Business industrial
“The Plastic Industry: Paving the Way for Sustainable Solutions”
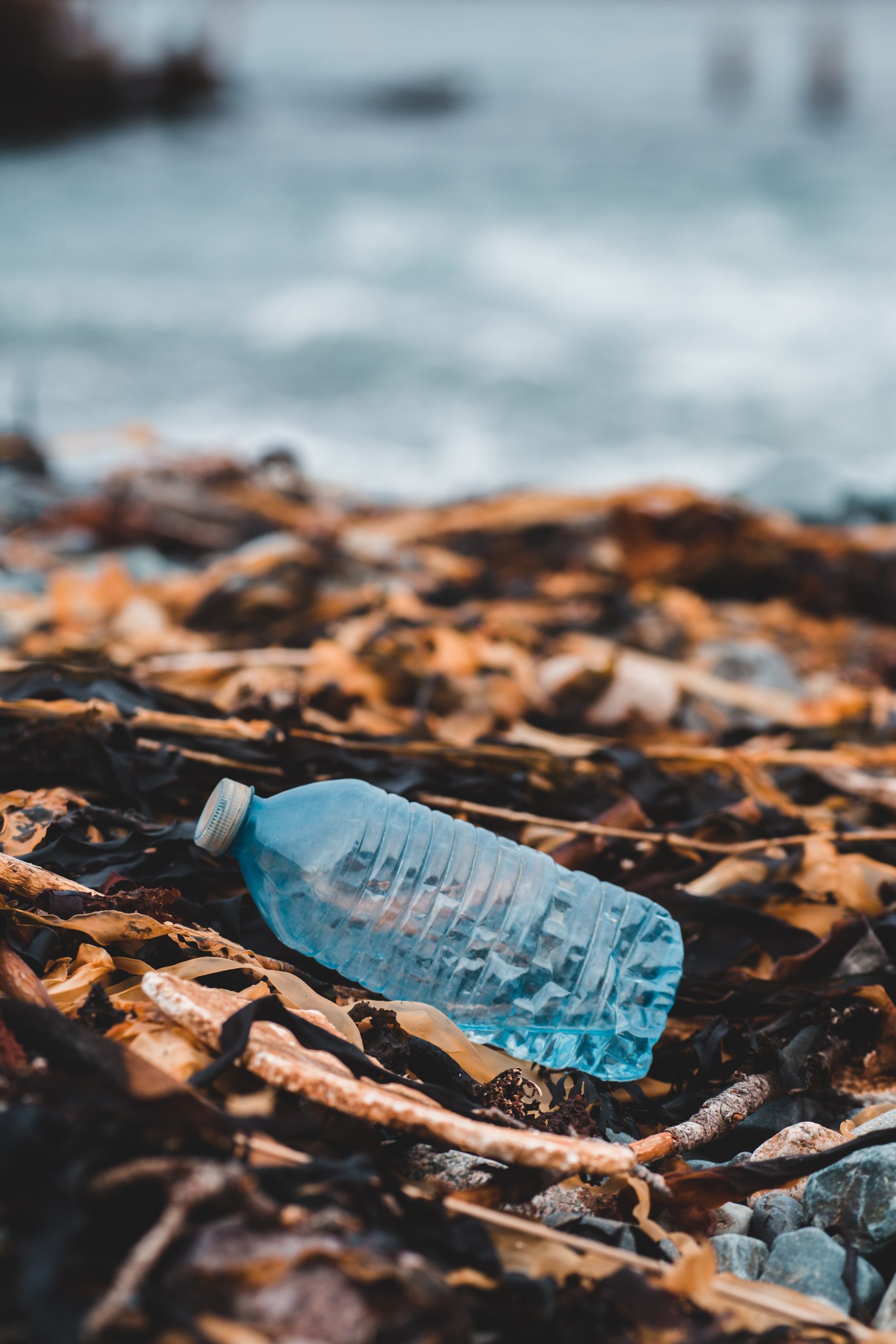

One of the biggest challenges facing the plastic industry is reducing the amount of plastic waste that ends up in our oceans and landfills. Many companies have taken steps to increase their use of recycled materials and decrease their reliance on single-use plastics. For example, some companies are developing new biodegradable plastics, while others are investing in recycling infrastructure to improve the recycling process.
Another significant step towards sustainability is the use of renewable resources in the production of plastics. Many companies are exploring the use of plant-based materials such as corn and sugarcane to create plastic products that are more environmentally friendly than traditional plastics made from fossil fuels.
In addition to reducing waste and using renewable resources, many companies are also focusing on reducing their carbon footprint. This includes investing in renewable energy sources like wind and solar, as well as improving energy efficiency in their production processes.
However, while these efforts are commendable, there is still much work to be done to address the plastic waste crisis. It is important for the plastic industry to continue to innovate and develop new solutions to reduce plastic waste and ensure the long-term sustainability of the industry.
As a journalist, it is essential to adhere to journalistic ethics when reporting on the plastic industry. This includes researching and verifying information from credible sources and presenting a balanced view of the issue. It is also crucial to avoid sensationalism and to provide accurate reporting that is free from bias.
In conclusion, the plastic industry is taking steps towards sustainability and developing innovative solutions to address the issue of plastic waste. While there is still much work to be done, it is encouraging to see companies in the industry taking responsibility for their impact on the environment and working towards a more sustainable future.
Business industrial
Moving Company Marketing: Integrating SEO and PPC

If a Los Angeles moving company puts all its marketing eggs in one basket, it leaves money—and customers—on the table. Relying on a single strategy in today’s crowded digital landscape is no longer a risk; it is a missed opportunity. Search engine optimization builds long-term visibility, slowly and steadily. Pay-per-click advertising, on the other hand, delivers immediate traffic almost overnight. Alone, each has limitations. Together, they form a powerhouse.
The most successful moving companies in Los Angeles understand this. They do not choose between SEO and PPC. They use both, creating a synergy that drives leads through every season.
Why an Integrated Approach Matters
Unlike businesses that enjoy consistent demand year-round, the moving industry rises and falls with the calendar. Summer months bring a flood of relocating families. Winter brings silence. This seasonal rhythm makes marketing flexibility essential.
When demand spikes, PPC allows companies to scale instantly. A well-managed campaign puts your business at the top of search results within hours. You pay for each click, but when those clicks turn into booked moves, the investment pays off. During slower months, SEO steps in. It pulls in organic traffic without ongoing ad spend. Your website works for you, even when your budget is resting.
An integrated approach ensures you are never left chasing leads or waiting for rankings. You have both speed and stability.

The Hidden Limits of SEO Alone
Yes, ranking organically for competitive moving keywords is possible. But it is neither quick nor easy. Los Angeles is home to countless moving companies, many of which have spent years building their domain authority. Terms like “moving company near me” or “best movers in LA” are fiercely contested. Breaking into that space takes time—typically three to six months before you see meaningful movement.
Even the most skilled SEO professionals face constraints. They can optimize your site structure, improve internal linking, and publish high-value content. They can implement a content delivery network to ensure your pages load instantly whether a user searches from downtown or Santa Monica. These efforts matter. But they do not deliver instant gratification.
If you rely solely on SEO, you risk remaining invisible during the very months when customers are actively searching for movers. By the time your rankings improve, peak season may have already passed.
The Unsustainable Cost of PPC Alone
PPC fixes the visibility gap. It places your business in front of ready-to-book customers immediately. For moving companies entering a competitive market, this is invaluable. But it comes at a price.
In Los Angeles, high-intent moving keywords often carry a cost-per-click between fifteen and thirty dollars. Some exceed that. Without organic rankings to fall back on, every single visitor to your website must be paid for. Turn off the campaign, and the traffic stops. There is no residual presence, no lingering brand awareness.
Over time, this model becomes difficult to sustain. Competitors with stronger organic visibility can afford to outspend you because their overall customer acquisition cost is lower. If you rely entirely on paid traffic, you are always one budget cut away from disappearing from search results entirely.
Maximizing Return Through Strategic Integration
Savvy moving companies treat SEO and PPC as a unified system. They track performance across both channels and adjust accordingly. When a PPC campaign generates high-quality leads, they build SEO-optimized landing pages around those same themes. When A/B testing reveals which ad copy converts best, they weave that language into their organic content.
Retargeting adds another layer. Visitors who arrive via organic search but leave without booking can be re-engaged through strategic PPC ads. These potential customers already know your brand. A gentle reminder is often all it takes to bring them back.
This cross-channel intelligence does more than increase visibility. It reduces waste. Companies that integrate their SEO and PPC efforts typically lower overall marketing costs by thirty to forty percent while increasing total lead volume. The two strategies are not separate budgets. They are interdependent investments.
The Combined Advantage: What Integration Unlocks
When an experienced agency manages both SEO and PPC for a moving company, the results extend beyond what either channel could achieve alone. Several distinct advantages emerge.
First, data flows freely between campaigns. PPC reveals exactly which search terms lead to conversions—not just clicks, but actual bookings. SEO teams can then build content strategies around those proven keywords, attracting organic traffic from people already inclined to hire you.
Second, dominating the search results page becomes possible. When a potential customer sees your business listed both as a paid ad and an organic result, trust compounds. You appear more credible, more established, more reliable. Click-through rates rise accordingly.
Third, budget flexibility improves. As organic rankings strengthen for certain keywords, you can reduce spend on those terms and reallocate funds to new opportunities or seasonal pushes. Your marketing dollars stretch further.
Fourth, technical enhancements benefit both channels. Implementing a content delivery network improves site speed across Los Angeles neighborhoods. Faster load times boost organic rankings and improve your PPC quality score, which directly lowers your cost per click.
Fifth, seasonality becomes manageable. You can increase PPC investment during peak months while maintaining consistent SEO work year-round. When demand drops, your organic presence sustains visibility without draining your budget.
Finding the Right Agency Partner
Not every SEO provider understands the unique demands of the moving industry. Seasonal fluctuations, local competition, and high-intent search behavior all require specialized knowledge. The right agency brings more than technical skill. It brings context.
Look for a partner that offers integrated management of both SEO and PPC. They should demonstrate experience working with moving companies in competitive urban markets, should understand why site speed matters not just for rankings, but for user behavior. They should provide clear, transparent reporting that connects marketing activities to real business outcomes.
Most importantly, they should view your campaigns not as isolated efforts but as a single, cohesive strategy.
The Bottom Line
SEO and PPC are not competing philosophies. They are complementary engines. One builds a foundation for the long haul. The other drives immediate results and delivers insights that make organic efforts smarter.
In a city as competitive as Los Angeles, moving companies that embrace both strategies do not merely survive seasonal shifts and aggressive competitors. They dominate, capture demand when it peaks and retain visibility when it fades. They spend smarter, convert more, and grow steadily.
The question is no longer whether to invest in SEO or PPC. It is whether you can afford to leave either one on the table.
Business
URB Bearing Supplier in India: Key Factors for Industrial Success

In many industrial setups, bearings rarely receive attention until something goes wrong. A minor bearing issue can slow production, increase maintenance costs, or in some cases bring operations to a complete stop. This is why sourcing bearings from the right supplier is just as important as selecting the right brand. When it comes to URB bearings, which are widely used across Indian industries, the reliability of the supplier directly affects overall equipment performance.
A dependable URB Bearing Supplier India is not defined by loud claims or short-term pricing advantages. Reliability develops over time through experience, consistency, technical understanding, and transparent business practices. For buyers who rely on URB bearings in critical applications, knowing what separates a reliable supplier from an average one can make a meaningful difference.

Why Supplier Reliability Matters More Than Ever
URB bearings are known for their strength, durability, and ability to perform under demanding industrial conditions. However, even a well-manufactured bearing can fail if it is mismatched, improperly stored, or sourced through unreliable channels. In India’s complex industrial supply environment, buyers often encounter challenges such as inconsistent quality, unclear sourcing, or limited technical support.
A trustworthy URB Bearing Supplier helps reduce these risks. Instead of simply supplying products, reliable suppliers focus on correct selection, application suitability, and long-term performance. This approach becomes especially important in industries such as manufacturing, power generation, mining, and heavy engineering, where downtime can have serious financial consequences.
Clear and Transparent Sourcing Practices
One of the strongest indicators of a reliable URB bearing supplier is transparency. Genuine suppliers are open about sourcing, handling, and documentation. They provide proper invoices, clear product details, and traceable information that helps buyers verify authenticity.
When sourcing information is unclear or documentation is incomplete, doubts naturally arise about product quality. A reliable URB Bearing Supplier India understands that trust is built through openness and consistency rather than promises or claims.
Strong Technical Understanding of Bearings
Bearings are not universal components. Load conditions, operating speed, temperature, alignment, and surrounding environment all influence how a bearing performs. A dependable URB bearing supplier understands these variables and takes them into account when guiding buyers.
Rather than pushing a specific product, reliable suppliers focus on suitability. Many buyers compare their experiences with suppliers who also operate as a ZWZ bearing supplier India and often notice a shared characteristic among the most trusted ones: correct application is given priority over quick transactions. This technical understanding helps prevent premature failures and supports longer service life.
Consistency in Product Quality
Consistency is often overlooked, yet it is one of the clearest signs of supplier reliability. A trustworthy URB bearing supplier delivers the same level of quality every time, whether supplying a single URB bearing or fulfilling bulk requirements. Proper storage conditions, careful handling, and appropriate packaging all play a role in maintaining bearing integrity.
In the Indian industrial market, where demand is high and supply chains can vary, consistent quality over time builds confidence. Buyers tend to continue working with suppliers who deliver predictable results without unexpected variations.
Experience in the Indian Industrial Market
Experience brings practical understanding. Suppliers who have operated in the Indian bearing market for many years are familiar with industry cycles, operating challenges, and changing machinery requirements. This experience allows them to respond more effectively to customer needs and offer practical insights rather than generic recommendations.
Companies such as S. Goel Bearing & Co are often mentioned within industry discussions due to their long-standing involvement in bearing distribution. Such market presence reflects continuity and familiarity with industrial requirements rather than short-term participation.
Knowledge Beyond a Single Brand
Reliable suppliers typically work with multiple bearing brands and applications. This broader exposure helps them develop balanced technical judgment. While URB bearings are suitable for many operating conditions, experienced suppliers also recognize situations where different solutions may be required.
Buyers often observe that suppliers who also function as a ZWZ bearing supplier India tend to have wider application knowledge. This multi-brand exposure helps ensure that URB bearings are recommended only where they genuinely fit the operating requirement.
Ethical Business Practices and Honest Communication
Ethical conduct plays a quiet but important role in supplier reliability. Honest pricing, realistic delivery commitments, and clear communication indicate a supplier focused on long-term relationships. Reliable URB bearing suppliers avoid exaggerated claims and unclear assurances.
Instead, they focus on accuracy when discussing specifications, availability, and lead times. This clarity helps buyers plan effectively and reduces uncertainty in procurement decisions.
Importance of After-Sales Support
Supplier responsibility does not end once the bearing is delivered. A reliable URB Bearing Supplier India remains available for technical clarification, installation guidance, and issue resolution when needed. This support is especially valuable in critical machinery where even small errors can lead to major operational disruptions.
Suppliers who also guide customers on proper storage, handling, and maintenance contribute to better bearing performance and longer equipment life.
The Buyer’s Role in Choosing the Right Supplier
While supplier reliability is essential, informed buyers also play an important role. Understanding machinery requirements, operating conditions, and bearing specifications helps buyers ask relevant questions and evaluate suppliers more effectively. Clear communication on both sides leads to stronger working relationships and better outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How can buyers identify a reliable URB Bearing Supplier India?
Buyers should focus on transparency, technical understanding, consistent product quality, and proper documentation rather than relying only on pricing.
Q. Why is supplier experience important when buying URB bearings?
Experienced suppliers understand real operating conditions and can guide buyers toward suitable bearing solutions, reducing the risk of failure.
Q. Is it risky to buy URB bearings without technical guidance?
Yes. Incorrect selection can lead to premature wear, increased maintenance costs, and unplanned downtime.
Q. Do reliable URB bearing suppliers usually work with other brands?
Many trusted suppliers also deal with other brands, including those recognized as a ZWZ bearing supplier India, which strengthens their overall application knowledge.
Q. How does after-sales support affect bearing performance?
Proper guidance on installation, handling, and maintenance helps ensure that URB bearings perform as intended throughout their service life.
Final Thoughts
Reliability in bearing supply is built through consistent actions rather than marketing claims. A dependable URB Bearing Supplier in India combines technical understanding, ethical practices, and long-term market experience to support industrial operations effectively. For buyers who value consistency and performance, choosing the right supplier is not just a purchasing decision, it is a practical, long-term consideration.
Business industrial
Fire Risk Assessment London: Legal Compliance for Landlords

A Fire Risk Assessment London is a fundamental legal requirement for landlords, property managers, and business owners responsible for buildings that contain shared or non-domestic areas. It is designed to identify potential fire hazards, assess the level of risk to occupants, and ensure appropriate fire safety measures are in place to protect lives and property.
In a city like London, where buildings vary widely in age, layout, and occupancy, carrying out a suitable and sufficient fire risk assessment is not just a legal formality—it is a critical responsibility.

Understanding Fire Risk Assessment in London
A fire risk assessment is a systematic inspection of a property to evaluate fire hazards and determine whether existing safety controls are adequate. The process considers how a fire could start, how it could spread, and how occupants would escape in an emergency.
Under the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, the duty to carry out a fire risk assessment falls on the “Responsible Person.” This is typically the landlord, building owner, managing agent or employer who oversees the property.
A valid Fire Risk Assessment London applies to:
-
Blocks of flats and apartment buildings (communal areas)
-
Houses in Multiple Occupation (HMOs)
-
Commercial properties and offices
-
Retail units and hospitality venues
-
Care homes, schools, and mixed-use buildings
Failing to comply can lead to enforcement notices, significant fines, or legal action.
Why Fire Risk Assessment Is Crucial for Landlords
For landlords, fire safety compliance is not optional. A professional fire risk assessment demonstrates that reasonable steps have been taken to protect tenants and visitors from fire hazards. It also supports broader legal obligations related to property management and tenant safety.
A compliant assessment plays an important role in achieving and maintaining a valid Landlord Safety Certificate London, which demonstrates that a property meets essential safety standards. This is particularly important for landlords managing rental properties, HMOs, or portfolios with shared spaces.
By keeping fire risk assessments up to date, landlords can:
-
Reduce the risk of fire incidents
-
Protect tenants and occupants
-
Meet legal and insurance requirements
-
Avoid penalties and enforcement action
-
Improve overall building safety management
What a Professional Fire Risk Assessment Covers
A comprehensive Fire Risk Assessment London goes beyond a simple checklist. It involves a detailed evaluation of both active and passive fire safety measures within the building.
Key areas assessed include:
-
Identification of fire hazards and ignition sources
-
Assessment of combustible materials and fire load
-
Condition and suitability of escape routes
-
Fire doors, compartmentation, and passive fire protection
-
Fire alarm and detection systems
-
Emergency lighting and fire signage
-
Firefighting equipment such as extinguishers
-
Risk to occupants, including vulnerable individuals
-
Fire safety management procedures and documentation
The assessment concludes with a clear action plan, prioritizing necessary improvements and providing practical recommendations to reduce risk.
Frequency and Review of Fire Risk Assessments
Fire risk assessments are not one-off documents. They must be reviewed regularly and updated whenever significant changes occur. This encompasses modifications to the structure, shifts in occupancy, or enhancements to fire safety procedures.
Landlords and property managers should also review assessments following:
-
Fire incidents or near misses
-
Structural modifications
-
Changes in use of the building
-
Updates to fire safety legislation
Maintaining an up-to-date Fire Risk Assessment London is essential for ongoing compliance and effective risk management.
Fire Risk Assessment and Legal Compliance
Fire safety law in the UK places a strong emphasis on prevention and risk management. Enforcement authorities expect fire risk assessments to be suitable, sufficient, and carried out by a competent person.
A professionally conducted assessment provides documented evidence of compliance and can be requested during inspections by fire authorities, insurers, or local councils. For landlords, this documentation is often required as part of wider compliance checks associated with a Landlord Safety Certificate London.
Choosing a Professional Fire Risk Assessment Provider
Competency is a key requirement when appointing a fire risk assessor. The assessor must have appropriate knowledge, training, and experience to identify risks accurately and provide reliable recommendations.
Safety Spectrum London provides professional fire risk assessment services designed to meet legal requirements and support long-term fire safety management. Their assessments are tailored to the specific risks associated with each property type.
To learn more about professional services, visit their dedicated page for Fire Risk Assessment London:
Benefits of a Professional Fire Risk Assessment
Engaging a competent provider ensures:
-
Accurate identification of fire hazards
-
Practical, prioritized recommendations
-
Clear and compliant reporting
-
Reduced risk of enforcement action
-
Improved safety for occupants and visitors
-
Support for landlord and property compliance obligations
A well-managed fire risk assessment strategy protects both people and property while demonstrating responsible ownership and management.
Final Thoughts
A Fire Risk Assessment London is a legal necessity and a vital part of responsible property management. For landlords, it plays a central role in meeting safety obligations and maintaining a compliant Landlord Safety Certificate London.
By ensuring assessments are carried out professionally, reviewed regularly, and acted upon appropriately, landlords and property owners can create safer environments, meet regulatory requirements, and protect their investments in the long term.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom