Finance
Cheniere Doubles Down On US Gas Exports as Demand Remains Strong
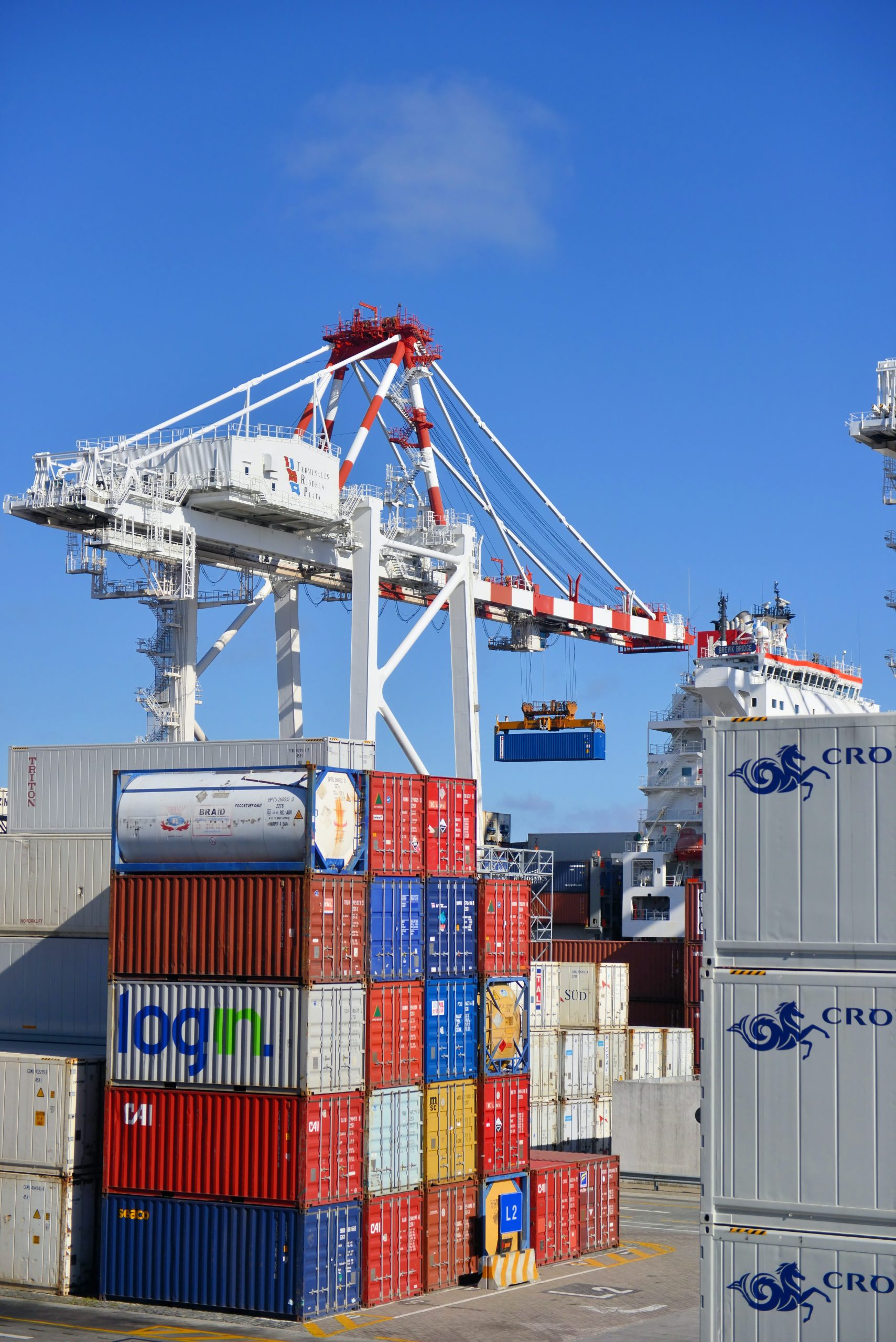

Cheniere Doubles Down On US Gas Exports as Demand Remains Strong
Cheniere Energy Inc. has been the leading natural gas exporter in the United States for years now, with no signs of slowing down. In 2020, Cheniere doubled down on their US gas exports by signing two long-term deals with two of Europe’s biggest utilities. These deals demonstrate Chenier’s commitment to meeting increasing global demand for natural gas and solidifies their position as an industry leader in the space. In this blog post, we will explore Cheniere’s recent moves and discuss why US natural gas exports remain so strong despite the pandemic. We will also examine what impact these developments have on the US energy landscape and how other companies can benefit from similar initiatives.
Who is Cheniere?
Cheniere Energy is one of the leading developers, owners and operators of liquefied natural gas (LNG) assets in the United States. The company owns and operates the Sabine Pass LNG terminal in Louisiana, which is the first large-scale LNG export facility in North America.
In addition to its Sabine Pass facility, Cheniere also has two other LNG export terminals under construction: Corpus Christi LNG in Texas and Cameron LNG in Louisiana. Both of these terminals are expected to come online by 2019.
Once all three terminals are operational, Cheniere will have a combined export capacity of over 30 million tonnes per annum (mtpa). This will make it the largest LNG exporter in the United States.
Cheniere’s expansion into the LNG export market comes as global demand for natural gas continues to grow. According to the International Energy Agency, global demand for natural gas is expected to increase by nearly 50% by 2030.
With its three world-class LNG export facilities, Cheniere is well positioned to meet this growing demand.
What is LNG?
LNG, or liquefied natural gas, is a versatile fuel that can be used for electricity generation, heating, and transportation. LNG is produced by cooling natural gas to -260°F (-162°C), at which point it becomes a liquid. This process reduces the volume of natural gas by up to 600 times, making it easier to store and transport.
LNG is typically transported by tanker ship and must be kept cold during transit. Once it reaches its destination, it is regasified and can be used as a clean-burning fuel for power generation, home heating, and transportation.
LNG is an increasingly popular fuel choice due to its low emissions and high efficiency. In fact, LNG emits up to 60% less carbon dioxide than coal when used for electricity generation. Additionally, LNG is a versatile fuel that can be used in a variety of applications including power generation, transportation, and home heating.
What are the benefits of exporting LNG?
As the world looks to decarbonize its energy mix, gas – and specifically LNG – is playing an increasingly important role. Not only is gas cleaner than coal when burned, but the rise of renewables has created a need for flexible “dispatchable” power that can be called on when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing. This has led to strong demand for US LNG exports, which are expected to grow from around 10 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) in 2019 to over 30 Bcf/d by 2030.
There are a number of reasons why exporting LNG makes sense for the United States:
1) Gas is abundant and relatively cheap in the United States thanks to the shale revolution. This abundance has driven down domestic gas prices, making US LNG exports competitive in global markets.
2) Exporting LNG provides an important outlet for excess gas production, helping to avoid potential supply gluts and price collapses in domestic markets.
3) The growing demand for LNG globally creates an opportunity for the United States to capitalize on its strategic location and well-developed infrastructure.
4) Selling LNG abroad helps to improve the trade balance, as export revenues exceed import costs. This is an important consideration at a time when the United States is looking to reduce its trade deficit.
5) Exporting LNG supports jobs throughout the supply chain, from exploration and
Who are Cheniere’s customers?
As the leading exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in the United States, Cheniere Energy serves customers all over the world. In 2019, Cheniere shipped LNG to customers in Asia, Europe, Latin America, and the Middle East.
One of Cheniere’s most notable customers is British Petroleum (BP), which signed a 20-year contract with Cheniere in 2011 for the purchase of LNG. Under the deal, BP will buy up to 3 million tons of LNG per year from Cheniere’s Sabine Pass facility in Louisiana.
Other major customers of Cheniere include Total SA, Shell, and South Korea’s KOGAS. Together, these four companies accounted for over 60% of Cheniere’s LNG exports in 2019.
How has the pandemic affected LNG demand?
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound effect on LNG demand, with global consumption falling by around 15% in 2020. This is largely due to economic activity slowing down in many countries, as businesses have been forced to close their doors and people have been confined to their homes. This has led to a reduction in energy consumption, as factories and power plants have been idled and transportation has been limited.
While the pandemic has caused a drop in demand for LNG, Cheniere remains bullish on the prospects for US gas exports. The company is investing heavily in new export terminals, betting that the long-term fundamentals for natural gas remain strong. There is growing demand for cleaner-burning fuels like natural gas, as countries look to transition away from coal and oil. And with the US shale boom showing no signs of slowing down, there is an abundance of cheap gas available for export.
Despite the challenges posed by the pandemic, Cheniere is doubling down on its bet that US gas exports will remain strong in the years to come.
What’s next for Cheniere?
As the leading exporter of liquefied natural gas (LNG) in the United States, Cheniere is well-positioned to take advantage of the growing demand for LNG around the world.
In the short-term, Cheniere is focused on completing construction of its Sabine Pass Liquefaction Facility in Louisiana and bringing it into full commercial operation. Once operational, the facility will have a nominal production capacity of approximately 4.5 million metric tons per annum of LNG.
Looking further ahead, Cheniere is actively pursuing opportunities to expand its liquefaction capacity at its Sabine Pass facility and build additional export facilities elsewhere in North America. With strong demand for LNG expected to continue, Cheniere is well-positioned to grow its business and become an even more important player in the global LNG market.
Conclusion
Cheniere’s decision to double down on US gas exports shows that the demand for US natural gas remains strong. With its advanced infrastructure and vast reserves of inexpensive natural gas, Cheniere is well-positioned to take advantage of this increasing demand. The company’s dedication to providing clean, affordable energy will help ensure that the United States maintains a competitive edge in global markets and keeps up with rising consumer demands for green energy sources.
Business
Smart Budgeting Tips for Freelancers in 2025

Introduction
Freelancers enjoy the freedom of setting their own schedules, but managing money can be challenging. Unlike traditional employees who receive a steady paycheck, freelancers experience fluctuating income, which makes budgeting for freelancers especially important. Without a clear budget plan, it’s easy to overspend during busy months and struggle during slow periods.
In 2025, freelancers have access to more resources than ever to help them manage their finances and interest rates. From financial apps to smart budgeting strategies, there are plenty of ways to stay on top of your money. This article will explore smart budgeting tips that will help you manage your freelance income,credit score, save effectively, and build a sustainable financial future.
What Makes Freelance Budgeting Different?

Image by: Yandex.com
Freelancers have unique challenges when it comes to managing finances. Unlike salaried workers, freelancers do not receive regular paychecks. This can create uncertainty, especially when clients delay payments or work slows down unexpectedly.
However, with the right strategies, freelancers can thrive financially. Here’s how you can budget for freelance success:
1. Track Your Income and Expenses
To create a realistic budget, the first step is to track your income and business expenses. This can be more difficult for freelancers because your income isn’t fixed. To stay on top of your finances, you need to know exactly how much you’re earning and spending each month.
Tip: Use tools like QuickBooks, FreshBooks, or Wave to easily track income and expenses. These apps are designed specifically for freelancers and can help simplify your financial management.
2. Create a Flexible Budget Plan
A solid budget plan is essential, but as a freelancer, you need one that’s flexible. Your income can vary from month to month, so a flexible budget lets you adjust your spending based on how much you earn.
Tip: Start with a 50/30/20 rule:
- 50% for needs (rent, utilities, etc.)
- 30% for wants (entertainment, dining out)
- 20% for savings and debt repayment
Adjust the percentages based on your personal financial goals.
3. Set Aside a Portion of Your Income for Taxes
Freelancers are responsible for paying their own taxes, and this can sometimes catch people off guard. To avoid scrambling for money when tax season arrives, set aside a portion of your income each month for taxes.
Tip: Save at least 25-30% of your income for taxes, depending on your tax bracket and location. Set up a separate savings account to keep this money safe and easy to access when needed.
4. Build an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is crucial for freelancers. Since you don’t have a steady paycheck, unexpected expenses or gaps between projects can create financial stress. An emergency fund provides a safety net, allowing you to cover your living expenses when income is lower than usual.
Tip: Aim for 3-6 months of living expenses in your emergency fund. Start small and gradually increase your savings over time.
5. Automate Savings
One of the best ways to build your savings as a freelancer is to automate your savings. This means setting up automatic transfers to your savings account each time you get paid, so you don’t have to think about it.
Tip: Set up automatic transfers for both your emergency fund and long-term savings goals. Many banks and apps, like Acorns or Chime, allow you to automatically round up purchases and transfer the difference to a savings account.
6. Separate Business and Personal Finances
As a freelancer, it’s tempting to mix business and personal finances, but this can make budgeting and tax filing more difficult. To stay organized, open a separate bank account for your business and use it exclusively for freelance income and business-related expenses.
Tip: Set up a business credit card and use it for work-related expenses. This will also help you build business credit, which can be beneficial for securing loans in the future.
7. Plan for Retirement
Freelancers don’t have the luxury of employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s. However, it’s still important to save for retirement. In 2025, there are more retirement savings options available for freelancers, such as SEP IRAs and Solo 401(k)s.
Tip: Consider setting up a Solo 401(k) or IRA for tax-deferred growth. Contribute regularly to build your retirement fund.
Challenges of Smart Budgeting
Building and sticking to a budget can be tough when income jumps up and down. One month might bring high pay and the next nothing at all. It takes discipline to save more when money flows and resist extra spending. Tracking every expense can feel like extra work when deadlines loom. Freelancers also face unknown costs for taxes, insurance, or tools. Choosing the right app or method can feel overwhelming at first. Overcoming these hurdles requires patience, trial and error, and small wins to build confidence.
Future of Smart Budgeting Tips for Freelancers

Image by: Yandex.com
Looking ahead, smart budgeting tools will grow even more helpful and personal. Apps may use AI to predict slow seasons and suggest the best savings targets. Freelancers might get real‑time alerts when they overspend or when tax deadlines approach. Social platforms could connect them with mentors for money advice. Virtual assistants may automate bill payments and track subscriptions. Yet the core will stay the same: track income, plan costs, and save for goals. In 2025 and beyond, mastering these simple steps will remain key to freelance success.
Comparative Table: Key Budgeting Tips for Freelancers
| Tip | Description | Why It Works |
|---|---|---|
| Track Income and Expenses | Use tools like QuickBooks or FreshBooks | Understand where your money goes and track your finances |
| Create a Flexible Budget | Adjust spending based on income fluctuations | Allows you to manage income variability effectively |
| Save for Taxes | Set aside 25-30% of income for taxes | Avoid tax surprises and manage funds for tax season |
| Build an Emergency Fund | Save 3-6 months of living expenses | Provides a financial cushion during slow months |
| Automate Savings | Set up automatic transfers to savings accounts | Ensures consistent saving and financial growth |
| Separate Business and Personal Finances | Open separate accounts for business expenses | Keeps your finances organized and simplifies taxes |
| Plan for Retirement | Contribute to a retirement fund like a Solo 401(k) | Builds long-term wealth and provides financial security |
Conclusion: Manage Your Freelance Finances Like a Pro
Budgeting as a freelancer can seem overwhelming, but with the right strategies, you can take control of your finances and ensure long-term success. By tracking your income, creating a flexible budget, and saving for taxes and retirement, you can achieve financial stability as a freelancer.
In 2025, the tools and strategies available make it easier than ever to manage your money. Start implementing these smart budgeting tips today and build a secure financial future.
Finance
Investment Strategies for Young Professionals in 2025

Introduction
Starting your investment journey as a young professional can be both exciting and overwhelming. With the right investment strategies for young professionals, you can build wealth, achieve financial independence, and secure your future. 2025 presents new opportunities and challenges in the financial landscape, and understanding how to navigate these changes is essential for success.
In this article, we’ll explore effective investment strategies that young professionals can adopt in 2025. From stock market investments to real estate opportunities, we’ll cover the best ways to grow your wealth, manage risks, and make smart financial decisions.
What is Investment for Young Professionals?

Image by: Yandex.com
Investment is the process of putting your money into various assets, such as stocks, bonds, or real estate, with the expectation that they will grow over time. For young professionals, investing is one of the most effective ways to build wealth and achieve financial goals freedom.
In 2025, investment strategies for young professionals are focused on long term goal, diversification, and risk management. By starting early and making informed decisions, young professionals can take advantage of compounding returns, lower initial investment amounts, and the opportunity to learn about the market indexes over time.
Why Should Young Professionals Invest?

Image by: Yandex.com
Investing is important for young professionals because it helps you build wealth outside of your regular income. Here are some of the key benefits of investing early:
- Compounding Returns: Starting early allows you to take advantage of the power of compounding, where your investment earns interest on both the initial amount and the accumulated interest over time.
- Wealth Building: Investments, such as stocks or real estate, can provide higher returns than savings accounts, helping you accumulate wealth faster.
- Financial Independence: Building an investment portfolio early can help you achieve financial independence and retire comfortably.
Best Investment Strategies for Young Professionals in 2025

Image by: Yandex.com
1. Start with a Strong Emergency Fund
Before you dive into investments, it’s essential to build an emerging markets fund. An emergency fund provides a financial cushion for unexpected expenses, such as medical bills or job loss. This will ensure that you don’t have to dip into your investments in times of crisis.
Why It Matters:
Having an emergency fund manager prevents you from buy or sellling investments during market downturns or emergencies, allowing your investments to grow as intended.
Tips for Building an Emergency Fund:
- Aim to save 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses.
- Store your emergency fund in a high-yield savings account for easy access and higher returns.
2. Invest in Index Funds and ETFs
For young professionals just starting out, index funds and ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) are excellent choices. These funds track the performance of major market indices and share prices, such as the S&P 500, providing broad market exposure with lower risks compared to individual stocks.
Why It’s Great for Young Professionals:
- Low cost and diversification: Index funds and ETFs have low fees and spread risk across many different assets.
- Long-term growth: They are ideal for long-term investments with the potential for steady returns.
Tips for Investing in Index Funds and ETFs:
- Invest in low-cost index funds that track major indices or sectors.
- Consider using a robo-advisor to automate your investments in ETFs and index funds.
3. Explore Real Estate Investment
Real estate continues to be a popular investment choice for young professionals looking to build wealth. While it may require more initial capital, it offers both passive income and the potential for significant appreciation over time.
Why It’s Great for Wealth-Building:
- Rental income: Investing in rental properties provides regular cash flow.
- Appreciation: Real estate properties tend to increase in value over the long term, offering both short-term income and long-term capital gains.
Tips for Investing in Real Estate:
- Start with real estate investment trusts (REITs) if you don’t have enough capital for a property.
- Research areas with high rental demand or growing real estate markets to increase profitability.
4. Focus on Sustainable and Ethical Investments
In 2025, there is an increasing trend towards sustainable investing. Many young professionals are choosing to invest in companies and funds that align with their values, such as those focused on renewable energy, environmental conservation, and social responsibility.
Why It’s Popular:
- Aligns with personal values: Sustainable investing allows you to support industries that have a positive impact on society.
- Growing market: Companies focused on sustainability often see long-term growth due to increasing consumer demand for ethical practices.
Tips for Sustainable Investing:
- Look for ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) funds that invest in ethical companies.
- Research companies that focus on clean energy or green technologies for long-term growth.
5. Diversify Your Portfolio
One of the most important principles in investing is diversification. Diversification means spreading your investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) to reduce risk. In 2025, young professionals are choosing to diversify by combining traditional investments with alternative investment options like cryptocurrency or commodities.
Why Diversification Matters:
- Reduces risk: Diversifying protects you if one market or asset class performs poorly.
- Increases potential returns: By holding various assets, you can take advantage of growth in different sectors.
Tips for Diversifying Your Portfolio:
- Mix stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternative investments like cryptocurrency or commodities.
- Regularly review your portfolio to ensure it remains well-balanced.
6. Use Tax-Advantaged Accounts
To maximize your investment returns, young professionals should consider using tax-advantaged accounts like Roth IRAs, Traditional IRAs, or 401(k) plans. These accounts allow your investments to grow tax-free or tax-deferred, which means more of your money stays invested.
Why It’s Important for Young Professionals:
- Tax savings: You can save on taxes by contributing to retirement accounts.
- Compound growth: Investments in tax-advantaged accounts grow faster since they are not taxed yearly.
Tips for Using Tax-Advantaged Accounts:
- Contribute the maximum amount to your 401(k) if your employer offers a match.
- Open a Roth IRA to invest for retirement without paying taxes on your gains.
Challenges of Investment for Young Professionals
While investing is a powerful tool, there are also challenges young professionals face when starting out. One of the biggest challenges is figuring out where to invest and how much to risk. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to choose the right investment opportunities. Another challenge is managing emotions many new investors may panic during market downturns, making impulsive decisions. Additionally, young professionals may not have a lot of disposable income to invest, making it difficult to build a portfolio. However, with the right education and guidance, these challenges can be overcome.
The Future of Investment Strategies for Young Professionals

Image by: Yandex.com
As we move into the future, investment strategies for young professionals will continue to evolve. In 2025 and beyond, new technologies and platforms will make it even easier for young people to invest wisely. Automated investment tools and robo-advisors will become more common, offering personalized advice based on individual goals and risk tolerance. The rise of sustainable and socially responsible investing (SRI) is also gaining traction, as many young professionals want to align their investments with their values. The future of investing will likely involve more options, better tools, and a deeper understanding of financial markets, empowering young professionals to take even more control over their financial future.
Comparative Table: Best Investment Strategies for Young Professionals in 2025
| Investment Strategy | Why It’s Great for Young Professionals | Tips for Success |
|---|---|---|
| Index Funds & ETFs | Low-cost, diversification, and long-term growth | Invest in broad market funds like S&P 500 or sector ETFs |
| Real Estate | Passive income, property appreciation | Consider REITs if you lack capital for property |
| Sustainable Investing | Aligns with values, growing market | Invest in ESG funds or clean energy stocks |
| Diversification | Risk reduction, increased returns | Mix stocks, bonds, real estate, and alternatives |
| Tax-Advantaged Accounts | Tax savings, compound growth | Max out your 401(k) and Roth IRA contributions |
Conclusion
In 2025, young professionals have more opportunities than ever to grow their wealth and achieve financial independence through smart investment strategies. Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your approach, adopting diversified investments, focusing on sustainable growth, and using tax-advantaged accounts can help you achieve long-term success.
By making informed decisions, staying consistent, and educating yourself, you can set a solid foundation for your financial future. Start investing today to secure a prosperous tomorrow.
Call to Action
Ready to start your investment journey? Explore these investment strategies for young professionals and take the first step toward building your financial future. Visit our website for more tips, tools, and resources to help you make the best investment decisions in 2025!
Finance
Sustainable Fashion: Brands Leading Eco-Friendly Movement

Introduction
Recently, there’s been a big push for sustainable fashion. People are more concerned about the environment, and the fashion world is changing to be more eco-friendly. With growing worries about pollution and waste, many shoppers are choosing brands that care about the planet and treat workers fairly. In this article, we’ll look at some top sustainable fashion brands in 2025 and how they’re changing how we think about clothes, shopping, and style.
What Is Sustainable Fashion?

Image by: Yandex.com
Sustainable fashion means clothing, shoes, and accessories that are made in a way that’s good for the environment and people. This includes using materials that don’t harm the planet and making sure workers are treated fairly. Sustainable fashion also means buying fewer clothes that last longer, and taking care of them by fixing or reusing them instead of throwing them away.
Why Is Sustainable Fashion Important?

Image by: Yandex.com
The fashion industry is one of the biggest causes of pollution, using lots of water and making a lot of waste. Sustainable fashion tries to fix this by encouraging brands and shoppers to make eco-friendly choices. By choosing brands that care about the environment, we can help protect the Earth and make sure workers are paid fairly. Supporting these brands can push bigger companies to do the same. Sustainable fashion is not just a trend, but a way to help the planet.
Top 5 Sustainable Fashion Brands Leading the Way in 2025
1. Patagonia

Image by: Yandex.com
Patagonia has been a leader in sustainable fashion for a long time. The brand uses recycled materials in its clothing and helps protect nature. Patagonia encourages customers to buy used clothes and repair their old ones instead of buying new.
Why It’s Leading the Movement
- Uses recycled materials
- Focuses on helping the environment
- Treats workers fairly
2. Reformation

Image by: Yandex.com
Reformation makes stylish clothes using eco-friendly fabrics like organic cotton and linen. They work to use less water and energy, and they care about how their workers are treated. The brand is also open about its environmental impact.
Why It’s Leading the Movement
- Uses eco-friendly fabrics
- Is open about its environmental impact
- Stylish but sustainable
3. Stella McCartney

Image by: Yandex.com
Stella McCartney is a high-end brand that shows you can be fancy and eco-friendly at the same time. They use organic cotton, recycled fabrics, and avoid using animal products like leather. Stella also works to reduce waste and its carbon footprint.
Why It’s Leading the Movement
- Luxury designs using eco-friendly materials
- No animal products used
- Reduces waste and carbon emissions
4. Everlane

Image by: Yandex.com
Everlane is all about being honest and open with customers. They use materials like organic cotton and recycled fabrics, and they make sure all their workers are paid fairly. Everlane is working toward becoming a climate-neutral brand by 2025.
Why It’s Leading the Movement
- Honest about pricing and how clothes are made
- Focuses on fair wages
- Committed to becoming climate neutral
5. Allbirds

Image by: Yandex.com
Allbirds is known for its sustainable shoes. The brand uses materials like merino wool and recycled foam made from sugarcane. They also try to reduce their carbon footprint and make sure their shoes are both comfortable and eco-friendly.
Why It’s Leading the Movement
- Uses eco-friendly materials
- Focuses on reducing carbon emissions
- Promotes recycling and reusing
The Challenges of Sustainable Fashion: What’s Holding the Industry Back?
Despite the many benefits of sustainable fashion, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main obstacles is the higher cost of eco-friendly materials and production methods. Sustainable fashion often requires more time and effort to make, which can drive up prices. This makes it less accessible for some consumers who may find it difficult to afford eco-friendly clothing. Additionally, the industry faces issues with scaling sustainable practices, as it can be challenging for small brands to compete with the fast fashion giants. While there are many eco-conscious brands out there, changing the entire fashion industry to adopt more sustainable practices will take time, effort, and collaboration across various sectors.
The Future of Sustainable Fashion: What’s Next for Eco-Friendly Brands?

Image by: Yandex.com
Looking ahead, the future of sustainable fashion seems promising. With increasing awareness about climate change and environmental issues, more consumers are turning to eco-friendly options. Fashion brands are innovating with new materials, such as plant-based fabrics, recycled textiles, and biodegradable garments, which will help reduce the environmental impact of fashion production. Technology is also playing a role, with advancements in recycling and sustainable manufacturing methods making it easier for brands to produce eco-friendly clothing at scale. As the demand for sustainable fashion grows, more companies will likely adopt sustainable practices. The future of fashion is moving towards a world where looking good and protecting the planet can go hand in hand.
Comparative Table: Top Sustainable Fashion Brands
| Brand | Sustainable Practices | Key Materials | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patagonia | Recycled materials, eco-friendly production | Recycled polyester, organic cotton, wool | Environmental conservation, repair & reuse |
| Reformation | Transparent supply chain, eco-friendly fabrics | Organic cotton, linen, Tencel | Stylish, eco-conscious fashion |
| Stella McCartney | Vegan fashion, sustainable luxury | Organic cotton, recycled polyester, vegan leather | Luxury fashion, animal rights |
| Everlane | Radical transparency, ethical manufacturing | Organic cotton, recycled polyester, Tencel | Transparency, fair wages, carbon neutrality |
| Allbirds | Carbon offsetting, circular fashion | Merino wool, sugarcane foam, recycled materials | Sustainable footwear, carbon footprint reduction |
Conclusion
Sustainable fashion isn’t just a trend it’s a big change in how we buy clothes and think about shopping. Brands like Patagonia, Reformation, Stella McCartney, Everlane, and Allbirds are showing the way by offering eco-friendly, stylish, and high-quality clothes and shoes. As we move into 2025, supporting these brands and making better choices about what we wear is important for a better future.
Call to Action
Ready to make better choices for the planet with your clothes? Check out these eco-friendly brands and start shopping for items that are stylish and good for the Earth. Visit their websites to learn more about their sustainable practices and join the movement toward a greener future!
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoCybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoTeam Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoProject Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-

 Business2 years ago
Business2 years agoHow Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-

 health2 years ago
health2 years agoBreast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-

 Sports2 years ago
Sports2 years agoUnstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-

 Art /Entertainment2 years ago
Art /Entertainment2 years agoEmbracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-

 Finance2 years ago
Finance2 years agoThe Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom