health
Diabetes Demystified: How to Take Control of Your Health and Improve Your Quality of Life
Introduction: What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a serious chronic disease that occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When blood sugar levels are too high, it can damage your organs, cause problems with your vision and lead to serious health complications.
There are two main types of diabetes – type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes or insulin-dependent diabetes, occurs when the body doesn’t produce any insulin. People with type 1 diabetes must take daily insulin injections to control their blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset diabetes or non-insulin dependent diabetes, occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively. Type 2 diabetes is much more common than type 1 diabetes – about 90% of all people with diabetes have type 2.
If you have diabetes, it’s important to manage your condition by eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly and taking medication as prescribed by your doctor. With proper treatment and self-care, you can enjoy a good quality of life.
The Different Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, and usually develops in adulthood. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is born.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
There are a number of risk factors for diabetes, and some of them may surprise you. Here are the most common risk factors for this disease:
– being overweight or obese
– having a family history of diabetes
– being over the age of 45
– having high blood pressure
– having high cholesterol
– having a sedentary lifestyle
– smoking cigarettes
If you have any of these risk factors, it’s important to be extra vigilant about your health. Work with your doctor to create a plan to prevent or manage diabetes.
Symptoms of Diabetes
There are a few different types of diabetes, but Type 2 diabetes is the most common form. If you have Type 2 diabetes, your body doesn’t use insulin properly. This is called insulin resistance. Insulin is a hormone that helps your body move sugar from your blood into your cells to be used for energy. When you have insulin resistance, too much sugar stays in your blood. Over time, this can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, eye problems, and nerve damage.
The early symptoms of Type 2 diabetes can be subtle—you might not even notice them at first. But if the disease isn’t treated, it can progress quickly and become very serious. That’s why it’s important to know the signs and symptoms of diabetes and get tested for the disease if you have any concerns.
Some of the early signs and symptoms of Type 2 diabetes include:
• Frequent urination
• Increased thirst
• Fatigue or feeling tired all the time
• blurred vision
• Slow-healing wounds or sores
• Dry mouth
• Itchy skin
• Nausea or vomiting (in severe cases)
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor right away so you can be diagnosed and treated as soon as possible.
Diagnosing Diabetes
If you think you might have diabetes, it’s important to see a doctor right away. They will ask about your symptoms and medical history and may order a blood sugar test. This test measures your blood sugar levels at a specific point in time.
If your blood sugar levels are higher than normal, but not high enough to be diabetes, this is called pre-diabetes. Pre-diabetes means you have a greater chance of developing diabetes in the future. If you have pre-diabetes, making lifestyle changes can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
If your blood sugar levels are higher than normal and you have symptoms of diabetes, such as increased thirst and urination, weight loss, and fatigue, then you may have diabetes. Your doctor will likely order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Complications of Diabetes
There are a number of complications that can arise from diabetes, some of which can be quite serious. These include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and amputation.
Heart disease and stroke are two of the leading causes of death in those with diabetes. Diabetes can damage the blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). This increases the risk for both heart attack and stroke.
Kidney disease is another common complication of diabetes. The kidneys play an important role in filtering waste from the blood, but diabetes can damage them and cause them to fail. This can lead to dialysis or even kidney transplant.
Blindness is another potential complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy. This can eventually lead to blindness if left untreated.
Amputation is another serious complication that can occur as a result of diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high, it can damage the nerves in the feet and legs. This can lead to infections and ulcers that may require amputation if they don’t heal properly.
Treating and Managing diabetes
If you have diabetes, your body does not make or use insulin well. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose get into your cells to give them energy. When there is not enough insulin or the insulin doesn’t work properly, too much glucose stays in your blood. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious problems with your heart, eyes, kidneys, nerves, and gums and teeth.
You can take steps to treat and manage diabetes so that you feel better and live a long and healthy life.
The first step is to see your doctor or health care provider and find out if you have diabetes. If you do have diabetes, they will work with you to create a treatment plan. The plan may include taking medications, making changes to your diet and physical activity level, and regularly checking your blood sugar levels.
You will also need to monitor your own blood sugar levels at home. This involves using a home blood sugar meter to test your blood sugar levels before meals and at bedtime. You will also need to record the results of these tests in a logbook. Your health care provider will use these numbers to adjust your medication doses or make other changes to your treatment plan as needed.
It is important to follow your treatment plan even when you are feeling good. This will help you avoid complications from diabetes such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, eye problems, and gum disease.
Living with diabetes
If you have diabetes, you’re not alone. In the United States, over 30 million people—that’s nearly 10% of the population—have diabetes. But just because diabetes is common doesn’t mean it’s not serious. Diabetes is a chronic disease that can lead to heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and other health problems.
The good news is that you can take control of your diabetes and improve your quality of life. Learning about your diabetes and taking steps to manage your blood sugar, weight, and cholesterol can help you prevent or delay complications. And living a healthy lifestyle—eating healthy foods, being active, and quitting smoking—is important for everyone, whether or not they have diabetes.
If you have diabetes, talk to your doctor about how you can best manage your condition. Together, you can create a treatment plan that’s right for you.
Conclusion
Taking control of your diabetes is not as difficult as it may seem. By following the tips in this article, you can start to better understand how diabetes works and take steps to improve your quality of life. With dedication, lifestyle changes, and help from medical professionals, you can start managing your diabetes and live a healthy life. Taking control of your health with regards to diabetes has never been easier!
Care
Leukoplakia: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for Oral Health
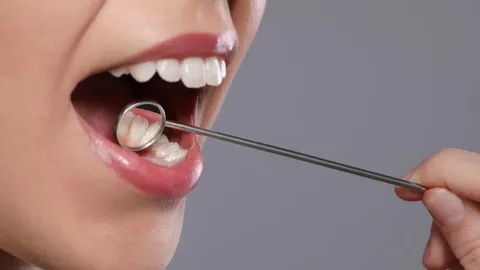
White patches inside the mouth can be worrying, especially when they appear unexpectedly or refuse to go away. Among the most common causes of such patches is a condition known as leukopakia. While it is often harmless, leukoplakia can occasionally signal early signs of more serious problems, making awareness and early detection essential.
Understanding what leukoplakia looks like, why it develops, and how it is treated empowers individuals to take charge of their oral health. This guide walks you through the key facts, symptoms and treatment options, offering clarity and confidence for those who may be noticing unusual changes in their mouth.
What Is Leukopakia?
Leukoplakia refers to thickened white or grey patches that form inside the mouth due to excessive cell growth, often triggered by long-term irritation. These patches may appear on the gums, inner cheeks, tongue, or roof of the mouth. While many cases are harmless, some require monitoring to ensure no further complications develop. Early detection is important because changes can sometimes indicate underlying issues.
Types of leukoplakia:
- Ordinary leukoplakia: Commonly linked to tobacco use and continual irritation.
- Hairy leukoplakia: Associated with viral infections and seen more frequently in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Identifying leukoplakia early helps ensure abnormalities are evaluated promptly and managed before they progress.

What Do Leukoplakia Patches Look Like?
Leukoplakia patches usually appear as uneven, slightly raised areas that feel rough and range in color from white to grey. They cannot be scraped off, which helps distinguish them from conditions like oral thrush. Although generally painless, some people may notice mild sensitivity or irritation, especially when consuming hot or spicy foods. Sudden changes in appearance should be taken seriously.
Warning signs that require urgent evaluation:
- Patches turning red or darkening
- Rapid growth in size
- Increasing discomfort or sensitivity
These changes are often first spotted during brushing or routine dental visits, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups with a dentist or a hygienist in Chichester.
Common Causes & Risk Factors
Leukopakia can be triggered by several factors. Some of the most common include:
Lifestyle-related causes
- Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco remains the most significant cause, responsible for the majority of diagnosed cases.
- Excessive alcohol consumption: Alcohol irritates the oral tissues and magnifies the effects of smoking when combined.
Irritation-related causes
- Rough or sharp teeth rubbing against the inside of the mouth
- Poorly fitted dentures
- Chronic cheek or tongue biting
Medical and biological factors
- Viral infections such as Epstein–Barr virus
- Weakened immune systems
- Ageing and prolonged exposure to irritants
In some instances, individuals discover leukoplakia when visiting an emergency dentist in Chichester due to pain, bleeding or sudden irritation, even though these signs are not always directly caused by the patches themselves.
Diagnosis: How Professionals Identify Leukoplakia
Diagnosing leukoplakia usually starts with a clinical examination, where a dental professional assesses the affected area, reviews medical history, and asks about habits such as smoking or alcohol use. If a patch persists for more than two weeks, further investigation is required to determine the cause. A biopsy is commonly recommended to rule out precancerous changes, involving the removal of a small tissue sample for laboratory analysis. This quick, straightforward procedure helps identify whether the cells show signs of concern.
Additional diagnostic steps may include:
- Extra testing for hairy leukoplakia, especially if a viral condition is suspected
- Imaging or specialist assessment when needed
- Close monitoring of changes in size, texture, or color
Early diagnosis ensures that any potentially harmful developments are addressed promptly. Routine check-ups with a dental professional or a hygienist in Chichester also support long-term monitoring and early detection of new or evolving patches.
Treatment Options
1. Lifestyle and Habit Changes
The first step in managing leukoplakia often involves removing the source of irritation. This may include:
- Stopping smoking or chewing tobacco
- Reducing alcohol intake
- Improving daily oral hygiene practices
For many people, simply eliminating the irritant leads to noticeable improvement or complete resolution of the patches.
2. Dental and Medical Interventions
If leukoplakia is caused by irritation from a sharp tooth or poorly fitting denture, adjustments or replacements may be needed. Hairy leukoplakia may require medication, especially when linked to viral or immune issues. Sudden discomfort, bleeding, or rapid changes should prompt a visit to an emergency dentist in Chichester.
3. Surgical Treatments
If a biopsy reveals dysplasia or if the patches become particularly large or concerning, removal may be recommended. This can be done through:
- Laser therapy
- Cryotherapy (freezing the tissue)
- Traditional surgical excision
These procedures are typically quick and carried out under local anaesthesia, offering reassurance and protection against further risk.
Can Leukoplakia Turn Into Cancer?
Although most cases of leukoplakia remain harmless, a small number can develop into oral cancer over time. Factors that increase this risk include:
- Red patches mixed with white (erythroplakia)
- Rapid growth of the patch
- Persistent soreness or pain
- A long history of smoking and drinking
This is why regular monitoring is essential. With professional guidance and periodic check-ups, any suspicious changes can be caught early, significantly reducing long-term risk.
Prevention Tips
Good oral health habits are key to lowering your risk of developing leukoplakia. Consider the following preventive strategies:
| Preventive Action | Benefit |
| Quit smoking/tobacco | Reduces irritation and cancer risk |
| Limit alcohol use | Protects oral tissues |
| Address dental issues promptly | Prevents chronic friction |
| Maintain strong oral hygiene | Promotes healthier tissue |
| Attend regular dental check-ups | Ensures early detection |
A balanced diet, hydration and regular cleanings can further help maintain healthy oral tissues and reduce irritation.
When to See a Dental Professional
You should seek professional advice if:
- A white or grey patch lasts longer than two weeks
- There is persistent pain, discomfort or bleeding
- The patch changes shape, size or color
- You are a long-term smoker or drinker and notice new symptoms
Early assessment ensures greater peace of mind and more effective treatment options.
Conclusion
Leukoplakia may be a common condition, but paying attention to changes in your oral health is crucial. While most cases remain harmless, staying aware of symptoms, eliminating risk factors and seeking timely professional advice can significantly reduce complications. With the support of experienced dental professionals and proactive habits, you can maintain long-term oral health and confidence. For reliable care and regular check-ups, you can always count on Chichester to guide you toward better oral health and peace of mind.
Care
Enhance Your Career with the OSHA Industrial Safety Course

Introduction
Safety at work is a need in the contemporary industrial and construction industries which are experiencing rapid expansion. The manufacturing sectors also require skilled workers who are conversant with the international safety measures as well as preventing accidents before they occur. This is whereby the OSHA Industrial Safety Course in Rawalpindi comes in.
United College of Technology is pleased to provide a single and career oriented OSHA course in Rawalpindi that is intended to incorporate the current industry demand and global safety measures. This course is best suited to students, individuals, and organizations that would wish to enhance workplace safety and compliance.
What Is OSHA and Why Is It Important?
OSHA is an acronym of Occupational Safety and Health Administration, which is an internationally acclaimed author that establishes the safety standards in the places of work. OSHA guidelines have been used to minimize workplace hazards, injuries, and in favor of a robust safety culture in industries like:
- Construction
- Manufacturing
- Oil & Gas
- Engineering
- Power Plants
- Factories and Warehouses
Students can obtain real knowledge about rules of industrial safety which are recognized in the world by attending an OSHA course in Rawalpindi.

OSHA Industrial Safety Course in Rawalpindi – Course Overview.
United College of Technology provides the OSHA Industrial Safety Course in Rawalpindi that concentrates on the practical aspects of safety concerns in an industrial setting. The course involves both theoretical and practical studies to make sure that everything is understood.
Key Learning Areas Include:
- Detection of hazards in industries.
- Risk evaluation and management.
- The prevention of accidents at work.
- Safety signs and symbols
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
- Fire and emergency response.
- Safety of electricity and mechanical.
- Standards of health and environmental safety.
The course is an OSHA in Rawalpindi course which is appropriate to both the novice and the already established professionals in need of certification regarding safety.
Why United College of Technology to take OSHA Course in Rawalpindi?
The selection of the appropriate institute is of important concern to quality education and progress of career. United College of technology is among the most reputable technical colleges that provide professional courses in terms of safety in the city of Rawalpindi.
The advantages of studying at United College of Technology are as follows:
- Well trained, professional teachers.
- Industry-relevant curriculum
- On-the-job training model.
- Affordable course fees
- Recognized OSHA certification.
- Career guidance and support
We would like to have qualified safety professionals who are capable of fulfilling both local and international industry requirements.
Career Scope Following OSHA Industrial Safety Course.
On finishing the OSHA Industrial Safety Course in Rawalpindi, students have an opportunity to take different jobs in the sphere of safety in Pakistan and other countries.
Career Opportunities It includes:
- Safety Officer
- Supervisor of industrial safety.
- HSE Officer
- Site Safety Inspector
- Safety Coordinator
- Health and Safety Manager (experienced).
The OSHA-certified professionals are in high demand particularly in the construction work, factories, and multinational enterprises.
Who Can enroll in OSHA Course in Rawalpindi?
The course is an OSHA program in Rawalpindi that is accessible to a large group of learners, and they include:
- Fresh students
- Diploma holders
- Engineers
- Site supervisors
- Technicians
- Factory workers
- Safety professionals
There is no higher education level needed and this is why it is easy to use and accessible to any person interested in workplace safety.
Experiential Training and Industry-Based Learning.
We are of the opinion that theory is not as valuable as practice is at United College of Technology. The OSHA Industrial Safety Course of Rawalpindi has real life case studies, safety drills and analysis of hazards to equip the students with the real work conditions.
Such practical method enables students to be able to use safety regulations with a lot of confidence in their job sites and industrial workplaces.
The importance of OSHA Certification in Pakistan and Europe.
The employers nowadays are attracted to the candidates who have professional safety certification. An OSHA course in Rawalpindi is not only one that is going to enhance your knowledge of safety but also improve your CV and employment opportunities.
The certification of OSHA demonstrates that you:
- Know the international standards of safety.
- Can reduce workplace risks
- Trained to deal with emergencies.
- Appreciate health and safety compliance.
- That would make you a valuable investment in any company.
Conclusion
The industrial Safety Course provided by the OSHA in Rawalpindi by United College of Technology is a good chance to have a good career in industrial and workplace safety. As more industry expands, the need to have professional safety workers is more than ever.
Studying this OSHA course in Rawalpindi you obtain internationally accepted knowledge, practical skills and get better employment opportunities not only in Pakistan but also in the abroad. United College of Technology is the place to begin in case you are serious about safety, professionalism and career development.
Care
Hijama: Benefits and Applications of Cupping Therapy
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom