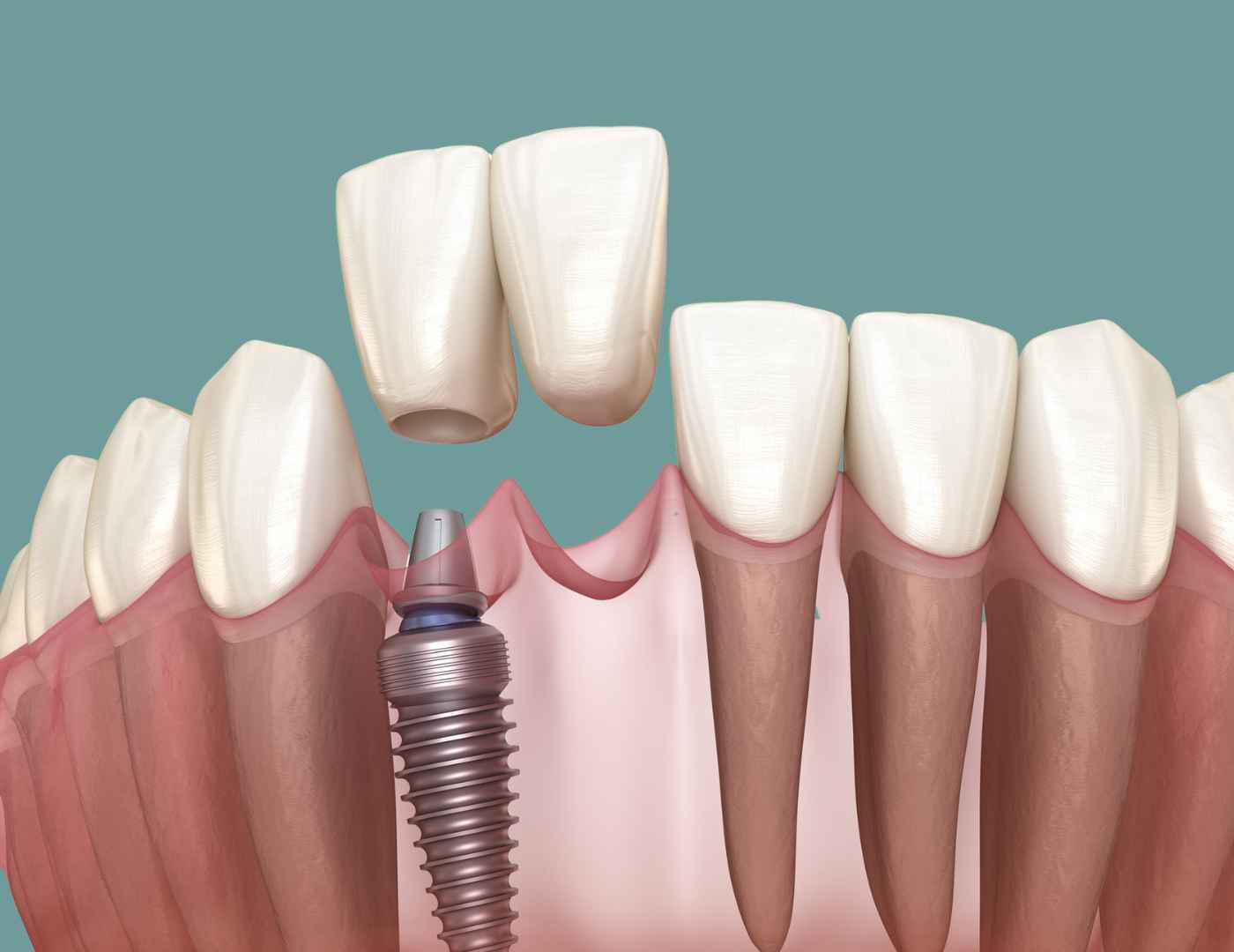
A confident smile can change the way people perceive you, and dental implants offer a remarkable way to restore both appearance and function. Dental implants have become a leading solution for individuals seeking a permanent and natural-looking replacement for missing teeth. By seamlessly integrating with the jawbone, Dental Implants Dubai provide stability and durability that other options often cannot match. From enhancing oral health to boosting self-confidence, the benefits of dental implants are extensive and transformative.
Understanding the Dental Implant Process
Dental implants are designed to replace missing teeth with results that feel and look natural. The process typically begins with a thorough evaluation to determine bone density and oral health, ensuring that the foundation is suitable for implantation. Once the assessment is complete, the implant is surgically placed into the jawbone.

Key Benefits of Dental Implants
Enhancing Aesthetic Appeal
A radiant smile plays a crucial role in self-confidence and personal presentation. Dental implant are custom-designed to match the shape, size, and color of natural teeth, creating a seamless appearance. Unlike other options, dental implants do not rely on neighboring teeth for support, ensuring a natural contour and symmetry. The result is a smile that looks authentic and enhances facial aesthetics. Individuals often notice an immediate boost in self-esteem after completing the implant process, enjoying the freedom to express themselves without hesitation.
Functional Advantages of Dental Implant
Dental implants offer more than visual enhancement. They provide a level of stability and functionality that mimics natural teeth. The secure fit allows for comfortable chewing and clear speech, restoring the ability to enjoy all types of foods without restriction. Because implants are anchored directly to the jawbone, they eliminate concerns about dentures slipping or causing discomfort. This functional reliability contributes to overall oral health by making everyday activities easier and more comfortable.
Longevity and Durability
One of the most compelling aspects of dental implant is their long-lasting nature. With proper care, dental implants can last a lifetime, making them a sustainable solution for tooth replacement. The materials used are highly resistant to decay and wear, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene ensure that implants remain strong and functional. This combination of durability and minimal maintenance makes dental implant an excellent choice for anyone seeking a permanent solution to missing teeth.
Promoting Oral Health
Common Questions
How long does the process take?
The timeline for dental implants varies depending on individual needs. Typically, the process from initial consultation to final restoration can take several months. This period allows for proper healing and osseointegration, ensuring the implant is securely anchored and ready for the final restoration.
Is the procedure painful?
Most patients report minimal discomfort during the dental implant procedure. Local anesthesia is used to ensure a comfortable experience, and post-procedure soreness is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relief. The process is designed to prioritize patient comfort and recovery.
Can anyone get dental implants?
While dental implants are suitable for many individuals, candidates must have sufficient bone density and good oral health. A thorough evaluation helps determine whether dental implants are the best solution. In some cases, preparatory procedures may be recommended to strengthen the jawbone before implant placement.
How do dental implants compare to other tooth replacement options?
Dental implants offer unique advantages, including long-term durability, natural appearance, and preservation of surrounding teeth. Their ability to restore function and aesthetics makes them a preferred choice for individuals seeking a permanent and reliable solution.
How should dental implants be cared for?
Caring for dental implants is similar to maintaining natural teeth. Daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups help ensure longevity. Because dental implants do not decay, they offer a consistent and reliable solution for maintaining oral health.
Why Choose Dental Implants Today
Cheapest Dental Implants in Dubai are more than a cosmetic enhancement—they are a comprehensive solution that addresses both functional and aesthetic needs. They empower individuals to regain confidence in their smile and enjoy everyday activities without restriction. Whether addressing a single missing tooth or multiple gaps, dental implants offer flexibility, strength, and a natural appearance. Their long-term benefits, combined with the ease of care and durability, make them a worthwhile investment in oral health and self-confidence.
Conclusion
Dental implants provide an effective, natural-looking solution for anyone seeking a complete and confident smile. By restoring function, enhancing appearance, and supporting oral health, they offer unmatched advantages over other options. Those considering dental implant can enjoy a seamless process, long-lasting results, and a boost in self-esteem that transforms both personal and social interactions. Embracing dental implant today can be the first step toward a smile that exudes confidence, health, and elegance. Take the opportunity to explore dental implants and discover how they can perfectly elevate your smile with ease.
Book literature
Effective Literature Review for Multi-Disciplinary Dissertations

Each dissertation involves a literature survey, which is the first step. It summarizes and analyzes knowledge about a particular field. In the case of multi-disciplinary dissertations, this becomes even more important because such a literature review requires the integration of diverse bodies of knowledge.
For students in need, services such as a personal statement writing service can also advise on how to provide a structured and analytical approach to academic writing. This article provides an overall guide on conducting an effective literature review in multi-disciplinary dissertation writing, with a focus on coherence and thorough analysis.

1. Understand the Purpose of a Literature Review
Every dissertation has a literature survey to lay the ground for inquiry. The ability to understand how to write a literature review for a research paper is important, as it may serve different purposes: it gives a big picture of the research already undertaken within your topic. It also pinpoints the gaps in knowledge and justifies the pursuit of your question.
2. Define the Objectives and Scope
There is a need to know how to write a literature review for a dissertation for which to understand the objectives as well as scope. Ask yourself questions like:
- What are the main themes or topics relevant to your research?
- What subjects or disciplines are central to your dissertation?
- Are there key theories, models, or frameworks to be researched?
In multidisciplinary dissertations, the literature review serves to link various disciplines together so always keep that in mind while conducting a survey.
3. Conduct a Systematic Search for Materials
A literature survey is the foundation of every dissertation. For students looking for dissertation help in London, it is important to know how to conduct a literature review, especially when it comes to multidisciplinary dissertations.
Systematic material searching involves effective planning and organization. Here are some steps to follow:
a. Keywords and Synonyms
Develop a list of keywords relevant to the research theme, including synonyms and their different alternatives which can be delivered. For example, if the research topic is artificial intelligence in education, keywords which may be included will be “AI,” “machine learning,” “educational technology,” and “adaptive learning systems.”
b. Use Diverse Databases
Search for literature in databases that serve various disciplines. For example:
- ScienceDirect for natural sciences
- PubMed for health and biomedical research
- JSTOR and Project MUSE for humanities and social sciences
- IEEE Xplore for engineering and technology
c. Check Reference Lists
References listed in scholarly articles or books will help you locate other valuable resources. This is called backward citation searching, and this is very helpful to identify core works in the area.
d. Keep Current
Set up Google Scholar alerts or database notices to remain up-to-date on new releases about your subject area.
4. Organize Sources
With sources from multiple disciplines, organizing your materials is crucial. Consider the following strategies:
a. Categorize by Discipline
Group sources by their respective fields. This helps in identifying how each discipline contributes to your research topic.
b. Use Thematic Grouping
Organize sources based on themes, such as methodology, theoretical frameworks, or key findings.
c. Create an Annotated Bibliography
Write summaries and critical evaluations of each source. Include information on its relevance, strengths, and limitations.
5. Analyze and Synthesize Information
Examine study sources beyond summaries: The literature review is an analysis and synthesis of sources. For multi-disciplinary reviews:
a. Highlight Contrasts and Commonalities
Find points of convergence, divergence, and overlap between the disciplines. For example, what are the different methods used by sociologists and economists to articulate the issue of poverty?
b. Discuss Theoretical Frameworks
Consider how theories in one area can be informed or complemented by theories in another. For instance, psychological learning theories could bring a rich addition to the design of AI-based educational tools.
c. Gaps and Limitations
Indicate any research gaps, especially those that are created because of disciplinary silos. Mention areas where knowledge integration may be able to provide new insights.
6. Organize Your Literature Review
A multi-disciplinary literature review requires a clear and logical structure. Here is a suggested framework:
a. Introduction
- Introduce your research topic and objectives briefly
- Provide the rationale for the multi-disciplinary approach
- Outline the structure of the review
b. Body
Arrange the body into sections related to the themes or disciplines. For instance,
- Section 1: Environmental Science Perspective
- Section 2: Public Health Findings
- Section 3: Policy Implications
In each section:
- Summarize key studies
- Critically evaluate methodologies and findings
- Show connections with other disciplines
c. Integration Section
Dedicate a section to synthesizing insights across disciplines. Discuss how integrating knowledge provides a comprehensive understanding of your research problem.
d. Conclusion
- Summarize the main findings of your review
- Reiterate the relevance of a multi-disciplinary approach
7. Write Clearly and Cohesively
Multi-disciplinary literature reviews can be dense and complex. To maintain clarity:
- Use Transitional Phrases: Connect ideas across sections and disciplines for example, “Building on insights from sociology, we now explore the economic dimensions…”
- Define Key Terms: Terms may be used differently across different disciplines; it is important to define terms specifically to ensure clarity
- Avoid Jargon: Generally, write to a large academic audience and avoid terms unique to your specific discipline(s)
8. Use Technology to Enhance Your Review
Employ technology to organize and present your literature review:
- Reference Managers: Such apps, such as Zotero, endnote, or Mendeley, help in arranging citations and generating bibliographies
- Visualization Tools: Map concepts or make diagrams to visualize the relationships within and among disciplines and themes
9. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your literature review, seek feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the relevant disciplines. They can provide insights on:
- The comprehensiveness of your review
- The accuracy of your interpretations
- The coherence of your synthesis
10. Revise and Edit
Editing is an important means of honing your literature review. Pay close attention to:
- Consistency: Your writing style, terminology, and formatting should be consistent
- Clarity: Use simple language to explain complicated ideas; avoid repetition
- Accuracy: Double-check citations and verifiable facts
Conclusion
Since reconciling diverse perspectives through careful planning, critical analysis, and writing can be a difficult and sometimes very rewarding process, developing a literature review for a multi-disciplinary dissertation becomes the basis upon which a literature review could be constructed that serves to not only set the stage for a person’s research but also helps to fill the gaps between disciplines. The aim is to generate a cohesive narrative that will take understanding forward and open ways toward innovative solutions to complex problems.
News
Unbelievable Sword From 3000 Years Ago Uncovered Intact!

Introduction
Archaeology never fails to amaze. Imagine unearthing a weapon that hasn’t seen battle for three millennia—yet remains almost pristine. That’s exactly what happened when experts realized a sword in Chicago’s Field Museum, long thought to be a replica, is actually a genuine 3,000‑year‑old sword. At the same time, excavations in southern Germany’s Bavaria region uncovered another Bronze Age blade so well preserved it “almost still shines.” These finds rewrite parts of European Bronze Age history and offer a rare glimpse into ancient metalworking prowess. In this article, we take you behind the scenes of these incredible discoveries, explore how these swords survived intact, and explain why they matter today.
A Sword Mistaken for a Replica—Until Now
The Chicago Field Museum Surprise
One of the Field Museum’s most famous weapons—on display for decades—was believed to be a modern copy of a Bronze Age sword from the Danube region in Hungary. The sword, discovered in the 1930s in the Danube River near Budapest, sat in the museum’s collection as a replica, its true origins forgotten.
In July 2025, Hungarian archaeologists curating the “First Kings of Europe” exhibition began to suspect the sword’s alloy and patina didn’t match a modern forgery. Advanced testing using X‑ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis revealed an alloy composition of copper, tin, and trace elements perfectly matching Late Bronze Age metallurgy. The results dated the sword to between 1080 BCE and 900 BCE—making it over 3,000 years old and a once‑in‑a‑lifetime find DailyNewsHungary.
Why It Matters
- Preservation: The sword’s burial in river sediments and low‑oxygen water slowed corrosion, leaving the blade and handle corrosion‑free.
- Craftsmanship: Metallurgists note the even alloy mix and fine casting, indicating skilled smiths in Bronze Age Hungary.
- Cultural Context: As a deadly weapon, it speaks to the power and prestige of its owner, likely a local chieftain or warrior elite.
This rediscovery underscores the importance of reexamining museum collections with modern techniques—history’s treasures can hide in plain sight.
The Bavaria Blade That “Almost Still Shines”
Discovery in Nördlingen
In June 2023, archaeologists excavating a Bronze Age grave in Nördlingen, Bavaria, uncovered a sword alongside the remains of a man, woman, and child. Per Bavaria’s State Office for Monument Protection, the octagonal bronze hilt was cast directly over the blade in a single pour—an advanced technique practiced only by master smiths around the end of the 14th century BCE Smithsonian Magazine.
Key Features
- Octagonal Hilt: Rare design that required precision casting over the blade to ensure balance and durability.
- Pristine Condition: The sword shows no signs of battlefield damage, suggesting it may have been a ceremonial or high‑status object rather than a frontline weapon.
- Metallurgical Marvel: Analysis reveals a center of gravity optimized for slashing, meaning it could function as a real weapon if needed.
This Bavarian find is so well preserved that its surface reflects light—earning it the description “almost still shining.” It highlights how cold, alkaline soils can slow bronze corrosion, leaving intricate artifacts intact for millennia.
How Bronze Age Swords Survived Intact
1. Burial Environment
- Low Oxygen: Submersion in water or burial in dense clay creates an anaerobic environment, limiting oxidation and corrosion.
- Stable pH: Neutral to slightly alkaline soils help preserve metal objects by preventing acid‑driven degradation.
2. Metallurgy and Casting
- High‑Tin Bronze: A tin content of around 10–12% yielded a harder, more corrosion‑resistant alloy.
- Protective Patina: A thin, stable layer of copper oxide forms naturally, shielding the metal beneath from further decay.
3. Human Care
- Grave Goods Context: Swords buried with their owners were seldom disturbed by grave robbers, especially in remote or secret burial sites.
- Early Ceremonial Use: Some blades were placed intentionally unused—perhaps as offerings—limiting wear and damage.
Together, these factors allowed certain Bronze Age swords to endure for thousands of years, waiting to be rediscovered.
What These Swords Tell Us About Bronze Age Europe
Metallurgical Expertise
Both the Hungarian and Bavarian swords demonstrate that Bronze Age smiths possessed advanced knowledge of alloy composition and casting techniques. Octagonal hilts cast directly onto blades required precise temperature control and mold design—a testament to the era’s technical sophistication.
Social Structures
High‑quality weapons like these likely belonged to elites—warrior‑nobles or chieftains—who used them as status symbols. The decision to bury such swords intact suggests ritual importance, linking martial power with beliefs about the afterlife.
Trade and Interaction
The alloy components—copper from one region, tin from another—point to long‑distance trade networks across Europe. These networks supplied raw materials to specialized workshops, fostering cultural exchange and technological diffusion across the continent.
Modern Methods Reveal Ancient Secrets
Today’s archaeologists use an array of tools to study such artifacts:
- X‑Ray Fluorescence (XRF): Non‑destructive elemental analysis reveals alloy composition with pinpoint accuracy.
- 3D Laser Scanning: Creates detailed digital models of swords, preserving their shape and surface features for study and public display.
- Microscopic Imaging: Examines casting lines and tool marks to reconstruct ancient forging and finishing processes.
- Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) Dating: Carbon‑14 dating of associated organic materials (like wood or leather) provides precise burial dates.
These methods allow researchers to peer directly into the manufacturing choices and burial contexts of ancient societies.
Display and Preservation Today
Once analyzed, such swords undergo careful conservation:
- Stabilization: Mild chemical treatments remove corrosive salts without harming the patina.
- Controlled Environment: Museum cases maintain stable humidity (around 40–50%) and temperature (18–20 °C) to prevent further decay.
- Interpretive Exhibits: Display panels and interactive kiosks share the swords’ stories—how they were made, what they meant, and why their discovery matters.
In Chicago, the newly authenticated Hungarian sword will join Field Museum exhibits on European prehistory, while the Bavarian blade shines in regional museums, captivating visitors with its near‑perfect preservation.
Why These Discoveries Matter
- Cultural Heritage: They connect us to ancestors whose lives and beliefs shaped modern Europe.
- Technological Insight: Understanding Bronze Age metallurgy informs fields from materials science to historical linguistics.
- Public Engagement: Such finds ignite curiosity and support for archaeological research, leading to new discoveries across the globe.
Every intact artifact recovered after millennia becomes a bridge between past and present—an opportunity to learn, wonder, and preserve heritage for future generations.
Conclusion
The revelation that a sword in Chicago once dismissed as a replica is a 3,000‑year‑old masterpiece—and the discovery of a near‑shining Bavarian blade—remind us how the past can lie hidden in plain sight. These Bronze Age swords showcase extraordinary smithing skill, long‑distance trade, and deep ritual meaning. Thanks to modern archaeological science, we can now study their metals, shapes, and contexts in stunning detail. As these ancient swords take their place in museums, they will continue inspiring awe and curiosity—proof that, after three millennia, true craftsmanship endures. For archaeologists and enthusiasts alike, each discovery uncovers a new chapter in humanity’s shared story.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom