Business industrial
Global Plastics Market Overview and Key Trends 2025

Introduction
Plastics are a huge part of our everyday lives. From water bottles and packaging to car parts and electronics, plastics are everywhere. But have you ever wondered how big the plastics market really is? The global plastics market is one of the largest and fastest-growing industries in the world. It plays a key role in packaging, construction, automotive, healthcare, electronics, and many other sectors. In this article, we’ll take a close look at the plastics market, explore its major trends, challenges, and opportunities, and see where it is headed in the coming years.
What Is the Plastics Market?
The plastics market includes the production, distribution, and use of plastic materials across industries. Plastics are made from synthetic or semi-synthetic materials and are known for being lightweight, strong, and easy to shape. There are many types of plastics, each with different uses. Some common ones include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Used in packaging and plastic bags
- Polypropylene (PP): Found in food containers and car parts
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Used in pipes and window frames
- Polystyrene (PS): Found in disposable cups and insulation
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Used in bottles and textiles
The plastics market covers all these materials and the industries that use them.
Size and Growth of the Plastics Market
The global plastics market is massive and continues to grow. It is expected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars in value over the next few years. The growth is driven by rising demand in industries like packaging, automotive, healthcare, electronics, and construction. Emerging economies such as India, China, and Brazil are also playing a big role in market expansion due to urbanization, population growth, and industrial development.
Some key facts about market growth:
- Packaging remains the largest segment using plastics
- Automotive and electronics are fast-growing sectors
- Asia-Pacific leads the global plastics market in production and demand
- Recycled plastics and bioplastics are gaining importance
Major Industries Using Plastics
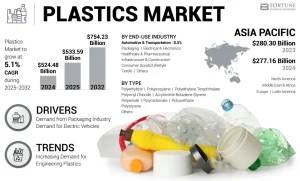
Image by: Yandex.com
1. Packaging
Packaging is the biggest use of plastics. Flexible and rigid plastic packaging is used for food, drinks, personal care, and many other consumer goods. Plastics help keep products fresh, reduce damage during transport, and lower costs due to their light weight.
2. Automotive
Plastics are widely used in car manufacturing because they are lighter than metals. Lighter cars are more fuel-efficient, which is good for the environment and cost-saving. Plastics are used in dashboards, seats, bumpers, and even under-the-hood parts.
3. Construction
In construction, plastics are used in pipes, window frames, flooring, roofing, insulation, and more. PVC is one of the most popular materials here. Plastics offer durability, resistance to corrosion, and ease of installation.
4. Healthcare
Plastics play a big role in the healthcare sector. They are used in syringes, IV bags, tubing, medical devices, and packaging for medicines. These materials must meet high safety and hygiene standards.
5. Electronics
The electronics industry uses plastics for wires, cables, phone casings, and computer components. Plastics are excellent insulators and can be shaped into many forms.
Trends Shaping the Plastics Market
1. Growing Demand for Sustainable Plastics
As more people become aware of environmental issues, there is growing pressure on the industry to reduce plastic waste. This is pushing the demand for biodegradable plastics, recycled materials, and eco-friendly packaging.
2. Focus on Recycling and Circular Economy
Governments and companies are working to increase recycling rates and reduce the use of single-use plastics. A circular economy means plastics are reused and recycled instead of thrown away. This shift is creating new business models and technologies.
3. Innovation in Plastic Materials
There is ongoing research into making plastics stronger, lighter, and more heat-resistant. New materials are also being created to meet specific industry needs, such as medical-grade or food-safe plastics.
4. Digital Technologies in Manufacturing
Digital tools like automation, AI, and data analytics are helping plastic manufacturers improve efficiency and reduce waste. These technologies also help with quality control and faster production.
Challenges Facing the Plastics Market
Despite strong growth, the plastics industry also faces several challenges.
1. Environmental Concerns
Plastic pollution is a global issue. Oceans and landfills are filling up with plastic waste, harming wildlife and ecosystems. This has led to bans on single-use plastics and stricter regulations in many countries.
2. Rising Raw Material Costs
Most plastics are made from petrochemicals, which are derived from oil and gas. When oil prices rise, so do the costs of producing plastic. This affects pricing and profit margins for manufacturers.
3. Regulatory Pressures
Governments are enforcing more rules on plastic use, especially for single-use items and packaging. Businesses must keep up with these rules and adapt their products to comply.
4. Public Opinion
More consumers are choosing products with less plastic packaging or looking for eco-friendly alternatives. Companies need to meet these expectations or risk losing customers.
Future Outlook for the Plastics Market
The future of the plastics market will be shaped by innovation, sustainability, and smarter production. While plastic demand will continue to grow, especially in developing countries, there will be more focus on recycling, reuse, and environmentally safe solutions.
Key points about the future:
- Bioplastics and plant-based plastics will grow in demand
- Recycled plastics will become more widely used
- Technology will make production faster and cleaner
- Companies that invest in green practices will lead the market
- Education and awareness will change how we use plastics
Even though challenges exist, the market is full of opportunities for growth and change. The companies that adapt to new trends will thrive.
Conclusion
The plastics market is a major part of the global economy and touches nearly every part of our lives. From packaging and healthcare to cars and electronics, plastics are essential materials. The market is growing fast, driven by demand from many industries and rising innovation. But it also faces serious challenges, especially around the environment and regulations. The future of the plastics market depends on how companies, governments, and consumers work together to find better and more sustainable solutions. With smart changes and new ideas, plastics can continue to play a useful role while also protecting our planet.
To view more details on this report, click on the link: https://www.rootsanalysis.com/plastics-market
Contact:
Roots Analysis Sales@rootsanalysis.com
Business industrial
Magna Mike Thickness Gauge: Precision in Material Measurement

In modern manufacturing and quality control processes, accurate material measurement is essential. Industries such as packaging, automotive, medical, plastic manufacturing, and consumer goods rely heavily on precise wall thickness measurement to maintain product quality and safety. The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge has become a trusted solution because it offers high accuracy, simple operation, and non-destructive testing capabilities. This advanced instrument helps manufacturers maintain consistency while saving time and reducing errors.
What Is a Magna Mike Thickness Gauge?
A Magna Mike Thickness Gauge is a magnetic thickness measurement instrument designed to measure the wall thickness of non-ferrous materials such as plastic, glass, aluminum, and composites. It uses magnetic technology to determine thickness without cutting or damaging the sample. This makes it ideal for industries where maintaining the integrity of the product is critical.
Unlike traditional mechanical measurement tools, this gauge provides digital readings quickly and accurately. Its easy-to-use interface allows operators to perform tests efficiently without extensive training.

How It Works
The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge works on a magnetic principle. A small magnetic target is placed on one side of the material, while a probe is placed on the other side. The magnetic field strength between the probe and the target changes based on the material thickness. The instrument calculates this variation and displays the exact thickness measurement.
This method ensures:
- Non-destructive testing
- Fast and reliable results
- Consistent accuracy
- Minimal operator error
Because the measurement process is simple, it improves productivity and reduces testing time in industrial environments.
Key Features of the Magna Mike Thickness Gauge
One of the main reasons industries prefer this instrument is its advanced features combined with ease of operation. Some important features include:
High Accuracy Measurement
The gauge delivers precise thickness readings, even for thin materials. This helps maintain strict quality standards and ensures product reliability.
User-Friendly Interface
The instrument has a simple display and intuitive controls, making it easy for operators to use without complicated training.
Non-Destructive Testing
Since the material does not need to be cut or damaged, products remain intact after testing.
Portable Design
Its compact and lightweight design allows easy use in laboratories, production floors, or field applications.
Data Storage and Analysis
Many models offer data storage features that help track measurement history and analyze quality trends.
Applications Across Industries
The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge is widely used in several industries due to its versatility and accuracy.
Packaging Industry
Manufacturers use it to measure plastic bottle thickness, container walls, and packaging films. This ensures product durability while reducing material waste.
Automotive Industry
It helps measure plastic components, fuel tanks, and interior parts to ensure safety and performance.
Medical Device Manufacturing
Medical equipment requires precise measurements for safety compliance. This gauge helps maintain strict quality standards.
Plastic and Glass Manufacturing
It is ideal for checking uniform thickness in molded products, ensuring consistent quality.
Aerospace and Engineering
Engineers use it to measure composite materials where precision is critical.
Benefits of Using Magna Mike Thickness Gauge
Using this instrument provides several advantages that improve quality control and operational efficiency.
Improved Product Quality
Accurate thickness measurement ensures consistent product performance and durability.
Reduced Material Waste
Producers can enhance material efficiency, resulting in reduced expenses.
Faster Testing Process
Quick digital readings increase productivity and reduce inspection time.
Reliable Quality Assurance
Consistent measurements help meet industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Ease of Use
Simple operation allows even new users to perform measurements confidently.
Why Accuracy Matters in Thickness Measurement
Thickness measurement plays a major role in product safety, performance, and cost control. Incorrect measurements can lead to product failure, increased material consumption, or customer dissatisfaction. High-precision instruments like the Magna Mike Thickness Gauge eliminate guesswork and provide dependable data for decision-making.
Accurate testing also helps manufacturers maintain brand reputation and comply with quality certifications. Consistent quality ultimately leads to better customer trust and market competitiveness.
Tips for Effective Use
To achieve the best results, users should follow a few basic practices:
- Always calibrate the instrument before use
- Ensure proper placement of the magnetic target
- Keep the probe clean for accurate readings
- Follow manufacturer guidelines for maintenance
- Store the device safely when not in use
These simple steps help maintain accuracy and extend the instrument’s lifespan.
Future of Thickness Measurement Technology
As industries continue to adopt automation and advanced quality control methods, thickness measurement technology is evolving. Modern gauges are becoming smarter, faster, and more connected. Features such as digital data integration, wireless connectivity, and advanced analytics are improving quality monitoring.
The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge represents this technological progress by combining precision, simplicity, and reliability in one solution.
Conclusion
The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge is an essential tool for industries that require accurate wall thickness measurement without damaging materials. Its magnetic measurement technology, high accuracy, and easy operation make it a preferred choice for quality control professionals. From packaging to automotive and medical manufacturing, this instrument helps ensure consistent product quality while improving efficiency.
By investing in reliable thickness measurement tools, manufacturers can enhance product performance, reduce waste, and maintain competitive standards. The Magna Mike Thickness Gauge stands out as a dependable solution that combines precision with user-friendly operation, making it a valuable asset for modern industrial testing.
Business
Packaging Companies in Sri Lanka: Innovations, and Sustainability

The packaging industry plays a vital role in modern business, supporting sectors such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, retail, and exports. Over the past decade, Packaging companies in Sri Lanka have experienced significant growth, driven by rising consumer demand, expanding export markets, and increased awareness of sustainable solutions. Today, the industry stands as one of the key contributors to the country’s manufacturing and supply chain ecosystem.
Sri Lanka’s strategic location in South Asia, combined with its growing industrial base, has positioned the country as an emerging hub for packaging innovation. From flexible plastic packaging to eco-friendly paper solutions, Food Packaging companies in Sri Lanka are adapting quickly to global standards while serving both local and international markets.

The Importance of Packaging in Modern Business
- Protecting products during transportation and storage
- Extending shelf life, especially for food items
- Enhancing brand visibility and customer appeal
- Meeting regulatory and safety standards
- Supporting sustainability goals
For food manufacturers in particular, packaging determines product freshness, hygiene, and compliance with international export requirements. As Sri Lanka’s food export industry continues to grow, the demand for reliable and innovative packaging solutions has increased accordingly.
The Growth of Food Packaging Firms in Sri Lanka
The food industry in Sri Lanka includes tea, spices, coconut-based products, seafood, confectionery, processed foods, and beverages. These products require specialized packaging to maintain quality and meet international safety standards.
Food Packaging companies in Sri Lanka now provide solutions such as:
- Flexible laminated pouches
- Vacuum-sealed packaging
- Retort pouches
- PET bottles and containers
- Paper-based food wraps
- Corrugated cartons for export
With strict hygiene requirements and increasing consumer awareness, food packaging must meet both local and global certifications. Many Sri Lankan packaging manufacturers have invested in advanced machinery and quality control systems to meet these expectations.
Innovation and Technology in the Packaging Industry
Technology has transformed Packaging companies in Sri Lanka. Modern facilities now incorporate:
- Automated printing systems
- High-speed sealing and filling machines
- Digital design and prototyping tools
- Quality testing laboratories
- Sustainable material development
Flexible packaging has become particularly popular due to its cost-effectiveness, lightweight nature, and reduced environmental footprint compared to traditional rigid packaging.
In addition, companies are increasingly offering customized solutions tailored to the branding needs of businesses. Attractive packaging design is now a key marketing tool, helping brands stand out in competitive retail environments.
Sustainability: A Growing Priority
One of the most significant shifts in the industry is the move toward eco-friendly solutions. Consumers and regulators alike are demanding sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic packaging.
As a result, many Packaging companies in Sri Lanka are investing in:
- Recyclable materials
- Biodegradable packaging
- Compostable food containers
- Reduced plastic thickness solutions
- Paper and cardboard alternatives
Sustainability is no longer optional. It has become a competitive advantage for packaging companies that aim to serve environmentally conscious brands and export markets in Europe, North America, and Australia.
The Role of Leading Industry Players
Several companies are contributing to the advancement of the packaging sector. One such name is Akhtari Group, which has been recognized for its commitment to quality, innovation, and customer-focused solutions.
Companies like akhtarigroup are helping bridge the gap between local manufacturing and international standards. By focusing on advanced production technology, strict quality control, and sustainable practices, they contribute to strengthening Sri Lanka’s reputation as a reliable packaging partner in the region.
Industry leaders are also playing an important role in supporting small and medium enterprises (SMEs) by offering scalable packaging solutions suitable for both startups and large exporters.
Supporting Sri Lanka’s Export Economy
Sri Lanka’s export economy heavily depends on proper packaging. Tea, spices, apparel accessories, processed foods, and coconut-based products all require packaging that ensures product safety during long-distance shipping.
Food Packaging companies in Sri Lanka are especially crucial for:
- Maintaining product freshness
- Preventing contamination
- Withstanding humidity and temperature changes
- Meeting international labeling requirements
Export-quality packaging enhances product value and builds consumer trust in overseas markets. Without reliable packaging solutions, even high-quality products may fail to compete globally.
The Future of Packaging Companies in Sri Lanka
The future of Packaging companies in Sri Lanka looks promising. With increasing demand from food processing, e-commerce, pharmaceuticals, and agriculture, the need for high-quality packaging will continue to grow.
Key future trends include:
- Smart packaging with QR codes
- Tamper-proof food packaging
- Fully biodegradable materials
- Automation and digital printing
- Sustainable supply chain integration
As consumer expectations evolve, companies that prioritize innovation, quality, and environmental responsibility will gain a competitive edge.
Autos & Vehicles
Stainless Steel: The Key Material for Modern Metro Rail Coaches

Metro rail systems are expanding rapidly across major cities in India and across the globe. With rising urban populations, increasing passenger density, and growing expectations for sustainable infrastructure, metro coaches must be built using materials that offer durability, safety, and long-term value. The material ensures long-term reliability without adding unnecessary weight.
From underground tunnels exposed to moisture to elevated corridors facing pollution and extreme weather, rolling stock materials must withstand harsh operating conditions every day. In this environment, stainless steel has emerged as the preferred material for modern metro rail coaches. It offers the right combination of structural strength, corrosion resistance, safety performance, and lifecycle efficiency.
This blog explains why stainless steel metro coaches dominate modern rail manufacturing and why stainless steel railway components are widely used in today’s metro systems.

Evolution of Materials in Metro Coach Manufacturing
Mild Steel in Early Railway Coaches
In the early years of rail transport, mild steel was commonly used for coach construction. While it provided reasonable structural strength, it required frequent maintenance due to rust and corrosion. Regular repainting and structural repairs increased long-term operational costs.
Aluminum as a Lightweight Alternative
To reduce overall train weight and improve energy efficiency, aluminum was later introduced in rail coach manufacturing. Although aluminum reduced mass, it has certain limitations:
- Lower fatigue strength under repetitive loading
- Higher susceptibility to dents and deformation
- Limited performance under high-impact stress
Transition to Stainless Steel
Over time, manufacturers began adopting stainless steel metro coaches because of their superior mechanical properties and durability. Stainless steel combines strength, corrosion resistance, and long service life, making it more suitable for demanding metro environments.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
One of the main reasons stainless steel is preferred in metro rail manufacturing is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Advanced stainless steel grades such as 200 series, 300 series, 400 series, and duplex variants provide:
- High tensile strength
- Strong fatigue resistance
- Structural stability
- Reduced thickness without compromising safety
This allows engineers to design lightweight yet strong metro coach bodies capable of handling high passenger density and operational stress.
Structural elements such as underframes, side walls, and roof panels benefit significantly from stainless steel’s strength characteristics. The substance guarantees enduring dependability while not increasing unnecessary heft.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Metro trains operate in challenging environments that can accelerate material degradation. These include:
- Underground tunnels with high humidity
- Coastal regions with salt exposure
- Industrial zones with airborne pollutants
- Frequent temperature variations
Stainless steel contains chromium, which forms a protective passive layer on the surface. This layer prevents rust and corrosion even under harsh environmental conditions.
Corrosion-resistant railway materials such as stainless steel significantly reduce maintenance requirements. This improves operational efficiency and ensures long-lasting metro coach durability.
Long Service Life and Lower Maintenance
Metro systems are long-term infrastructure investments. Coaches are expected to operate efficiently for several decades. Lifecycle cost becomes more important than initial material cost.
Stainless steel offers:
- Minimal repainting requirements
- Reduced corrosion-related repairs
- Extended service intervals
- Lower replacement frequency
Because stainless steel retains its structural integrity over time, metro operators benefit from reduced downtime and maintenance expenses. Over a 30–40 year operational period, stainless steel metro coaches often prove more economical than alternative materials.
Fire Resistance and Passenger Safety
Safety is a critical priority in metro rail systems. Materials used in coach construction must comply with strict fire safety and structural standards.
Stainless steel provides:
- High melting point
- Resistance to flame spread
- Structural stability during high-temperature exposure
In the event of fire incidents, stainless steel maintains its strength longer than many other materials. This enhances passenger protection and supports evacuation procedures.
Fire-resistant railway materials are essential for regulatory approvals, and stainless steel consistently meets these requirements.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Sustainability is increasingly influencing infrastructure decisions. Metro authorities aim to reduce environmental impact and improve material efficiency.
Stainless steel supports sustainable metro infrastructure in several ways:
- It is 100% recyclable
- It has an extended service life
- It reduces material replacement frequency
- It supports environmentally responsible manufacturing practices
At the end of a metro coach’s life cycle, stainless steel components can be recycled without losing their essential properties. This makes stainless steel an environmentally responsible choice for long-term urban transit systems.
Applications of Stainless Steel in Metro Coaches
Stainless steel is widely used in both structural and functional components of metro coaches.
Structural Shell Components
- Side walls
- Roof panels
- Underframes
- Car body shells
Enclosures and Protective Housing
Metro coaches contain several mechanical and electrical systems that require protection, including:
- Battery boxes
- Air reservoirs
- Valve boxes
Stainless steel enclosures protect these systems from corrosion, physical damage, and environmental exposure.
Interior Fittings and Safety Elements
Passenger safety and comfort rely on durable interior fittings such as:
- Handrails
- Grab poles
- Cable ducts
- Seating frames
Stainless steel interior components resist wear caused by continuous passenger use. They also maintain a clean and professional finish over time.
Stainless Steel vs Aluminum in Metro Coaches
When comparing stainless steel and aluminum in metro coach construction, several factors must be evaluated.
Structural Strength
Stainless steel generally offers higher tensile and fatigue strength, making it more suitable for structural applications subject to repeated loading.
Corrosion Performance
Both materials resist corrosion, but stainless steel performs better in polluted, humid, and coastal environments without requiring protective coatings.
Lifecycle Cost
Although aluminum reduces weight, stainless steel often provides better long-term value due to lower maintenance and higher durability.
Maintenance Requirements
Stainless steel requires minimal repainting and surface treatment, reducing operational downtime.
For these reasons, many metro manufacturers prefer stainless steel for critical structural and safety components.
Importance of Certifications and Standards
Metro rail manufacturing operates under strict global standards to ensure safety and reliability.
Key certifications include:
- IRIS (International Railway Industry Standard)
- EN15085 welding certification
- ISO quality management systems
These certifications ensure consistent quality, proper welding procedures, material traceability, and structural integrity. Stainless steel railway components manufactured under certified systems provide greater confidence to metro authorities and rolling stock manufacturers.
Role of Advanced Fabrication and Testing
Precision engineering is essential in metro coach manufacturing. Stainless steel fabrication involves advanced processes such as:
- Robotic welding
- Fiber laser cutting
- CNC bending and forming
- Non-destructive testing
Each component undergoes thorough testing for:
- Tensile strength
- Corrosion resistance
- Weld integrity
- Dimensional accuracy
Advanced manufacturing capabilities ensure that stainless steel metro components perform reliably under real-world conditions.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Metro Component Manufacturer
Material selection alone does not guarantee performance. The expertise and capability of the manufacturer play a critical role in ensuring compliance and reliability.
When selecting a stainless steel metro component manufacturer, decision-makers should evaluate:
- IRIS certification
- EN15085 welding compliance
- Production capacity
- In-house testing facilities
- Experience in metro and railway projects
- Capability to work with multiple stainless steel grades
Jindal Mobility specializes in stainless steel components for metro systems. With experience in manufacturing structural shells, enclosures, and interior fittings, the company supports metro projects from design and prototyping to mass production. Its certified processes, integrated facilities, and strong quality control systems make it a reliable partner for metro OEMs and system integrators.
Partnering with a qualified manufacturer reduces supply chain risks, ensures consistent quality, and supports the long-term success of metro projects.
Conclusion
Modern metro rail systems demand materials that deliver durability, safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Stainless steel meets these requirements effectively.
Its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, long lifecycle performance, fire safety characteristics, and recyclability make it the preferred material for modern metro rail coaches.
From structural shells and underframes to interior fittings and protective enclosures, stainless steel railway components form the backbone of reliable urban transit systems. When combined with certified manufacturing processes and advanced fabrication technology, stainless steel enables metro networks to operate safely and efficiently for decades.
As metro infrastructure continues to expand worldwide, stainless steel will remain central to the future of rolling stock material innovation.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom






























