Technology Explained
USB4 vs Thunderbolt 4: A Feature Comparison
Introduction to USB4 and Thunderbolt 4
USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 have garnered significant attention due to their impressive data transfer rates and compatibility. USB4, developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF), seeks to unify various connectivity standards, promising a single interface for multiple devices. Thunderbolt 4, on the other hand, is Intel’s creation, building upon the Thunderbolt 3 framework with enhanced features.
Speed and Bandwidth: Which Reigns Supreme?
When it comes to speed, both USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 excel, offering remarkable data transfer rates. USB4 boasts a maximum throughput of 40 Gbps, aligning itself closely with Thunderbolt 3’s capabilities. Thunderbolt 4, however, maintains its lead with a similar 40 Gbps speed while also providing support for dual 4K displays or a single 8K display. Despite the comparable speeds, Thunderbolt 4’s additional display capabilities provide an edge for users seeking high-performance connectivity.
Image by https://contrank.com/
Compatibility and Port Options
Compatibility plays a pivotal role in choosing between USB and Thunderbolt 4. USB4 utilizes the USB Type-C connector, offering backward compatibility with USB 2.0, USB 3.0, and Thunderbolt 3 devices. This wide range of compatibility makes USB4 a versatile choice for various setups. Thunderbolt 4, while also using the USB Type-C port, maintains a focus on modern Intel-based systems and offers full compatibility with Thunderbolt 3 devices. If you’re looking for compatibility across a broader spectrum of devices, USB4 might be the preferable option.
Versatility vs Specialization: Use Cases Explored
USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 cater to different use cases due to their design philosophies. USB4 emphasizes versatility, targeting a wide array of devices, including external hard drives, monitors, and more. It aims to provide a unified connectivity solution across various device types. Thunderbolt 4, on the other hand, caters to users seeking higher-end performance, making it an ideal choice for professionals working with resource-intensive tasks like video editing and 3D rendering. If you require specialized performance, Thunderbolt 4’s capabilities might align better with your needs.
In conclusion, both USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 offer exceptional connectivity options, each with its strengths and target audience. USB4’s versatility and wide compatibility make it suitable for general users, while Thunderbolt 4’s enhanced capabilities cater to professionals and power users. Your choice between the two will ultimately depend on your specific requirements and the devices you intend to connect. By understanding their features, speeds, compatibility, and use cases, you can confidently make the right decision for your connectivity needs.
Costumer Services
SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
If you’re facing problems with SBCGlobal email not receiving emails, you’re not alone. Many users experience email delivery issues caused by server settings, outdated configurations, or account security errors. This guide will walk you through why your SBCGlobal email might not be receiving messages, how to fix it step-by-step, and when to contact professional suppor for advanced troubleshooting.
What Is SBCGlobal Email?
SBCGlobal.net is a legacy email service originally provided by Southwestern Bell Corporation, which later merged with AT&T. Even though new SBCGlobal accounts are no longer being created, millions of users still access their SBCGlobal email through AT&T’s Yahoo Mail platform.
However, because SBCGlobal operates on older infrastructure and server settings, users sometimes experience email syncing, login, or receiving issues especially when using third-party apps or outdated settings.

Common Reasons SBCGlobal Email Is Not Receiving Emails
Before you start troubleshooting, it’s important to identify what might be causing the issue. Below are the most frequent culprits behind SBCGlobal email receiving problems:
- Incorrect Email Settings: If your incoming (IMAP/POP3) or outgoing (SMTP) settings are incorrect, emails won’t load properly.
- Server Outages: Temporary outages or server maintenance by AT&T or Yahoo may interrupt incoming mail delivery.
- Storage Limit Reached: When your mailbox exceeds its storage limit, new emails are automatically rejected.
- Spam or Filter Rules: Overly strict filters or incorrect spam settings might send legitimate emails to the Junk or Trash folder.
- Browser Cache or App Glitches: Cached data and outdated email apps can disrupt syncing or message retrieval.
- Blocked Senders or Blacklisted IPs: Accidentally blocking a sender or being on a spam blacklist may prevent messages from reaching your inbox.
- Security or Account Lock Issues: Suspicious login attempts or password errors can cause temporary account restrictions.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails
Let’s go through a series of troubleshooting steps to help you restore your email flow. You can perform these solutions on both desktop and mobile platforms.
1. Check SBCGlobal Email Server Status
- Sometimes, the issue isn’t on your end.
- Go to Downdetector or AT&T’s official website to see if SBCGlobal or AT&T Mail is down.
If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait until the service is restored.
2. Verify Your Internet Connection
Ensure your device has a stable and fast internet connection. Poor connectivity can stop your email client from syncing or fetching new messages.
3. Update Incoming and Outgoing Mail Server Settings
Outdated or incorrect settings are the most common reason SBCGlobal email stops receiving messages. Here are the correct configurations:
Common Reasons SBCGlobal Email Is Not Receiving Emails
Before you start troubleshooting, it’s important to identify what might be causing the issue. Below are the most frequent culprits behind SBCGlobal email receiving problems:
- Incorrect Email Settings: If your incoming (IMAP/POP3) or outgoing (SMTP) settings are incorrect, emails won’t load properly.
- Server Outages: Temporary outages or server maintenance by AT&T or Yahoo may interrupt incoming mail delivery.
- Storage Limit Reached: When your mailbox exceeds its storage limit, new emails are automatically rejected.
- Spam or Filter Rules: Overly strict filters or incorrect spam settings might send legitimate emails to the Junk or Trash folder.
- Browser Cache or App Glitches: Cached data and outdated email apps can disrupt syncing or message retrieval.
- Blocked Senders or Blacklisted IPs: Accidentally blocking a sender or being on a spam blacklist may prevent messages from reaching your inbox.
- Security or Account Lock Issues: Suspicious login attempts or password errors can cause temporary account restrictions.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails
Let’s go through a series of troubleshooting steps to help you restore your email flow. You can perform these solutions on both desktop and mobile platforms.
1. Check SBCGlobal Email Server Status
- Sometimes, the issue isn’t on your end.
- Go to Downdetector or AT&T’s official website to see if SBCGlobal or AT&T Mail is down.
If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait until the service is restored.
2. Verify Your Internet Connection
Ensure your device has a stable and fast internet connection. Poor connectivity can stop your email client from syncing or fetching new messages.
3. Update Incoming and Outgoing Mail Server Settings
Outdated or incorrect settings are the most common reason SBCGlobal email stops receiving messages. Here are the correct configurations:
- Server:
imap.mail.att.net - Port: 993
- Encryption: SSL
- Username: Your full SBCGlobal email address
- Password: Your email password
Outgoing Mail (SMTP) Server:
- Server:
smtp.mail.att.net - Port: 465 or 587
- Encryption: SSL/TLS
- Requires Authentication: Yes
If you’re using POP3, use:
- Incoming server:
inbound.att.net, Port 995 (SSL required) - Outgoing server:
outbound.att.net, Port 465 (SSL required)
Double-check these settings in your email client (Outlook, Apple Mail, Thunderbird, etc.) to make sure they match.
4. Review Spam and Junk Folder
- Sometimes, legitimate emails end up in the Spam or Junk folder. Open these folders and mark any wrongly filtered emails as “Not Spam.”
- Also, check your Filters and Blocked Addresses under email settings to ensure no important addresses are being redirected or blocked.
5. Clear Browser Cache or Update Your App
If you access SBCGlobal email through a browser:
- Clear your cache, cookies, and browsing history.
- Try opening email in incognito/private mode to rule out extensions or ad blockers causing problems.
If you use the Yahoo Mail App or Outlook, ensure the app is updated to the latest version. Outdated apps may not sync with the latest server configurations.
6. Check Mailbox Storage Limit
- SBCGlobal email accounts have a maximum storage quota.
- Delete unnecessary emails from your inbox, sent, and trash folders.
- After clearing space, refresh your inbox or restart your email client — new emails should start appearing.
7. Reset or Re-Add Your SBCGlobal Account
- If none of the above methods work, try removing your SBCGlobal account from your email client and re-adding it with the correct settings.
- This refreshes the connection and often resolves syncing or server timeout issues.
8. Reset Your Password
If you suspect your account might have been compromised or temporarily locked, resetting your password is a smart step.
- Visit the AT&T Password Reset page.
- Follow the on-screen steps to verify your identity.
- Set a strong, unique password and re-login to your email account.
9. Disable Security Software Temporarily
- Firewall or antivirus software can sometimes block email servers.
- Temporarily disable them (only if you’re confident about your network security) and check if you start receiving emails again.
10. Contact SBCGlobal Email Support
- If you’ve followed all the steps and your SBCGlobal email is still not receiving messages, the issue might be server-side or linked to account configuration.
- In that case, it’s best to contact SBCGlobal email support for expert help.
You can reach certified technicians.
They can assist with:
- Account recovery and login errors
- Server synchronization issues
- Email migration or backup
- Advanced spam and security settings
Having professional help ensures your account is restored quickly without losing any important messages or data.
Tips to Prevent Future SBCGlobal Email Problems
- Update Passwords Regularly: Keep your email account secure and avoid login lockouts.
- Use a Reliable Email App: Apps like Outlook or Apple Mail handle IMAP connections more efficiently.
- Backup Emails Periodically: Regular backups protect your messages from unexpected sync failures.
- Keep Storage Under Control: Delete old attachments and large files frequently.
- Monitor Account Activity: Check for unusual login attempts from unknown locations.
Final Thoughts
Facing issues like SBCGlobal email not receiving emails can be frustrating, especially when you rely on your email for important communications. However, most problems can be resolved by verifying server settings, clearing browser cache, managing storage, or resetting passwords.
If you continue to face challenges, don’t hesitate to reach out to expert SBCGlobal email support for personalized assistance. A few minutes of professional troubleshooting can save hours of frustration and get your SBCGlobalemail running smoothly again.
Development
Enhancing Mapping Accuracy with LiDAR Ground Control Targets
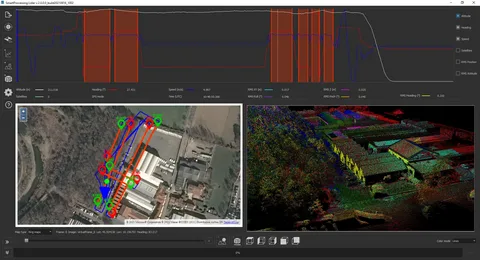
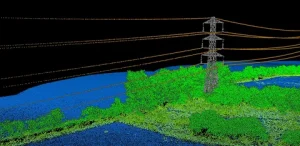
How Do LiDAR Ground Control Targets Work?
LiDAR technology uses laser pulses to scan the ground and capture a wide range of data, including elevation, shape, and distance. However, the data collected by LiDAR sensors needs to be aligned with real-world coordinates to ensure its accuracy. This is where LiDAR ground control targets come in.
Georeferencing LiDAR Data
When LiDAR sensors capture data, they record it as a point cloud, an array of data points representing the Earth’s surface. To make sense of these data points, surveyors need to assign them precise coordinates. Ground control targets provide reference points, allowing surveyors to georeference point cloud data and ensure that LiDAR data aligns with existing maps and models.
By placing LiDAR ground control targets at specific locations on the survey site, surveyors can perform adjustments to correct discrepancies in the data caused by factors such as sensor calibration, flight altitude, or atmospheric conditions.
Why Are LiDAR Ground Control Targets Essential for Accurate Mapping?
LiDAR technology is incredibly powerful, but the accuracy of the data depends largely on the quality of the ground control points used. Here are the key reasons why LiDAR ground control targets are essential for obtaining precise mapping results:
1. Improved Geospatial Accuracy
Without ground control targets, LiDAR data is essentially “floating” in space, meaning its position isn’t aligned with real-world coordinates. This can lead to errors and inaccuracies in the final map or model. By placing LiDAR ground control targets at known geographic coordinates, surveyors can calibrate the LiDAR data and improve its geospatial accuracy.
For large projects or those involving multiple data sources, ensuring that LiDAR data is properly georeferenced is critical. Ground control targets help ensure the survey data integrates seamlessly with other geographic information systems (GIS) or mapping platforms.
2. Reduction of Measurement Errors
LiDAR ground control targets help mitigate errors caused by various factors, such as:
- Sensor misalignment: Minor inaccuracies in the LiDAR sensor’s position or angle can cause discrepancies in the data.
- Aircraft or drone movement can slightly distort the sensor’s collected data.
- Environmental conditions: Weather, temperature, and atmospheric pressure can all affect the LiDAR signal.
By using ground control targets, surveyors can compensate for these errors, leading to more precise and reliable data.
3. Support for Large-Scale Projects
For larger mapping projects, multiple LiDAR scans might be conducted from different flight paths or at different times. Ground control targets serve as common reference points, ensuring that all collected data can be merged into a single coherent model. This is particularly useful for projects involving vast areas like forests, mountain ranges, or large urban developments.
How to Choose the Right LiDAR Ground Control Targets
Choosing the right LiDAR ground control targets depends on several factors, including the project’s size, the terrain, and the required accuracy. Here are some things to consider:
Size and Visibility
The size of the target should be large enough to be easily detectable by the LiDAR sensor from the air. Targets that are too small or poorly placed can lead to inaccurate data or missed targets.
Material and Durability
Ground control targets must have enough durability to withstand weather conditions and remain stable throughout the surveying process. Surveyors often use reflective materials to ensure that the LiDAR sensor can clearly detect the target, even from a distance.
Geospatial Accuracy
For high-accuracy projects, surveyors must place ground control targets at precise, known locations with accurate geospatial coordinates. They should use a GPS or GNSS system to measure and mark the exact position of the targets.
Conclusion
LiDAR ground control targets play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy of aerial surveys and LiDAR mapping projects. By providing precise reference points for geo referencing and adjusting LiDAR data, these targets reduce errors and improve the overall quality of the final model. Whether you’re working on a small-scale project or a large-scale survey, integrating ground control targets into your LiDAR workflow is essential for achieving high-precision results.
The right ground control targets, when placed correctly and properly measured, can make the difference between reliable, actionable data and inaccurate measurements that undermine the entire survey.
By understanding the importance of these targets and how they function in the context of LiDAR surveys, you’ll be better prepared to tackle projects that demand accuracy and precision.
Digital Development
Scalable Web Application Development: Strategies for Growth
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom