Technology
Transform Challenges into Solutions with a Design Thinking Workshop

Introduction
In today’s fast-moving world, every business and team faces new challenges. Whether it’s building a better product, solving customer pain points, or improving teamwork, it’s not always easy to know where to start. That’s where a design thinking workshop comes in.
A design thinking workshop is not just another meeting or training. It’s a fun, hands-on experience that brings people together to solve problems in smart and creative ways. These workshops are used by big companies, small startups, schools, and even government groups.
If you’re tired of the same old brainstorming sessions that don’t lead to real solutions, this guide will show you how a design thinking workshop can make a difference.
What is a Design Thinking Workshop?
A design thinking workshop is a step-by-step process where people work together to solve a problem. The idea is to focus on people’s real needs and come up with ideas that are helpful, creative, and doable.
It’s not about guessing or going with your first idea. Instead, design thinking helps you understand the problem better and test different solutions before you build anything big or spend money.
Workshops usually include activities like drawing, talking with customers, building quick models (called prototypes), and testing ideas. You don’t have to be a designer to join. Anyone can take part, from marketers and engineers to teachers and students.
Rise of Design Thinking Workshops
In recent years, Design Thinking workshops have become more common across industries such as business, education, healthcare, and technology. These workshops offer a fresh way of solving problems by focusing on people’s real needs. Instead of using old methods that may not work anymore, teams use creative steps to understand the problem and test new ideas. As the world becomes more complex, more organizations are seeing the value of thinking differently. This rise shows that many are moving toward human-centered approaches to find better, more practical solutions.
Why Design Thinking Works
Design thinking works because it starts with people. Most problems in business come from not really understanding what the users or customers want. Design thinking helps fix that.
Here’s why it works so well:
- Focus on the user: You learn what people really need, not just what you think they need.
- Teamwork: Everyone on the team helps shape the idea, so people feel involved and motivated.
- Creative ideas: It’s easier to think outside the box when you’re using fun tools like sketching or role-play.
- Try before you build: You make quick, small versions of your ideas to see what works before spending time or money on a big plan.
Benefits of Design Thinking Workshops
Design Thinking workshops offer many benefits. First, they encourage teamwork by bringing people from different backgrounds together. Each person adds their unique view, which leads to more creative ideas. Second, these workshops help teams deeply understand the user, making sure the final solution truly fits their needs. Third, the process helps teams test ideas quickly with simple models before spending too much time or money. This saves resources and reduces risks. In the end, the goal is not just to solve a problem but to make sure the solution really works for the people it’s meant for.
Role of Design Thinking in Solving Problems
Design Thinking plays an important role in solving complex problems. It’s not just about coming up with ideas—it’s about finding the right ideas. The process includes five key steps: empathize (understand the user), define (clearly state the problem), ideate (brainstorm ideas), prototype (build simple models), and test (see what works). These steps help teams avoid jumping to quick fixes and instead focus on solutions that are thoughtful and tested. It also builds a mindset of learning from failure, which is key to innovation. Design Thinking turns confusing problems into clear paths forward.
The Five Stages of the Design Thinking Process

Image by: Yandex.com
A design thinking workshop often follows these five steps:
1. Empathize
Start by learning about the people who will use the product or service. This can mean talking to customers, asking questions, or watching how they do things. The goal is to feel what they feel and see things from their point of view.
2. Define
Now that you know more about the users, it’s time to define the real problem. You take all the things you’ve learned and write a clear problem statement. For example, instead of saying, “We need a better website,” you might say, “Busy parents can’t find daycare information quickly on our website.”
3. Ideate
This is where the fun begins. In the ideate step, everyone shares ideas. There are no bad ideas in this stage. You can use sticky notes, draw sketches, or shout out thoughts. The goal is to come up with many ideas, even wild ones.
4. Prototype
Pick a few top ideas and create simple versions of them. These can be paper models, rough website designs, or role-playing a service idea. You want to make something fast and cheap that you can show to users.
5. Test
Show your prototype to real users and see how they react. Ask questions like, “What did you like?” or “What was confusing?” Use their feedback to improve your idea or go back and try something new.
Who Should Attend a Design Thinking Workshop?
One of the best things about a design thinking workshop is that anyone can join. You don’t need a design background or special training. A good mix of people actually makes the workshop better.
Here are some common groups that benefit:
- Product teams trying to improve or create new features
- Marketing teams looking for new campaign ideas
- HR teams trying to improve employee experience
- Teachers or schools working on better learning methods
- Startups building a new business from scratch
What Happens During a Typical Workshop?
Design thinking workshops can be one day or spread over a few days. Here’s what you might expect:
- Welcome and warm-up: Fun team games to get everyone talking
- User research: Share what you know about the users or interview someone
- Define the problem: Create clear problem statements
- Idea generation: Brainstorm as many solutions as possible
- Build prototypes: Use paper, cardboard, or simple tools to build ideas
- Testing: Show your work to others and gather feedback
- Reflection: Talk about what worked and what you learned
Workshops are usually led by a trained facilitator who keeps things on track and makes sure everyone has a chance to share.
Tools You Can Use
Here are some tools often used in design thinking workshops:
- Sticky notes: Great for writing and moving ideas
- Markers and paper: For sketching quick ideas
- User personas: A simple way to describe your target users
- Journey maps: To see how users interact with a product or service
- Prototype kits: Cardboard, scissors, glue, and other craft materials
Real-Life Benefits of Design Thinking Workshops
Still wondering why you should try one? Here are some real-life benefits:
- Better understanding of your customers
- Stronger team collaboration and morale
- More creative and effective ideas
- Faster problem-solving
- Less risk and wasted resources
Companies like Google, Apple, and IBM use design thinking to stay ahead. But it’s not just for big names. Even small teams or schools can get great results.
Tips for a Successful Workshop
- Create a safe space: Make sure people feel comfortable sharing ideas
- Stay open-minded: Be ready to explore even strange ideas
- Keep it visual: Draw things, use colors, and make models
- Don’t rush: Take time to listen and understand before jumping to solutions
- Have fun: Creative work should feel exciting, not like a chore
Challenges in Using Design Thinking
Even though Design Thinking has many benefits, it also comes with some challenges. For example, not all team members may be comfortable with the open and creative style it requires. Some may prefer to follow strict plans and may resist trying new methods. Another challenge is time—Design Thinking can take longer at first, especially for teams that are new to it. Also, without proper support from leaders, teams may not be given enough space to experiment and learn. Finally, some people may expect instant results, but this process takes patience and practice. Overcoming these challenges takes commitment and trust in the process.
Future of Design Thinking Workshops
Looking ahead, the future of Design Thinking workshops is very promising. As more companies and organizations face new types of problems, the need for creative problem-solving will only grow. Design Thinking will likely be used not only in businesses but also in schools, non-profits, and even local governments. New tools, online platforms, and better training will make workshops easier to run and more accessible to all. In the future, more people will be trained to think like designers—to be curious, open-minded, and focused on real human needs. This shift can help create smarter, kinder, and more useful solutions for the world.
Conclusion
A design thinking workshop is more than just a problem-solving tool. It’s a way to unlock new ideas, understand your users, and build better solutions with your team. From students and teachers to tech teams and business leaders, anyone can benefit from this creative and human-focused process.
By following the design thinking steps empathize, define, ideate, prototype, and test you turn confusion into clarity and problems into possibilities. These workshops bring people together in fun and powerful ways, helping you move from “What now?” to “We’ve got it!”
Whether you’re trying to improve a service, build a new product, or just spark more creativity in your team, a design thinking workshop could be the perfect place to start. Give it a try and see how challenges can turn into smart, real-world solutions.
Cars
Luxury Car Seats: The Pinnacle of Comfort and Engineering

Seats play a defining role in every luxury car. They shape the driving experience, influence posture, and determine long-term comfort. While engines provide motion and materials define appearance, seats create the most direct connection between the vehicle and its occupants. For this reason, luxury car manufacturers treat seat design as a blend of science, craftsmanship, and advanced engineering.
Unlike standard automotive seating, luxury car seats focus on ergonomics, adaptability, and sensory comfort. Every curve, stitch, and mechanism serves a purpose. This article explores how luxury car seats are formed, how they work, and why they represent one of the most complex components in premium vehicles.
The Formation of Luxury Car Seats
The formation of a luxury car seat begins at the design stage. Engineers first analyze human anatomy, driving posture, and pressure distribution. They then translate these findings into seat geometry.
Manufacturers build seat frames using high-strength steel or lightweight aluminum. These materials provide rigidity while allowing controlled flexibility. Once the frame is complete, engineers add foam layers with varying densities. Firmer foam supports posture, while softer foam enhances comfort.
Brands such as Mercedes-Benz invest years in seat research. Their development process ensures that seats remain supportive during long journeys without causing fatigue.

Advanced Engineering Behind Seat Structure
Luxury car seat engineering goes far beyond cushioning. Engineers design multi-layered structures that adapt to body movement. These structures absorb road vibrations while maintaining stability.
Many luxury seats include reinforced side bolsters. These bolsters hold occupants securely during cornering. At the same time, they remain unobtrusive during relaxed driving.
In vehicles like the BMW 7 Series, seat engineering balances firmness and softness. This balance allows the seat to respond dynamically to both driver input and road conditions.
How Luxury Car Seats Work
Luxury car seats rely on mechanical, electrical, and software systems working together. Electric motors control adjustments such as height, tilt, lumbar support, and headrest position. Memory systems store personalized seating preferences.
Sensors embedded within the seat detect body position and movement. Based on this data, the seat adapts support levels automatically. This responsiveness improves comfort during extended drives.
Additionally, advanced suspension seats isolate occupants from road imperfections. As a result, passengers experience smoother rides, even on uneven surfaces.
Performance Contribution of Luxury Seats
Seat performance directly affects driving precision. Proper seating position improves steering control, braking response, and overall safety.
Luxury car seats keep the driver stable during acceleration and cornering. This stability reduces muscle strain and enhances focus. In high-end sedans and grand tourers, seats also contribute to passenger comfort at higher speeds.
For example, the Audi A8 integrates performance-oriented seat contours with comfort-focused padding. This approach supports both dynamic driving and relaxed travel.
Materials Used in Luxury Car Seats
Material selection defines the tactile experience of luxury seats. High-quality leather remains the most popular choice. However, manufacturers use different grades and treatments to achieve softness, durability, and breathability.
Some luxury brands also use premium fabrics and microfiber materials. These options offer excellent temperature regulation and wear resistance. Stitching patterns further enhance visual appeal while reinforcing structural integrity.
In ultra-premium vehicles from Rolls-Royce, artisans hand-stitch seats using carefully selected hides. This craftsmanship ensures uniform texture and long-lasting elegance.
Climate Control and Seat Comfort Technology
Modern luxury car seats actively manage temperature. Heating systems warm seats during cold conditions, while ventilation systems circulate air during warm weather.
Ventilated seats use perforated materials and internal fans. These components prevent heat buildup and moisture retention. Consequently, occupants remain comfortable in all climates.
Some models even include massage functions. These systems use air bladders or rollers to stimulate muscles. Over time, massage features reduce fatigue and improve circulation.
Ergonomics and Long-Distance Comfort
Ergonomics represent a core principle in luxury seat design. Engineers shape seats to support the spine’s natural curvature. Adjustable lumbar support ensures proper alignment.
Headrests also receive special attention. Active headrests adjust position during sudden stops to reduce neck strain. This feature enhances safety without compromising comfort.
Luxury car seats allow drivers to maintain a relaxed posture over long distances. This ergonomic advantage differentiates luxury vehicles from conventional cars.
Noise Reduction and Vibration Control
Luxury seats also contribute to cabin quietness. Specialized foam and padding absorb vibrations transmitted from the chassis. This absorption reduces road noise felt through the body.
Seat mounts include isolation elements that separate the seat from the vehicle floor. These elements dampen movement and vibration. As a result, the cabin feels calm even at highway speeds.
This refinement supports the overall luxury driving experience.
Customization and Personalization Options
Customization plays a major role in luxury seating. Buyers can choose seat colors, stitching patterns, and materials. Some brands even offer bespoke embroidery.
Seat configuration options include executive rear seating with extended leg rests and reclining functions. In vehicles like the Lexus LS, rear seats provide near-lounge comfort.
Personalization allows owners to align the interior with their preferences. This exclusivity strengthens emotional connection to the vehicle.
Safety Integration in Luxury Seats
Safety features integrate seamlessly into luxury car seats. Airbags deploy from seat sides to protect occupants during side impacts. Seatbelt pre-tensioners work in coordination with seat sensors.
Child seat anchoring systems blend into the design without affecting aesthetics. Meanwhile, structural reinforcement protects occupants during collisions.
Luxury seats combine safety and comfort without visible compromise.
Sustainability in Seat Design
Sustainability now influences luxury seat production. Manufacturers increasingly use eco-friendly leather processing and recycled materials.
Plant-based foams and vegan leather alternatives reduce environmental impact. These materials meet strict durability standards while supporting sustainability goals.
This shift reflects changing consumer expectations within the luxury car market.
The Future of Luxury Car Seating
Future luxury seats will become more intelligent and adaptive. Artificial intelligence may adjust seating posture in real time based on fatigue levels.
Biometric sensors could monitor heart rate and stress. Seats may then activate massage or climate features automatically.
Despite technological growth, craftsmanship will remain essential. Comfort, elegance, and human-centered design will continue to guide innovation.
Conclusion
Seats represent one of the most important components in a luxury car. From formation and engineering to performance and personalization, luxury seats reflect thoughtful design and advanced technology. They support the body, enhance safety, and elevate comfort across every journey.
As luxury cars evolve, seats will continue to define the driving experience. Through innovation and craftsmanship, they transform travel into a refined and effortless pleasure.
Beauty Fitness
Transform Your Skin with Micro Needling in Tomball

Living in Tomball, we know just how much we cherish our sunny days and outdoor adventures. However, the Texas heat, humidity, and intense UV exposure can take a toll on our skin. Whether it’s persistent acne scars, sun spots, or the fine lines that seem to deepen every year, we all know how difficult it can be to maintain that youthful, glowing complexion.
At Enfield Royal Med Spa Tomball, we believe in a holistic approach to skincare — healing from within. That’s why we’re big fans of Micro needling, a gold-standard treatment that’s transforming the skin of many Tomball locals.
What is Micro needling?
Micro needling, or Collagen Induction Therapy, is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a specialized device to create thousands of tiny, microscopic channels in your skin’s surface.
Although the idea of tiny needles poking your skin might sound intimidating, don’t worry! It’s actually a gentle and highly effective process. These micro-injuries stimulate your body’s natural healing response, triggering the production of new collagen and elastin — essential building blocks for firm, smooth, and youthful-looking skin.
Why Tomball Locals Love Micro needling: 5 Key Benefits
If you’re still undecided about whether Micro needling is the right fit for you, here’s why this treatment is a fan favorite in Tomball:
1. The Ultimate Multi-Tasker
One of the best things about Micro needling is its versatility. Unlike treatments that only address one skin concern at a time, Micro needling tackles multiple issues in a single session. With just one treatment, we can improve:
- Fine lines and deep wrinkles
- Acne scars and pockmarks
- Enlarged pores
- Uneven skin texture and tone
- Sun damage and hyperpigmentation
It’s like a skin reset button that gives you a more youthful, even complexion from head to toe.
2. Natural, Effortless Results
One of the biggest advantages of Micro needling is that it works with your body’s own collagen production. That means no artificial-looking changes — just you, looking fresher, more rested, and glowing. Unlike Botox or fillers that can give a “frozen” appearance, Micro needling enhances your natural beauty, leaving you looking like the best version of yourself.
3. Minimal Downtime
Unlike other aggressive treatments like chemical peels or lasers, Micro needling offers a low-impact recovery time. Most clients experience redness similar to a mild sunburn for 24-48 hours, after which they’re ready to go about their normal routine — and even wear makeup! There’s no peeling, flaking, or discomfort that might make you want to hide at home. You’ll be glowing and ready to face the world in no time.
4. Boosts the Power of Your Skincare
Micro needling doesn’t just improve your skin; it also enhances the effectiveness of the skincare products you already use. After the treatment, your skin is primed to absorb serums and moisturizers up to 300% deeper than usual, allowing those pricey products to work even harder for you.
5. Safe for All Skin Types and Tones
If you’ve ever been hesitant to try laser treatments due to concerns about your skin tone, you’ll be happy to know that Micro needling is a great option for almost everyone. Unlike thermal treatments like lasers, which can be risky for darker skin tones, Micro needling uses mechanical action, making it safe and effective for all skin types. Whether your skin is fair or deep-toned, you can enjoy the benefits of a smoother, healthier complexion.
What to Expect at Enfield Royal Med Spa Tomball
We understand that trying a new treatment can be nerve-wracking, but rest assured that your comfort is our top priority. Here’s a look at what a typical Micro needling session at our spa involves:
- Numbing: To ensure the treatment is comfortable, we start by applying a high-quality numbing cream to the treatment area. Most clients only feel a light vibration during the process.
- The Treatment: A trained provider will gently glide the micro needling device over your skin. We can adjust the depth of the needles to target specific concerns like deep acne scars or fine lines around the eyes. The procedure usually takes 30-60 minutes, depending on the area treated.
- Soothe: Once the treatment is complete, we’ll apply soothing serums or a cooling mask to help calm your skin and kickstart the healing process.
Ready to Glow?
If you’ve been dealing with dull texture, stubborn scars, or uneven skin tone, Micro needling could be just the treatment you need to refresh your complexion.
At Enfield Royal Med Spa in Tomball, we specialize in creating personalized skincare plans tailored to your unique needs. Whether you want to smooth out fine lines, minimize sun spots, or rejuvenate your skin’s texture, we’re here to help you look and feel your best.
Stop by for a consultation today, and let’s discuss how Micro needling can help you achieve healthy, glowing skin that’s ready for anything.
Care
Gas Furnace Heating and Its Impact on Indoor Air Quality
Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) has become a defining metric of building performance. Across residential, commercial, and light industrial spaces, occupants expect heating systems not only to deliver thermal comfort but also to support a healthy indoor environment. Gas furnace heating remains one of the most widely adopted solutions globally due to its reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. However, its impact on Indoor Air Quality depends heavily on system design, installation, and maintenance.
This article examines how gas furnaces influence Indoor Air Quality and outlines practical strategies to optimize performance while protecting occupant health.
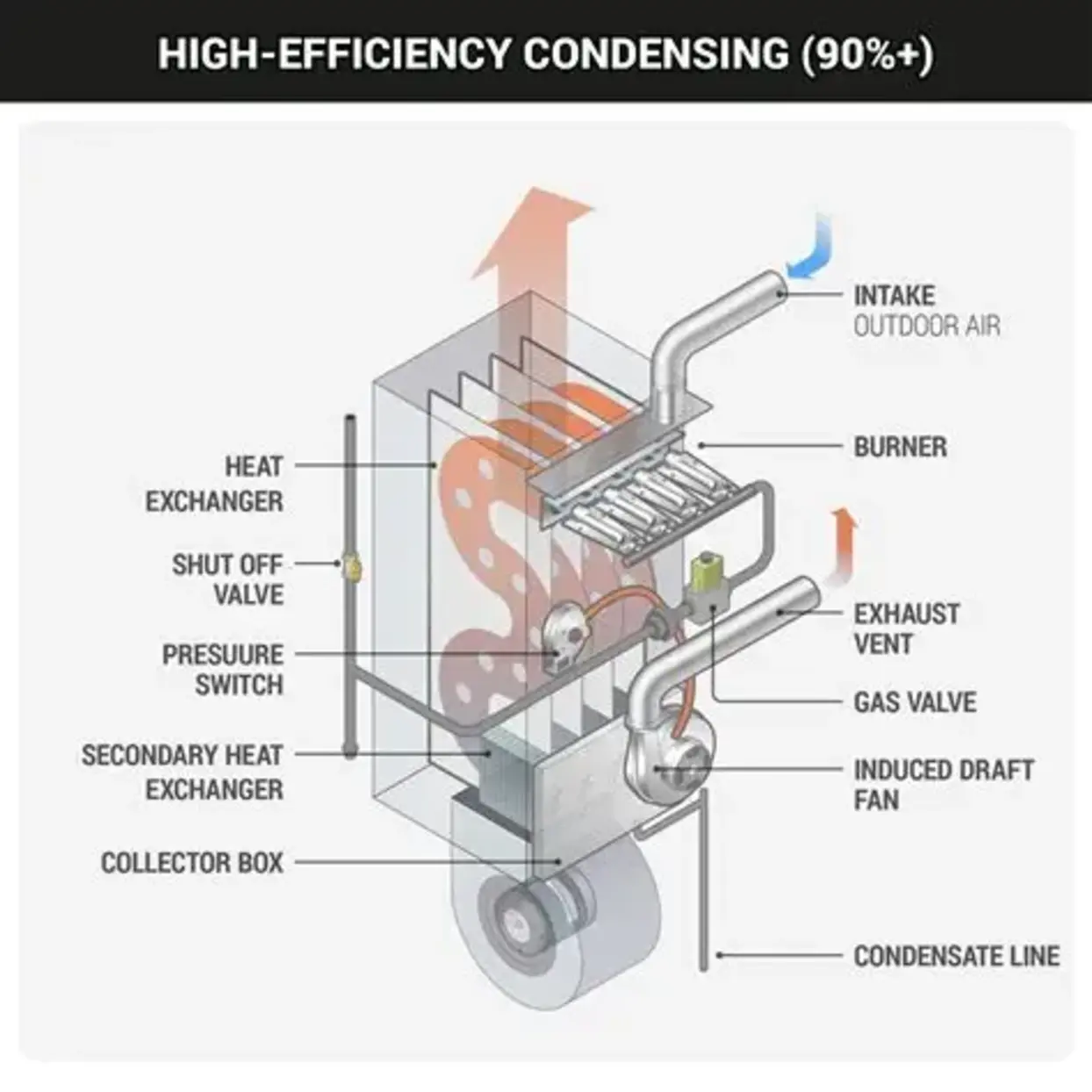
Understanding How Gas Furnaces Operate
A gas furnace generates heat by burning natural gas or propane in a sealed combustion chamber. The combustion gases pass through a heat exchanger, transferring warmth to circulating air, which is then distributed throughout the building via ductwork. Modern high-efficiency furnaces use sealed combustion and direct venting systems to isolate combustion air from indoor air.
This distinction is critical. Older, non-sealed systems may draw combustion air from inside the building, which can negatively affect Indoor Air Quality if ventilation is inadequate. High-efficiency sealed combustion systems, by contrast, significantly reduce indoor contamination risk.

Key Indoor Air Quality Concerns with Gas Furnace Heating
1. Combustion Byproducts
Incomplete combustion can generate pollutants such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), and trace particulate matter. Carbon monoxide is particularly dangerous due to its colorless and odorless nature.
Properly installed and tuned gas furnaces minimize these risks. Modern units incorporate advanced burner design, flame sensors, and safety shutoff controls to ensure stable combustion. Routine inspections and combustion analysis remain essential to maintaining Indoor Air Quality standards.
2. Particulate Circulation Through Ductwork
Gas furnaces rely on forced-air systems. If ductwork is poorly sealed or filtration is inadequate, dust, allergens, and debris can circulate through indoor spaces.
High-performance filtration systems play a central role here. MERV-rated filters capture varying particle sizes, and advanced systems can integrate HEPA filtration for enhanced Indoor Air Quality in sensitive environments such as healthcare or educational facilities.
3. Humidity Imbalance
Gas furnaces produce dry heat. During winter months, prolonged operation can reduce indoor relative humidity levels below recommended thresholds (30–50%). Low humidity can contribute to respiratory irritation, dry skin, static electricity, and increased viral transmission risk.
Integrated humidification solutions counteract this effect and help stabilize Indoor Air Quality.
Positive Contributions of Modern Gas Furnaces to Indoor Air Quality
While risks exist, modern gas furnace systems are engineered to actively support healthier indoor environments.
Sealed Combustion Technology
Sealed combustion furnaces isolate the combustion process from indoor air, drawing intake air from outside and venting exhaust externally. This prevents back drafting and reduces pollutant exposure. For new installations and retrofits, sealed systems are now the industry standard in high-performance buildings.
Advanced Filtration Integration
Today’s gas furnace platforms are designed to accommodate:
- High-efficiency media filters
- Electronic air cleaners
- UV germicidal lamps
- Bipolar ionization systems
When integrated correctly, these solutions significantly enhance Indoor Air Quality by targeting airborne particulates, microbial growth, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Variable-Speed Blower Motors
Variable-speed ECM blower motors maintain consistent airflow and enable continuous low-speed circulation. This improves air mixing, reduces temperature stratification, and increases the effectiveness of filtration systems—ultimately contributing to better Indoor Air Quality across the entire space.
Installation Quality: The Deciding Factor
Even the most advanced furnace will fail to deliver optimal Indoor Air Quality if improperly installed.
Key installation considerations include:
- Correct furnace sizing based on load calculations
- Proper venting configuration
- Airtight duct sealing
- Balanced airflow distribution
- Adequate fresh air ventilation
Oversized systems short-cycle, reducing filtration time and humidity control. Undersized systems overwork and may stress components. Professional commissioning ensures that combustion efficiency and airflow performance align with Indoor Air Quality objectives.
Maintenance and Monitoring Best Practices
Maintaining Indoor Air Quality with gas furnace heating requires proactive care.
1. Regular Filter Replacement
Filters should be replaced according to manufacturer guidelines, typically every 1–3 months depending on usage and environmental conditions.
2. Annual Professional Inspection
Certified technicians should inspect burners, heat exchangers, venting systems, and safety controls annually to prevent combustion-related air quality issues.
3. Carbon Monoxide Detection
CO detectors should be installed on every occupied level. This is a non-negotiable safety requirement in gas-heated environments.
4. Duct Cleaning and Sealing
Periodic duct inspections prevent particulate buildup and leakage, supporting consistent Indoor Air Quality performance.
Integrating Gas Furnace Systems with IAQ-Focused Solutions
Forward-looking manufacturers are engineering gas furnace platforms that serve as central hubs for Indoor Air Quality management. These integrated systems may include:
- Smart thermostats with air quality monitoring
- Humidity sensors and control modules
- Ventilation energy recovery units (ERVs/HRVs)
- Real-time filter status alerts
By combining heating and air purification into a unified system, building owners can manage comfort and Indoor Air Quality simultaneously through centralized controls.
Global Considerations
In colder regions across North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, gas furnace heating remains a cornerstone of building infrastructure. However, regional air quality standards, building codes, and fuel availability vary widely.
Manufacturers serving a global market must design systems that:
- Meet local emissions regulations
- Accommodate diverse climate conditions
- Support both natural gas and propane options
- Integrate with varying ventilation standards
Global compliance and adaptability are now essential components of product development in the heating sector.
The Bottom Line
Gas furnace heating, when properly designed, installed, and maintained, does not inherently compromise Indoor Air Quality. On the contrary, modern high-efficiency systems can enhance IAQ through sealed combustion, advanced filtration compatibility, and integrated humidity management.
The true impact depends on system quality and lifecycle care. Building owners, facility managers, and HVAC professionals should prioritize equipment that supports comprehensive Indoor Air Quality strategies rather than viewing heating as an isolated function.
As Indoor Air Quality continues to gain global attention, gas furnace technology is evolving beyond simple heat delivery. The future lies in integrated, intelligent systems that provide comfort, safety, and cleaner indoor environments—without compromise.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom