Autos & Vehicles
Navigating the Complexity: Unlocking the Secrets Behind Modern Cars’ Tricky Door Designs

Introduction
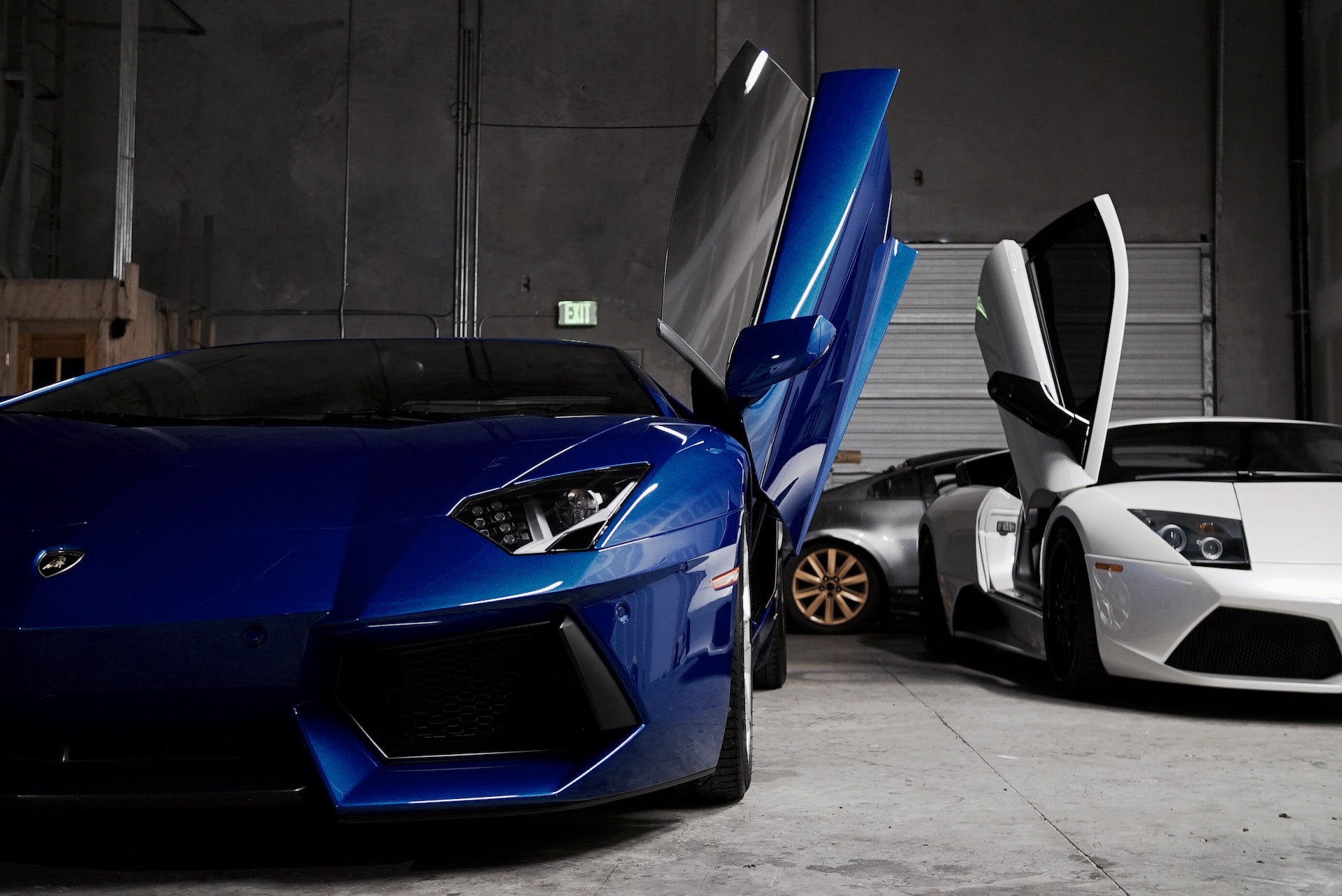
Modern cars are marvels of engineering, with intricate designs and advanced features that enhance the driving experience. Among the many elements that contribute to a car’s overall design, door designs play a crucial role in aesthetics, functionality, and safety. In this article, we delve into the secrets behind the complex door designs of modern cars. By understanding the intricacies and challenges associated with these designs, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering mastery behind them.
The Evolution of Car Door Designs
Car door designs have evolved significantly over time, driven by various factors such as aesthetics, safety regulations, and technological advancements. Let’s explore some of the key milestones in car door design evolution:
1. Traditional Hinged Doors
Hinged doors have been the most common door design for decades. They feature hinges attached to the front or rear edge of the door, allowing it to swing open horizontally. This design offers simplicity, reliability, and ease of use.
2. Scissor Doors
Scissor doors, also known as butterfly doors, gained popularity through iconic sports cars like the Lamborghini Countach. These doors open vertically and then pivot outward, creating a unique and eye-catching entrance. However, they require precise engineering and additional space to operate smoothly.
3. Gullwing Doors
Gullwing doors, made famous by the Mercedes-Benz 300SL, open vertically like wings, providing a dramatic entrance. These doors offer a wide opening for easy access, but they require reinforced structures and careful engineering to ensure safety and functionality.
4. Sliding Doors
Sliding doors are commonly found in minivans and some SUVs, providing convenient access for passengers in tight spaces. These doors slide horizontally along tracks, creating a wide opening without the need for extra space for door swing.
5. Suicide Doors
Suicide doors, also known as rear-hinged doors, open opposite to the conventional front-hinged doors. They offer a unique aesthetic and easier access to the rear seats. However, their safety and structural considerations require careful engineering.
The Challenges of Modern Car Door Designs
While modern car door designs offer numerous benefits, they also present unique challenges for automakers. Here are some of the key challenges associated with these designs:
1. Structural Integrity and Safety
Modern door designs require meticulous engineering to ensure structural integrity and meet safety standards. The doors must withstand crash forces, provide occupant protection, and allow for easy exit during emergency situations. Balancing safety with innovative design features is a top priority.
2. Weight and Fuel Efficiency
Innovative door designs often incorporate complex mechanisms, reinforcement, and additional materials, which can increase the weight of the vehicle. This added weight affects fuel efficiency and overall performance. Automakers strive to find the right balance between safety, functionality, and weight optimization.
3. Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Unconventional door designs introduce manufacturing complexities, requiring specialized engineering, tools, and techniques. The production processes become more intricate, resulting in higher manufacturing costs. Achieving cost-effective production while maintaining high quality and consistency is a constant challenge.
4. User Experience and Accessibility
While unique door designs can be visually appealing, they may present challenges in terms of user experience and accessibility. Some designs require more space to fully open, making entry and exit difficult in tight parking spaces or crowded environments. Balancing aesthetics with practicality and convenience is essential.
Solutions and Innovations
Automakers and engineers are continuously striving to overcome the challenges associated with modern car door designs. Here are some solutions and innovations that have emerged:
1. Advanced Materials and Design Optimization
Using advanced materials, such as high-strength steel and aluminum alloys, helps reduce weight without compromising safety and structural integrity. Design optimization techniques, such as computer simulations and finite element analysis, enable engineers to enhance door performance and minimize weight.
2. Integrated Safety Systems
To ensure the safety of occupants, modern car doors often incorporate advanced safety features such as side impact beams, energy-absorbing materials, and reinforced structures. These systems mitigate crash forces and enhance occupant protection.
3. Power-Assisted Doors
Power-assisted doors, including automatic or motorized systems, enhance convenience and ease of use. These systems allow doors to open and close smoothly with minimal effort, improving accessibility for passengers, especially those with mobility challenges.
4. Sensor-Based Technologies
Sensor-based technologies, such as proximity sensors and obstacle detection systems, assist in parking and maneuvering with limited space. These technologies provide warnings and prevent accidental collisions or door damage.
5. Interior Space Optimization
Automakers focus on optimizing interior space to accommodate various door designs. Clever interior packaging, including compact mechanisms, slim panels, and creative storage solutions, maximize cabin space while ensuring functionality and comfort.
Conclusion
Modern car door designs are a testament to the continuous evolution and innovation in the automotive industry. From traditional hinged doors to the unconventional and striking designs we see today, car doors have come a long way. While these designs present challenges in terms of safety, weight, manufacturing, and user experience, automakers and engineers are constantly pushing the boundaries to overcome these obstacles. Through the integration of advanced materials, innovative technologies, and a focus on safety and user convenience, modern car doors are becoming more than just entry points—they are sophisticated components that enhance the overall driving experience.
Autos & Vehicles
Caribbean Generator Set Market: Growth Prospects and Keys

The geographical and infrastructural peculiarities of the Caribbean region offer both opportunities and challenges for energy reliability. Because a few island countries are scattered across the Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, governments and utility companies have found it difficult and expensive to introduce a fully interconnected and reliable power grid.
As a result, the high demand for reliable backup power has made generator sets an essential energy component. According to a recent study by MarkNtel Advisors. The Caribbean Generator Set Market is poised to experience robust growth in the forecast period until 2032, driven by constant power reliability concerns, the threat of natural disasters, and ongoing infrastructure development within the region.
Caribbean Generator Set Market Size and Forecast
The Caribbean Generator Set Market is estimated at USD 144.04 million in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 230 million in 2032. This anticipated growth reflects a healthy compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 8.11% during the 2026-2032 period, indicating a growing dependence on gensets for uninterrupted power supply.
Fluctuating utility grids, frequent power shortages, and a high rate of extreme weather events like hurricanes, floods, and earthquakes have all heightened the desire for reliable power. Stakeholders deploy generator sets not only in residential and commercial buildings but also in vital sectors such as healthcare, transport, telecommunication, and construction, where power cuts can significantly inconvenience critical services and disrupt economies.

Drivers of Growth
Several major forces underpin the growth of the Caribbean Generator Set Market. The region’s isolated grid systems make it difficult for utility companies to provide a constant electricity supply across all islands. Regular grid power disruptions, such as the lengthy blackouts that have affected countries like Cuba and Puerto Rico, highlight the need for businesses and homeowners to use backup power sources to keep operations running during such outages. Besides grid instability, the Caribbean’s susceptibility to natural disasters makes generator sets necessary for emergency preparedness and recovery.
Continuous infrastructure and construction work also add to market growth. For instance, large-scale projects like road construction, which regional development banks often support, require a reliable electricity supply in isolated places where grid power is limited or unavailable. In such environments, portable and sturdy generator sets—especially diesel-driven ones—are essential for providing power to equipment and tools, allowing construction and development to continue without disruptions.
Market Segments and Trends
When segmenting the Caribbean Generator Set Market by fuel type, diesel-based generator sets account for the largest share. Diesel gensets are popular because of their longevity, cost-effectiveness, and low maintenance needs. They are reliable and perform well in different environmental conditions, making them suitable for construction sites, commercial buildings, equipment rental services, and various industries across the region.
Although diesel is the major fuel type, interest is growing in potential alternatives, including natural gas, gasoline, hybrid, and other emerging technologies. As sustainability and emission concerns become more prominent, hybrid generator sets that combine traditional fuel with battery systems or renewable energy integration could gain popularity in some segments, especially where environmental standards are evolving and governments implement clean energy policies.
End-User Demand Dynamics
The Caribbean has a large number of end users of generator sets. Hospitality, retail, schools and data centers in the business world use backup power to maintain operations of their businesses and protect business critical functions. Electrical power is needed at all times by healthcare facilities especially to support life-saving medical equipment and services to patients. The transport and government sectors are other essential users of generator sets particularly in the disaster response and the operations of the social security in the event of grid outage.
Industrial uses such as manufacturing plants, assembly plants, mines, and oil and gas facilities are also a source of demand of generator sets. These are remote facilities that usually have restricted grid power supply and therefore gensets become very necessary in ensuring the facility is productive and operating at its usual pace. Moreover, equipment rental firms are increasingly gaining prominence in the provision of temporary power to companies and individuals who have a one-time demand of electricity.
Competitive Landscape
The Caribbean Generator Set Market has a competitive and varied environment of players on a global and regional level. As per the report prepared by the MarkNtel Advisors, the following companies target this market:
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Cummins Inc.
- Generac
- Discovery Energy, LLC (Rehlko)
- AGG Power Group
- INGCO
- PowerLink
- Mitsubishi Heavy industries.
- Genesal Energy
- Forest City Generators
- Atlas Copco
- Others
These companies introduce both the worldwide brand reputation and local experience, which provide a broad mix of different genset models in various types of fuel, power output, and applications to suit the needs of the Caribbean market. Some of the most famous ones are Caterpillar and Cummins with their high reliability and large networks of service. Other companies such as Generac and AGG Power Group are also playing a role in diversified product offerings which serve residential, commercial as well as industrial markets.
The Future Strategic Opportunities.
The Caribbean Generator Set Market is facing a number of strategic opportunities that can be exploited by the stakeholders. The continuous growth of the commercial infrastructure, increase in the energy consumption by the residential and industrial sectors and the growth in investment in disaster resistant energy systems are opening up new avenues of growth. The manufacturers and suppliers of generator sets may also be able to increase market penetration by creating localized service networks, tailoring financing options. Also developing product innovations to increase fuel efficiency and decrease operation costs.
With the region looking into cleaner energy options and hybrid power brands, market participants could also look into partnering or integrating technologies, fusing genset reliability and renewable energy power sources and energy storage solutions.
Autos & Vehicles
Stainless Steel: The Key Material for Modern Metro Rail Coaches

Metro rail systems are expanding rapidly across major cities in India and across the globe. With rising urban populations, increasing passenger density, and growing expectations for sustainable infrastructure, metro coaches must be built using materials that offer durability, safety, and long-term value. The material ensures long-term reliability without adding unnecessary weight.
From underground tunnels exposed to moisture to elevated corridors facing pollution and extreme weather, rolling stock materials must withstand harsh operating conditions every day. In this environment, stainless steel has emerged as the preferred material for modern metro rail coaches. It offers the right combination of structural strength, corrosion resistance, safety performance, and lifecycle efficiency.
This blog explains why stainless steel metro coaches dominate modern rail manufacturing and why stainless steel railway components are widely used in today’s metro systems.

Evolution of Materials in Metro Coach Manufacturing
Mild Steel in Early Railway Coaches
In the early years of rail transport, mild steel was commonly used for coach construction. While it provided reasonable structural strength, it required frequent maintenance due to rust and corrosion. Regular repainting and structural repairs increased long-term operational costs.
Aluminum as a Lightweight Alternative
To reduce overall train weight and improve energy efficiency, aluminum was later introduced in rail coach manufacturing. Although aluminum reduced mass, it has certain limitations:
- Lower fatigue strength under repetitive loading
- Higher susceptibility to dents and deformation
- Limited performance under high-impact stress
Transition to Stainless Steel
Over time, manufacturers began adopting stainless steel metro coaches because of their superior mechanical properties and durability. Stainless steel combines strength, corrosion resistance, and long service life, making it more suitable for demanding metro environments.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
One of the main reasons stainless steel is preferred in metro rail manufacturing is its excellent strength-to-weight ratio. Advanced stainless steel grades such as 200 series, 300 series, 400 series, and duplex variants provide:
- High tensile strength
- Strong fatigue resistance
- Structural stability
- Reduced thickness without compromising safety
This allows engineers to design lightweight yet strong metro coach bodies capable of handling high passenger density and operational stress.
Structural elements such as underframes, side walls, and roof panels benefit significantly from stainless steel’s strength characteristics. The substance guarantees enduring dependability while not increasing unnecessary heft.
Superior Corrosion Resistance
Metro trains operate in challenging environments that can accelerate material degradation. These include:
- Underground tunnels with high humidity
- Coastal regions with salt exposure
- Industrial zones with airborne pollutants
- Frequent temperature variations
Stainless steel contains chromium, which forms a protective passive layer on the surface. This layer prevents rust and corrosion even under harsh environmental conditions.
Corrosion-resistant railway materials such as stainless steel significantly reduce maintenance requirements. This improves operational efficiency and ensures long-lasting metro coach durability.
Long Service Life and Lower Maintenance
Metro systems are long-term infrastructure investments. Coaches are expected to operate efficiently for several decades. Lifecycle cost becomes more important than initial material cost.
Stainless steel offers:
- Minimal repainting requirements
- Reduced corrosion-related repairs
- Extended service intervals
- Lower replacement frequency
Because stainless steel retains its structural integrity over time, metro operators benefit from reduced downtime and maintenance expenses. Over a 30–40 year operational period, stainless steel metro coaches often prove more economical than alternative materials.
Fire Resistance and Passenger Safety
Safety is a critical priority in metro rail systems. Materials used in coach construction must comply with strict fire safety and structural standards.
Stainless steel provides:
- High melting point
- Resistance to flame spread
- Structural stability during high-temperature exposure
In the event of fire incidents, stainless steel maintains its strength longer than many other materials. This enhances passenger protection and supports evacuation procedures.
Fire-resistant railway materials are essential for regulatory approvals, and stainless steel consistently meets these requirements.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Sustainability is increasingly influencing infrastructure decisions. Metro authorities aim to reduce environmental impact and improve material efficiency.
Stainless steel supports sustainable metro infrastructure in several ways:
- It is 100% recyclable
- It has an extended service life
- It reduces material replacement frequency
- It supports environmentally responsible manufacturing practices
At the end of a metro coach’s life cycle, stainless steel components can be recycled without losing their essential properties. This makes stainless steel an environmentally responsible choice for long-term urban transit systems.
Applications of Stainless Steel in Metro Coaches
Stainless steel is widely used in both structural and functional components of metro coaches.
Structural Shell Components
- Side walls
- Roof panels
- Underframes
- Car body shells
Enclosures and Protective Housing
Metro coaches contain several mechanical and electrical systems that require protection, including:
- Battery boxes
- Air reservoirs
- Valve boxes
Stainless steel enclosures protect these systems from corrosion, physical damage, and environmental exposure.
Interior Fittings and Safety Elements
Passenger safety and comfort rely on durable interior fittings such as:
- Handrails
- Grab poles
- Cable ducts
- Seating frames
Stainless steel interior components resist wear caused by continuous passenger use. They also maintain a clean and professional finish over time.
Stainless Steel vs Aluminum in Metro Coaches
When comparing stainless steel and aluminum in metro coach construction, several factors must be evaluated.
Structural Strength
Stainless steel generally offers higher tensile and fatigue strength, making it more suitable for structural applications subject to repeated loading.
Corrosion Performance
Both materials resist corrosion, but stainless steel performs better in polluted, humid, and coastal environments without requiring protective coatings.
Lifecycle Cost
Although aluminum reduces weight, stainless steel often provides better long-term value due to lower maintenance and higher durability.
Maintenance Requirements
Stainless steel requires minimal repainting and surface treatment, reducing operational downtime.
For these reasons, many metro manufacturers prefer stainless steel for critical structural and safety components.
Importance of Certifications and Standards
Metro rail manufacturing operates under strict global standards to ensure safety and reliability.
Key certifications include:
- IRIS (International Railway Industry Standard)
- EN15085 welding certification
- ISO quality management systems
These certifications ensure consistent quality, proper welding procedures, material traceability, and structural integrity. Stainless steel railway components manufactured under certified systems provide greater confidence to metro authorities and rolling stock manufacturers.
Role of Advanced Fabrication and Testing
Precision engineering is essential in metro coach manufacturing. Stainless steel fabrication involves advanced processes such as:
- Robotic welding
- Fiber laser cutting
- CNC bending and forming
- Non-destructive testing
Each component undergoes thorough testing for:
- Tensile strength
- Corrosion resistance
- Weld integrity
- Dimensional accuracy
Advanced manufacturing capabilities ensure that stainless steel metro components perform reliably under real-world conditions.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Metro Component Manufacturer
Material selection alone does not guarantee performance. The expertise and capability of the manufacturer play a critical role in ensuring compliance and reliability.
When selecting a stainless steel metro component manufacturer, decision-makers should evaluate:
- IRIS certification
- EN15085 welding compliance
- Production capacity
- In-house testing facilities
- Experience in metro and railway projects
- Capability to work with multiple stainless steel grades
Jindal Mobility specializes in stainless steel components for metro systems. With experience in manufacturing structural shells, enclosures, and interior fittings, the company supports metro projects from design and prototyping to mass production. Its certified processes, integrated facilities, and strong quality control systems make it a reliable partner for metro OEMs and system integrators.
Partnering with a qualified manufacturer reduces supply chain risks, ensures consistent quality, and supports the long-term success of metro projects.
Conclusion
Modern metro rail systems demand materials that deliver durability, safety, efficiency, and sustainability. Stainless steel meets these requirements effectively.
Its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, long lifecycle performance, fire safety characteristics, and recyclability make it the preferred material for modern metro rail coaches.
From structural shells and underframes to interior fittings and protective enclosures, stainless steel railway components form the backbone of reliable urban transit systems. When combined with certified manufacturing processes and advanced fabrication technology, stainless steel enables metro networks to operate safely and efficiently for decades.
As metro infrastructure continues to expand worldwide, stainless steel will remain central to the future of rolling stock material innovation.
Autos & Vehicles
What to Expect at an Auto Body Shop in Fort Lauderdale

An auto body shop visit can be more confusing than you may think, especially after your car is involved in an accident. Knowing what happens during the visit can ease anxiety and streamline the auto repair process at the auto body shop Ft Lauderdale FL. It also helps you stay informed while your car is getting repaired. That’s why we cover the whole process step-by-step in the following points. Let’s not waste any more time and dive into the blog.
What to Expect During an Auto Shop Visit
Here, we cover what happens during an auto repair and when you visit an auto shop. Keep reading with us for a better understanding.
Scheduling and Checking In
Auto shops generally prefer customers to schedule appointments, especially for significant repair work. You should know your car’s make, model, and issue. After learning these things, the shop can prepare accordingly and assign the right technician for your project. Early appointment slots reduce wait times. Some shops also offer rental vehicles or loaners if needed. When you arrive at the auto shop, check in at the front desk and provide paperwork like insurance details, DL, and vehicle registration.
Meeting the Technician
The assigned technician asks about the issues in your car and inspects it. Tell them everything, whether they are unusual noises, vibrations, or changes in performance. The more details you share with the technician, the better. Then, they explain the issues and show the areas of concern to you. The technician may also take photos of the damage if you have filed an insurance claim.

Reviewing Repair Options
After assessment, they offer repair options, ranging from quick fixes to comprehensive solutions. The technician will also discuss the use of OEM or aftermarket parts. OEM parts are long-lasting, compatible parts for your car, while aftermarket parts can save money but vary in reliability. After this, you receive a written estimate, including parts, labor, and extra charges, if there are any.
Explaining the Repair Process
The shop will thoroughly explain the repair process to you. Renowned auto shops update customers on each phase of the repair process via phone, email, or even an online portal. Each stage is performed with quality control in mind, and technicians review their work to ensure the car is restored to its pre-accident condition.
Managing the Repair Timeline
Timelines differ depending on factors like the extent of the damage, the availability of parts, and the workload at the shop. You should ask the shop about how long the repair would take. Trustworthy shops update you if there are delays due to unforeseen issues. Quality repairs take time, so don’t rush the job. Reputable shops aim to deliver results, not to complete the job ASAP.
Tracking Progress
You can ask the shop if they provide progress updates. Some auto body shops send digital updates and photos, so you know how your car is doing without coming to the shop. These services add peace of mind and reinforce accountability.
Handling Unexpected Delays
Delays can originate from various issues, such as part shortages, extra hidden damage, or shop workload. Reputable auto body shops keep customers notified about such setbacks. Proactive updates and clear explanations show the shop appreciates your time and trust. Some shops even offer rental car discounts or other assistance if repairs take longer than expected.
Working with Insurance
Auto shops are typically familiar with the insurance claim procedure and help you navigate it. They will help with paperwork, document the damage, and communicate with the insurance adjuster on your behalf. It minimizes stress and speeds up claim processing.
Getting Your Claim Approved
Auto repairs cannot be started without the insurance company approving the estimated repair costs. Your auto shop will act as a liaison, providing thorough documentation and photographs to support your claim, helping you obtain approval. If the insurance adjuster disputes the estimate, the shop may negotiate on your behalf, saving you time and frustration. You should stay in touch with the insurer and the shop and get regular updates. It helps move the claim process smoothly and keeps everything aligned between the two parties.
Coordinating Payment and Insurance
Some customers pay out-of-pocket, while others use insurance. Either way, a trustworthy shop will always walk you through costs and deductibles. If you are using insurance to pay for repairs, confirm what is covered, as policies differ widely. Some shops offer financing and payment plans for unexpected expenses. A good shop maintains transparency in billing, too, but you should ask about available options.
By now, you must have learned what happens during an auto shop visit. When your car needs repair, you should always go to a reputable auto shop. If you are looking for one, we are Superior Exotics Color and Paint, a reliable auto body shop Ft Lauderdale FL. We have high-quality parts, top-of-the-line products, a state-of-the-art facility, and a dedicated team of technicians. Contact us to book your auto repair service, or come to our shop.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom