Science
Revolutionizing Agriculture: How Genetic Engineering is Paving the Way for Sustainable Crops

As the world population continues to grow, so does the demand for food. With limited land and resources, sustainable agriculture practices have become a pressing issue. Genetic engineering has emerged as a promising solution that can revolutionize agriculture and pave the way for sustainable crops. However, it’s not without controversy and risks. In this blog post, we’ll explore how genetic engineering is changing the game in agriculture and what lies ahead for its future. Get ready to join us on an exciting journey of discovery!
The Challenge of Sustainable Agriculture
Agriculture is the backbone of our food system, and it faces a significant challenge in achieving sustainability. The current agricultural practices rely heavily on chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and monoculture farming that degrades soil quality over time. This leads to lower crop yields and increased production costs.
Moreover, agriculture accounts for nearly 25% of global greenhouse gas emissions due to deforestation, transportation of produce, and energy-intensive irrigation systems. Sustainable agriculture must address these challenges by focusing on reducing environmental impact while meeting the growing demand for food.
Sustainable agriculture aims to strike a balance between ecological health and economic prosperity without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs. It involves promoting biodiversity, conserving natural resources such as soil fertility and water supply through sustainable management practices.
To achieve sustainability in agriculture requires a paradigm shift from conventional methods towards more innovative techniques like gene editing that can increase crop yield with minimal environmental impact.
The Promise of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering has the potential to revolutionize agriculture, offering a wide range of benefits that could help tackle some of the biggest challenges facing our food systems. By manipulating an organism’s DNA, scientists can create crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, as well as plants that are drought-resistant or able to grow in poor soil conditions.
One promising area of genetic engineering is the development of crops with improved nutritional profiles. For example, researchers have been working on creating rice varieties that contain higher levels of vitamins and minerals such as iron and zinc, which could help address malnutrition in developing countries.
Another area where genetic engineering shows promise is in reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. By creating crops that require fewer pesticides or fertilizers or by making them more efficient at using water resources, we can reduce pollution and conserve natural resources while still producing ample amounts of food.
Furthermore, genetic engineering also presents opportunities for increasing crop yields without expanding farmland. This would lead to less deforestation and habitat loss while meeting the demand for food from a growing global population.
There is no doubt that genetic engineering holds significant promise for addressing many pressing issues in agriculture today. However, it’s important to proceed with caution and carefully evaluate any risks before implementing these technologies on a large scale.
The Risks of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering has been hailed as a solution to many of the problems facing modern agriculture, including drought resistance and pest control. However, there are also significant risks associated with the use of genetically modified crops.
One major concern is the potential for unintended consequences in the ecosystem. When genetically modified organisms are introduced into an environment, they can interact with other species in ways that are difficult to predict. This could lead to unintended harm to non-target species or disruption of natural ecosystems.
Another risk is the potential for genetic modification to increase pesticide resistance in pests. If genes for pesticide resistance are spread through populations of insects or weeds, it could make it more difficult to control these pests over time.
There is also some concern about the long-term health effects of consuming genetically modified foods. While most studies have found no negative health effects from eating GM foods, there have been some reports linking them to allergies and other health issues.
While genetic engineering holds promise for improving crop yields and sustainability, it is important that we carefully consider and address these risks before widespread adoption of GM crops.
The Debate Over Genetic Engineering
The debate over genetic engineering is a heated one, with strong opinions on both sides. Supporters argue that it has the potential to revolutionize agriculture by creating crops that are more resistant to pests and diseases, as well as more nutrient-dense. They also point out that genetic engineering can help reduce the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides.
However, opponents have their concerns about the long-term effects of genetically modified crops on human health and the environment. Some worry about unintended consequences such as cross-contamination between GMOs and non-GMOs or the creation of superweeds.
Another concern is whether or not GMO labeling should be mandatory for consumers so they know what they’re eating. This issue has been highly debated in recent years with some states passing laws requiring labels while others do not.
Despite these debates, many scientists agree that genetic engineering has enormous potential to create sustainable agriculture practices. It’s up to policymakers and consumers alike to weigh the risks against the benefits when making decisions about how best to move forward in this field.
The Future of Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
The future of genetic engineering in agriculture is promising yet unpredictable. As technology advances, we can expect to see more genetically modified crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, have increased yields, and require fewer resources.
One potential application of genetic engineering is the development of drought-resistant crops that can thrive in areas with limited water supply. This would be a significant breakthrough for farmers who struggle with water scarcity and could lead to greater food security around the world.
Another area where genetic engineering shows promise is in reducing the use of harmful pesticides and herbicides. By developing crops that are naturally resistant to pests and weeds, farmers may be able to reduce their reliance on these chemicals, which can harm both human health and the environment.
However, there are also risks associated with genetic engineering that cannot be ignored. The unintended consequences of modifying genes could potentially harm ecosystems or even trigger new diseases.
The debate over whether or not genetically modified organisms (GMOs) should be labeled has been ongoing for years. Some argue that consumers have a right to know what they’re eating while others believe it will only lead to unnecessary fear-mongering about GMOs.
Regardless of where one stands on this issue, it’s clear that the future of genetic engineering in agriculture will continue to shape our food system as we know it today. It’s up to us as consumers and stakeholders in agriculture to stay informed about new developments while also considering ethical implications along the way.
Conclusion
Genetic engineering has the potential to revolutionize agriculture and pave the way for sustainable crops. While there are risks and debates surrounding this technology, it cannot be denied that with responsible use, genetic engineering can help address some of the biggest challenges facing modern agriculture.
The benefits of genetically engineered crops are many: increased yield, better resistance to pests and disease, improved nutritional content, reduced environmental impact from pesticides and fertilizers. However, it’s important to always weigh these benefits against potential risks such as unintended effects on other organisms or long-term ecological impacts.
Ultimately, the future of genetic engineering in agriculture will depend on continued research and development as well as careful regulation by governments around the world. With proper oversight and a commitment to responsible innovation, we can ensure that genetic engineering helps us build a more sustainable agricultural system—one that meets the needs of both people and planet.
Science
Industrial Enzyme Production: Pioneering the Future of Manufacturing

In the rapidly evolving landscape of 2026, the global manufacturing sector is undergoing a profound and irreversible “biological pivot.” Industrial processes are decisively moving away from energy-intensive chemical syntheses toward the precision and elegance of biocatalysts. Central to this transformation is the Industrial Enzyme, a sophisticated biological catalyst capable of accelerating complex reactions with a level of specificity and environmental efficiency that traditional inorganic catalysts simply cannot match. These proteins have moved from the periphery to the very core of industrial innovation.
Why Industrial Enzymes Define Modern Manufacturing
From sustainable pharmaceuticals to carbon-neutral biofuels, these molecular machines are the invisible architects of the modern circular economy. Their widespread adoption is driven by several key advantages that address both economic and ecological imperatives:
- High Specificity: Enzymes function like precision tools, targeting specific substrates to minimize unwanted by-products. This lock-and-key mechanism increases product purity, reduces the need for costly separation processes, and ultimately lowers raw material consumption.
- Energy Efficiency: Unlike traditional catalysts that often require extreme heat and pressure, enzymes typically operate at ambient temperatures and atmospheric pressure. This characteristic allows manufacturers to significantly cut their carbon footprints and operational energy costs.
- Biodegradability: A major environmental concern with heavy metal catalysts is their toxicity and the challenge of safe disposal. Enzymes, being proteins, are inherently biodegradable. They break down naturally after use, reducing long-term environmental impact and simplifying waste management protocols.
However, despite these clear benefits, the industry has reached a critical inflection point: the challenge is no longer just about discovery, but about mastering the rigorous path of Industrial Enzyme Production to ensure robust and consistent performance at a commercial scale.

The Economic and Regulatory Landscape
The economic impetus behind this biological pivot is substantial, with the global market for high-performance Industrial Enzymes projected to exceed $16 billion by the close of 2026. This impressive growth is fueled by critical shifts across multiple sectors:
- Food & Beverage: In response to consumer demand, manufacturers are meeting “clean-label” demands by using enzymes for natural preservation, texture improvement, and sugar reduction, replacing artificial additives.
- Pharmaceuticals: Biocatalysis is now indispensable for synthesizing complex active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). By enabling more direct synthesis routes, enzymes often reduce hazardous waste by up to 70%, aligning with both cost and sustainability goals.
- Regulatory Compliance: As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) mandates evolve from voluntary guidelines into enforceable law, bio-based manufacturing has rapidly transitioned from a “niche choice” for eco-conscious brands to a global necessity for regulatory compliance and market access.
Overcoming the “Scaling Bottleneck”
The leap from “bench to bio-factory” represents the most significant technical hurdle in the industry. While a novel enzyme may show exceptional activity in a lab flask, its performance often falters under the mechanical stress, shear forces, and complex chemical environment of a 50,000-liter fermenter. Successful Industrial Enzyme Production requires a sophisticated, multi-pronged strategy to bridge this gap:
- Strain Improvement: The first step is selecting and engineering robust microbial hosts, such as the filamentous fungus Aspergillus niger or the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris, to maximize expression levels and protein folding efficiency.
- Process Optimization: Modern production relies on real-time bioreactor monitoring with advanced sensors. This allows for the dynamic adjustment of nutrient feeds, pH levels, temperature, and oxygen gradients to maintain an ideal environment for microbial growth and enzyme production.
- Downstream Processing (DSP): Perhaps the most delicate phase is the recovery and purification of the enzyme. Implementing advanced techniques like membrane filtration and gentle chromatography ensures high recovery rates without compromising the protein’s delicate structural integrity and activity.
The Digital Frontier: AI and Directed Evolution
In 2026, the current frontier of the Industrial Enzyme market is defined by the powerful combination of Generative AI and directed evolution. This “digital laboratory” approach allows researchers to bypass slow, trial-and-error methods:
- Predict Protein Folding: Using deep-learning models, scientists can now predict how an enzyme will fold and behave, enabling them to “pre-stress” designs for extreme industrial conditions before any physical experiment begins.
- Enhance Thermostability: A key goal is engineering catalysts that remain active at temperatures exceeding 90°C, making them compatible with existing high-temperature industrial processes.
- Accelerate Innovation: By simulating millions of years of evolution in a matter of days, AI helps generate hyper-efficient biocatalysts, thereby minimizing raw material waste and maximizing reaction speed.
Cross-Industry Impact: Biofuels and Textiles
The practical impact of these engineered catalysts is most visible in the global push for decarbonization:
- Biofuels: Advanced cellulase enzyme cocktails are now capable of efficiently converting agricultural waste (like corn Stover and wheat straw) into fermentable sugars. This process is the linchpin of second-generation ethanol, which does not compete with food crops.
- Textiles: In the fashion industry, “bio-stonewashing” using cellulases and laccase-based bleaching systems reduce water consumption by nearly 40%. These biological processes achieve superior fabric quality without the use of toxic chemicals, protecting both workers and the environment.
The Future: Metagenomics and Nanozymes
Looking ahead, the next frontier lies in the exploration of Earth’s most extreme environments and the convergence of biology with nanotechnology:
- Metagenomic Mining: Instead of culturing individual organisms, scientists are now directly extracting DNA from environmental samples, discovering powerful new enzymes in “extremophiles” from deep-sea vents and hot springs that are naturally resistant to industrial denaturation.
- Nanozymes: An exciting emerging field involves synthetic nanomaterials that mimic enzymatic activity. These robust, inorganic structures offer the potential for lower production costs and even higher stability than their purely biological counterparts, opening up entirely new applications.
Conclusion: The Blueprint for Success
Ultimately, the successful integration of these advanced technologies depends on a strategic transition from pure discovery to reliable execution. For companies looking to maintain a competitive edge in this fast-paced market, the choice of a partner for Industrial Enzyme Production is as critical as the enzyme design itself. A partner offering a fully integrated, “one-stop” pipeline—from initial feasibility studies and strain development to the production of tons of purified enzyme—is not just a vendor, but provides the fundamental blueprint for success and a leader in the future of global industry.
Care
Transform Your Smile with Dental Implants in Dubai
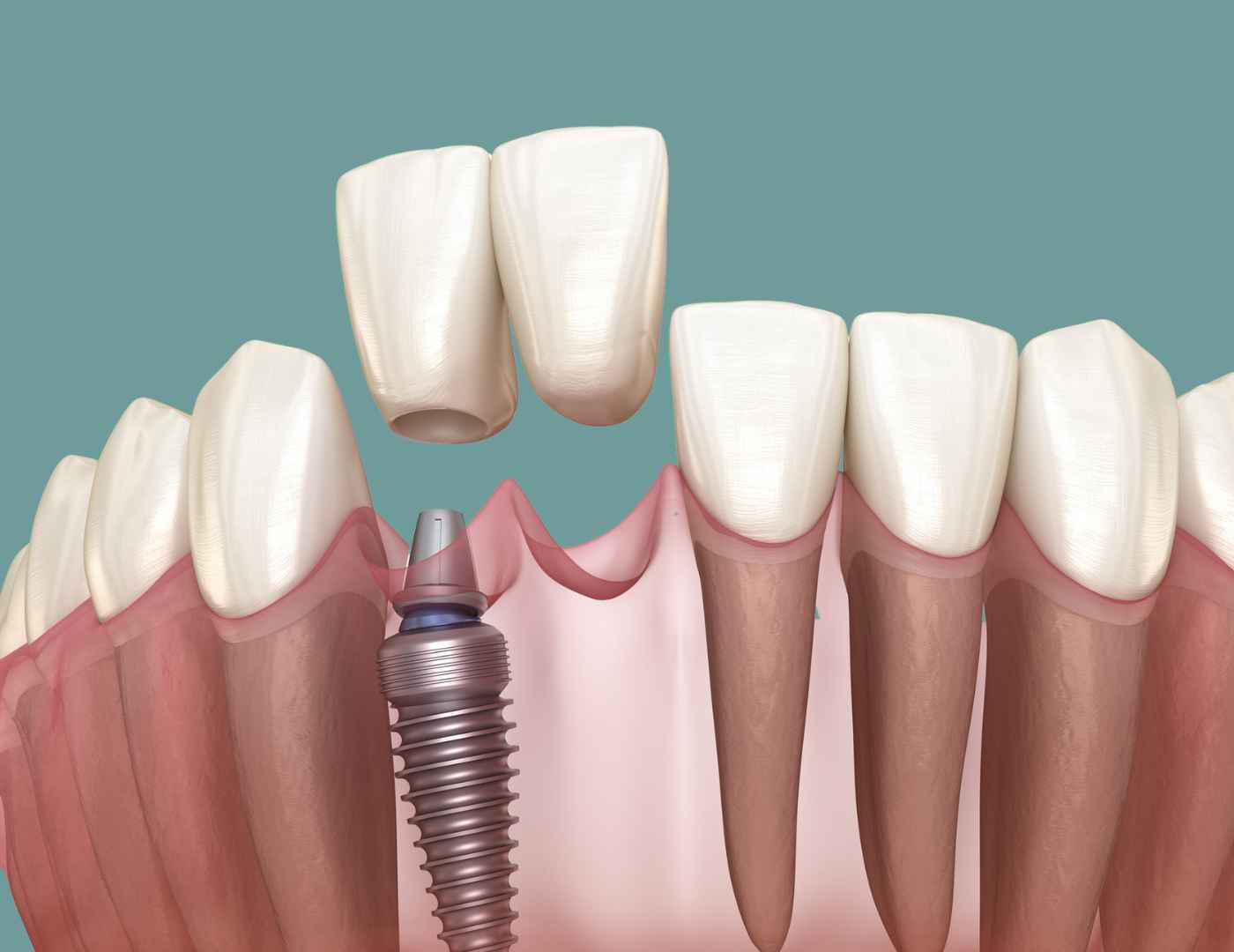
A confident smile can change the way people perceive you, and dental implants offer a remarkable way to restore both appearance and function. Dental implants have become a leading solution for individuals seeking a permanent and natural-looking replacement for missing teeth. By seamlessly integrating with the jawbone, Dental Implants Dubai provide stability and durability that other options often cannot match. From enhancing oral health to boosting self-confidence, the benefits of dental implants are extensive and transformative.
Understanding the Dental Implant Process
Dental implants are designed to replace missing teeth with results that feel and look natural. The process typically begins with a thorough evaluation to determine bone density and oral health, ensuring that the foundation is suitable for implantation. Once the assessment is complete, the implant is surgically placed into the jawbone.

Key Benefits of Dental Implants
Enhancing Aesthetic Appeal
A radiant smile plays a crucial role in self-confidence and personal presentation. Dental implant are custom-designed to match the shape, size, and color of natural teeth, creating a seamless appearance. Unlike other options, dental implants do not rely on neighboring teeth for support, ensuring a natural contour and symmetry. The result is a smile that looks authentic and enhances facial aesthetics. Individuals often notice an immediate boost in self-esteem after completing the implant process, enjoying the freedom to express themselves without hesitation.
Functional Advantages of Dental Implant
Dental implants offer more than visual enhancement. They provide a level of stability and functionality that mimics natural teeth. The secure fit allows for comfortable chewing and clear speech, restoring the ability to enjoy all types of foods without restriction. Because implants are anchored directly to the jawbone, they eliminate concerns about dentures slipping or causing discomfort. This functional reliability contributes to overall oral health by making everyday activities easier and more comfortable.
Longevity and Durability
One of the most compelling aspects of dental implant is their long-lasting nature. With proper care, dental implants can last a lifetime, making them a sustainable solution for tooth replacement. The materials used are highly resistant to decay and wear, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Regular dental check-ups and proper oral hygiene ensure that implants remain strong and functional. This combination of durability and minimal maintenance makes dental implant an excellent choice for anyone seeking a permanent solution to missing teeth.
Promoting Oral Health
Common Questions
How long does the process take?
The timeline for dental implants varies depending on individual needs. Typically, the process from initial consultation to final restoration can take several months. This period allows for proper healing and osseointegration, ensuring the implant is securely anchored and ready for the final restoration.
Is the procedure painful?
Most patients report minimal discomfort during the dental implant procedure. Local anesthesia is used to ensure a comfortable experience, and post-procedure soreness is usually manageable with over-the-counter pain relief. The process is designed to prioritize patient comfort and recovery.
Can anyone get dental implants?
While dental implants are suitable for many individuals, candidates must have sufficient bone density and good oral health. A thorough evaluation helps determine whether dental implants are the best solution. In some cases, preparatory procedures may be recommended to strengthen the jawbone before implant placement.
How do dental implants compare to other tooth replacement options?
Dental implants offer unique advantages, including long-term durability, natural appearance, and preservation of surrounding teeth. Their ability to restore function and aesthetics makes them a preferred choice for individuals seeking a permanent and reliable solution.
How should dental implants be cared for?
Caring for dental implants is similar to maintaining natural teeth. Daily brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups help ensure longevity. Because dental implants do not decay, they offer a consistent and reliable solution for maintaining oral health.
Why Choose Dental Implants Today
Cheapest Dental Implants in Dubai are more than a cosmetic enhancement—they are a comprehensive solution that addresses both functional and aesthetic needs. They empower individuals to regain confidence in their smile and enjoy everyday activities without restriction. Whether addressing a single missing tooth or multiple gaps, dental implants offer flexibility, strength, and a natural appearance. Their long-term benefits, combined with the ease of care and durability, make them a worthwhile investment in oral health and self-confidence.
Conclusion
Dental implants provide an effective, natural-looking solution for anyone seeking a complete and confident smile. By restoring function, enhancing appearance, and supporting oral health, they offer unmatched advantages over other options. Those considering dental implant can enjoy a seamless process, long-lasting results, and a boost in self-esteem that transforms both personal and social interactions. Embracing dental implant today can be the first step toward a smile that exudes confidence, health, and elegance. Take the opportunity to explore dental implants and discover how they can perfectly elevate your smile with ease.
Book literature
Effective Literature Review for Multi-Disciplinary Dissertations

Each dissertation involves a literature survey, which is the first step. It summarizes and analyzes knowledge about a particular field. In the case of multi-disciplinary dissertations, this becomes even more important because such a literature review requires the integration of diverse bodies of knowledge.
For students in need, services such as a personal statement writing service can also advise on how to provide a structured and analytical approach to academic writing. This article provides an overall guide on conducting an effective literature review in multi-disciplinary dissertation writing, with a focus on coherence and thorough analysis.

1. Understand the Purpose of a Literature Review
Every dissertation has a literature survey to lay the ground for inquiry. The ability to understand how to write a literature review for a research paper is important, as it may serve different purposes: it gives a big picture of the research already undertaken within your topic. It also pinpoints the gaps in knowledge and justifies the pursuit of your question.
2. Define the Objectives and Scope
There is a need to know how to write a literature review for a dissertation for which to understand the objectives as well as scope. Ask yourself questions like:
- What are the main themes or topics relevant to your research?
- What subjects or disciplines are central to your dissertation?
- Are there key theories, models, or frameworks to be researched?
In multidisciplinary dissertations, the literature review serves to link various disciplines together so always keep that in mind while conducting a survey.
3. Conduct a Systematic Search for Materials
A literature survey is the foundation of every dissertation. For students looking for dissertation help in London, it is important to know how to conduct a literature review, especially when it comes to multidisciplinary dissertations.
Systematic material searching involves effective planning and organization. Here are some steps to follow:
a. Keywords and Synonyms
Develop a list of keywords relevant to the research theme, including synonyms and their different alternatives which can be delivered. For example, if the research topic is artificial intelligence in education, keywords which may be included will be “AI,” “machine learning,” “educational technology,” and “adaptive learning systems.”
b. Use Diverse Databases
Search for literature in databases that serve various disciplines. For example:
- ScienceDirect for natural sciences
- PubMed for health and biomedical research
- JSTOR and Project MUSE for humanities and social sciences
- IEEE Xplore for engineering and technology
c. Check Reference Lists
References listed in scholarly articles or books will help you locate other valuable resources. This is called backward citation searching, and this is very helpful to identify core works in the area.
d. Keep Current
Set up Google Scholar alerts or database notices to remain up-to-date on new releases about your subject area.
4. Organize Sources
With sources from multiple disciplines, organizing your materials is crucial. Consider the following strategies:
a. Categorize by Discipline
Group sources by their respective fields. This helps in identifying how each discipline contributes to your research topic.
b. Use Thematic Grouping
Organize sources based on themes, such as methodology, theoretical frameworks, or key findings.
c. Create an Annotated Bibliography
Write summaries and critical evaluations of each source. Include information on its relevance, strengths, and limitations.
5. Analyze and Synthesize Information
Examine study sources beyond summaries: The literature review is an analysis and synthesis of sources. For multi-disciplinary reviews:
a. Highlight Contrasts and Commonalities
Find points of convergence, divergence, and overlap between the disciplines. For example, what are the different methods used by sociologists and economists to articulate the issue of poverty?
b. Discuss Theoretical Frameworks
Consider how theories in one area can be informed or complemented by theories in another. For instance, psychological learning theories could bring a rich addition to the design of AI-based educational tools.
c. Gaps and Limitations
Indicate any research gaps, especially those that are created because of disciplinary silos. Mention areas where knowledge integration may be able to provide new insights.
6. Organize Your Literature Review
A multi-disciplinary literature review requires a clear and logical structure. Here is a suggested framework:
a. Introduction
- Introduce your research topic and objectives briefly
- Provide the rationale for the multi-disciplinary approach
- Outline the structure of the review
b. Body
Arrange the body into sections related to the themes or disciplines. For instance,
- Section 1: Environmental Science Perspective
- Section 2: Public Health Findings
- Section 3: Policy Implications
In each section:
- Summarize key studies
- Critically evaluate methodologies and findings
- Show connections with other disciplines
c. Integration Section
Dedicate a section to synthesizing insights across disciplines. Discuss how integrating knowledge provides a comprehensive understanding of your research problem.
d. Conclusion
- Summarize the main findings of your review
- Reiterate the relevance of a multi-disciplinary approach
7. Write Clearly and Cohesively
Multi-disciplinary literature reviews can be dense and complex. To maintain clarity:
- Use Transitional Phrases: Connect ideas across sections and disciplines for example, “Building on insights from sociology, we now explore the economic dimensions…”
- Define Key Terms: Terms may be used differently across different disciplines; it is important to define terms specifically to ensure clarity
- Avoid Jargon: Generally, write to a large academic audience and avoid terms unique to your specific discipline(s)
8. Use Technology to Enhance Your Review
Employ technology to organize and present your literature review:
- Reference Managers: Such apps, such as Zotero, endnote, or Mendeley, help in arranging citations and generating bibliographies
- Visualization Tools: Map concepts or make diagrams to visualize the relationships within and among disciplines and themes
9. Seek Feedback
Before finalizing your literature review, seek feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the relevant disciplines. They can provide insights on:
- The comprehensiveness of your review
- The accuracy of your interpretations
- The coherence of your synthesis
10. Revise and Edit
Editing is an important means of honing your literature review. Pay close attention to:
- Consistency: Your writing style, terminology, and formatting should be consistent
- Clarity: Use simple language to explain complicated ideas; avoid repetition
- Accuracy: Double-check citations and verifiable facts
Conclusion
Since reconciling diverse perspectives through careful planning, critical analysis, and writing can be a difficult and sometimes very rewarding process, developing a literature review for a multi-disciplinary dissertation becomes the basis upon which a literature review could be constructed that serves to not only set the stage for a person’s research but also helps to fill the gaps between disciplines. The aim is to generate a cohesive narrative that will take understanding forward and open ways toward innovative solutions to complex problems.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business3 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom