Technology Explained
The Role of Cybersecurity in Protecting Financial Data

The Role of Cybersecurity in Protecting Financial Data
In today’s digital age, financial data is a highly coveted asset, making it a prime target for cybercriminals. As financial institutions increasingly rely on digital platforms for transactions and data management, the necessity of robust cybersecurity measures has never been more critical. This article explores the importance of cybersecurity in protecting financial data, highlights key threats and vulnerabilities, and examines the strategies and technologies used to safeguard this sensitive information.

Pexels.com
The Importance of Financial Data Security
Financial data, including personal and transactional information, is a valuable commodity for both legitimate financial institutions and malicious actors. Protecting this data is crucial not only for maintaining consumer trust but also for ensuring the stability and integrity of the financial system. A data breach can lead to severe financial losses, legal repercussions, and damage to an organization’s reputation. Therefore, implementing strong cybersecurity measures is essential for safeguarding financial data and ensuring business continuity.
Key Cybersecurity Threats to Financial Data
- Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks involve fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity. Cybercriminals use emails, fake websites, or phone calls to deceive individuals into disclosing personal or financial information. These attacks can lead to unauthorized access to financial accounts and significant financial losses.
- Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim’s data, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Financial institutions are particularly vulnerable to ransomware attacks due to their vast amounts of sensitive data. Such attacks can disrupt operations and cause substantial financial damage.
- Insider Threats
Insider threats occur when individuals within an organization misuse their access to financial data for malicious purposes. This can include data theft, sabotage, or espionage. Insider threats are challenging to detect and prevent, making them a significant concern for financial institutions.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm a network or system with a flood of traffic, causing it to become slow or completely inoperable. For financial institutions, such attacks can disrupt online services, causing inconvenience and potential financial loss.
Key Vulnerabilities in Financial Data Security
- Outdated Software and Systems
Financial institutions often rely on legacy systems and outdated software, which may have unpatched vulnerabilities that cybercriminals can exploit. Regular updates and patches are essential to mitigate these risks.
- Weak Passwords and Authentication
Weak or easily guessable passwords can provide a gateway for unauthorized access to financial data. Implementing strong, multi-factor authentication methods is crucial for enhancing security.
- Lack of Employee Training
Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats. Without proper training on recognizing and responding to potential threats, employees may inadvertently compromise financial data security.
- Inadequate Data Encryption
Data encryption is a fundamental component of cybersecurity. Inadequate encryption practices can leave financial data exposed to interception and unauthorized access.
Strategies for Protecting Financial Data
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA enhances security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification before accessing financial systems. This adds an additional layer of protection beyond just a password.
- Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Keeping software and systems up to date with the latest security patches is crucial for addressing known vulnerabilities and protecting against emerging threats.
- Conducting Regular Security Audits
Regular security audits help identify and address potential weaknesses in financial data security. These audits should include vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and compliance checks.
- Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Training employees on cybersecurity best practices and recognizing potential threats is essential for preventing insider threats and phishing attacks.
- Data Encryption
Encrypting sensitive financial data both at rest and in transit ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
Comparative Analysis of Cybersecurity Technologies
The following table compares various cybersecurity technologies used to protect financial data:
| Technology | Description | Strengths | Weaknesses |
| Firewalls | Network security systems that monitor and control incoming and outgoing traffic. | Prevent unauthorized access; customizable rules. | May not prevent advanced threats; needs regular updates. |
| Anti-Malware Software | Programs designed to detect, prevent, and remove malware. | Effective against known malware; regular updates available. | May not detect new or sophisticated malware; can impact system performance. |
| Encryption | Process of encoding data to prevent unauthorized access. | Protects data confidentiality; essential for secure transactions. | Can be complex to implement; may impact system performance. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Security method requiring two or more forms of verification. | Significantly enhances security; reduces the risk of unauthorized access. | Can be inconvenient for users; requires proper implementation. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for suspicious activity. | Provides early detection of potential threats; helps in incident response. | May generate false positives; requires proper configuration. |
The Future of Cybersecurity in Financial Data Protection
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, so too will the strategies and technologies used to protect financial data. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize cybersecurity by enhancing threat detection and response capabilities. AI and ML can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential threats, allowing for quicker and more accurate responses. Additionally, blockchain technology offers promising solutions for securing transactions and ensuring data integrity. However, as these technologies advance, cybercriminals will also adapt their tactics, necessitating ongoing innovation and vigilance in cybersecurity practices. Financial institutions must stay ahead of emerging threats by continuously updating their security measures, investing in advanced technologies, and fostering a proactive security culture. By doing so, they can better protect financial data and maintain trust in an increasingly complex digital environment.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity plays a pivotal role in protecting financial data from a wide array of threats. As financial institutions continue to evolve and expand their digital footprint, maintaining robust cybersecurity practices is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring operational resilience. By understanding key threats, addressing vulnerabilities, and implementing effective security measures, organizations can better protect their financial data and uphold their reputation in the digital age.
The importance of cybersecurity in the financial sector cannot be overstated. As technology continues to advance, so too must the strategies and technologies used to protect financial data. Investing in comprehensive cybersecurity solutions and fostering a culture of security awareness are crucial steps in defending against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
Business
Columbus Colleges: Enrollment Through Better Web Design

Columbus’s colleges are losing students to other schools simply because their websites are better structured. I found that when I audited 15 local colleges, poor design was running rampant across the board—most are fixable as well.
Slow Load Times on Mobile Devices
Ohio State’s primary website loads in just 2.3 seconds on a mobile device. Conversely, Columbus State’s website loads in 8.7 seconds. Given that 73% of prospective students use smartphones to browse, that’s not just slow, it’s a death sentence for admissions.
The Solution: Any reputable web design company in Columbus will tell you that mobile-first design is no longer up for discussion. Pages should load in 3 seconds or less, forms should be usable with a thumb, and navigation should be thumb-friendly. CCAD (Columbus College of Art and Design) just redesigned its website using these principles, and its applications have increased by 34% since the redesign.

Invisible in local search results
If you enter “colleges around Columbus” on a search engine (Google), you will see Ohio State as the only college that shows up. However, when searching for community colleges and other specialised institutions, you will find these institutions ranking around page 3 or lower for their named programs.
The problem: No GMB (Google My Business) optimisation. Franklin University even fails to fully claim their GMB listing. Their address is commonly listed as “temporarily closed.”
The Solution: Create and then optimize all campus addresses through both Google and business directory listings. Include photographs, create labels to respond to people reviewing your school, and post recent updates relating to the available enrollment periods. You want colleges to be able to locate you locally first when a prospective student types in “nursing programs Columbus” and you are visible in the map section.
Content That Converts Students
The college sites of most institutions are written in an academic style – high-density paragraphs about “excellence of the institution” and “a transformative learning experience.” When students are looking for information, they are looking for answers to questions such as how long it will take to complete the program, how much it will cost, and will there be any job opportunities upon completion.
For example, Otterbein University’s nursing website includes 847 words of content; however, it does not include the starting salary for a graduate until paragraph six. A competing institution’s website leads with, “96% job placement rate with an average starting salary of $65,000.”
Solution: answer the money questions up front and create program pages that convert:
- Job placement rates (with 3rd party sources).
- Graduate’s average starting salaries.
- Total program cost (not just tuition).
- Time to complete the program.
- Prerequisite information listed in plain English
Technical SEO Disasters
Most of the Columbus, Ohio college websites fail to meet the industry’s minimum criteria for Search Engine Optimization (SEO), which lead to decreased rankings in all search engines. The common issues we found include:
1. Broken internal links.
2. Missing alt tags on images.
3. Duplicate content across program pages (Capital University has 23 pages with the same meta description).
Some additional key technical issues that hamper the rankings on all college websites include:
1. No schema markup for either program or location.
2. Slow server response times.
3. Missing SSL certificate on multiple application forms.
4. Broken mobile navigation for multiple programs.
5. No local business structured data to support citation and rankings.
These common technical issues are far more than technical; they are also killing your rankings. Google cannot recommend college’s websites to its visitors if those sites are not accessible to Google through its crawler or can be understood once crawled.
The Death of Enrollment Forms
67% of potential students who fill out inquiry forms at Columbus colleges are lost at the inquiry stage. Why does this happen? Schools are using inquiry forms that require up to 15 fields when 4 would suffice, not having mobile-optimized inquiries, and having broken “Submit” buttons.
Delaware County Community College cut their inquiry form from 12 fields down to only 3 fields, resulting in an 89% increase in inquiries over 2 months.
Successful Examples of Results
Columbus State Community College worked with an SEO Services Columbus that specializes in local search engine optimisation and experienced the benefits:
- 156% more traffic through organic search
- 43% additional program inquiries
- Increased performance in local search results for targeted programs
Their formula for success: a mobile-first redesign, aggressive optimization of their Google My Business profile across their campuses, and totally answering students’ questions using quality content.
To sum it up
Ohio colleges have to compete against Arizona and Florida Colleges’ web-based programs with better web pages and better collegiate leads search engine optimization, so there’s no longer a local marketplace for columbus schools to get their students from.
It’s really easy to fix the problem. You’ll need to work with a web design company who understands education marketing, and to do that, you need to optimize the site for local search and generate content that gets visitors to apply.
Your competitors are already doing this, and if you wait to make decisions about how many more students you will lose to your competitors.
If you are ready to improve your school’s web presence, do a technical audit, make your mobile experience priority, and claim local search results. In a competitive academic landscape, your website serves not just for promotion, but as your enrollment powerhouse.
Technology
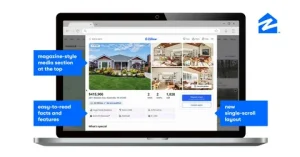
AI-Integrated Zillow Clone App Development
Digital Development
Boldify for Facebook: Quick Bold Text in Seconds

Scroll through Facebook for just five minutes and you’ll notice something: most posts look exactly the same. Plain text blends into the feed, making it easy for users to scroll past without noticing important messages. In a crowded social media environment, visual formatting plays a major role in grabbing attention and increasing engagement. This is where Boldify, a powerful bold text generator, makes a difference. Instead of struggling with plain, unformatted posts, Boldify allows you to create eye-catching Facebook bold text instantly. In this article, you’ll learn why bold text matters, how Boldify works, and how you can use it to stand out on Facebook within seconds.
Why Bold Text Matters on Facebook (User Engagement Psychology)
Facebook is a fast-moving platform. Users scroll quickly, often stopping only when something visually stands out. Bold text works because it creates contrast. When certain words appear heavier or more prominent, the brain processes them faster.
Here’s why bold text improves engagement:
- It grabs attention in crowded feeds.
- It improves readability and scan ability.
- It highlights key messages instantly.
Bold formatting is especially powerful in:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Facebook groups
If you’re building a brand or growing a personal profile, bold text strengthens your identity. It emphasizes important announcements, promotions, or calls to action, making your message harder to ignore.
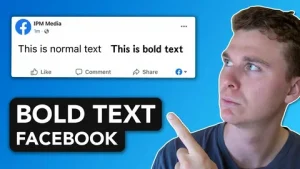
The Challenge: Facebook Doesn’t Offer Built-In Bold Formatting
One of the biggest frustrations for users is that Facebook does not provide built-in bold formatting for regular posts. Unlike word processors, you cannot simply select text and click “Bold.”
That’s why many people search for:
- how to bold text on Facebook
- Facebook bold text generator
- bold letters for Facebook
Without a proper tool, users are left copying complicated codes or trying ineffective formatting tricks. This creates a clear need for a reliable and easy-to-use bold font generator.
What Is Boldify?
Boldify is an online bold text generator designed to help users create stylish bold letters instantly. Instead of modifying Facebook’s formatting, Boldify uses Unicode-based bold fonts that are fully compatible with social media platforms.
Here’s what makes Boldify simple and powerful:
- No installation required
- Works directly in your browser
- Free and instant access
- Compatible with Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and WhatsApp
Because it uses special Unicode characters, the bold text appears naturally once pasted into Facebook posts, comments, bios, or Messenger chats. This makes Boldify a practical and beginner-friendly solution for anyone looking to create bold text online.
How Boldify Helps You Create Bold Facebook Text in Seconds
Using Boldify is straightforward and requires no technical knowledge. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Enter Your Text
Open Boldify and type your message into the input box. This could be a status update, promotional message, announcement, or bio line.
Example:
New Blog Post Live
Limited Time Offer
Join Our Community Today
Step 2: Automatic Bold Conversion
As soon as you enter your text, Boldify automatically converts it into multiple bold font styles. Within seconds, you’ll see several variations generated instantly.
Step 3: Copy and Paste to Facebook
Choose the bold style you like, click the copy button, and paste it directly into:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Messenger chats
That’s it. In just a few seconds, your plain text becomes visually powerful Facebook bold text.
Key Features That Make Boldify Stand Out
There are many tools online, but Boldify offers specific advantages that make it reliable and user-friendly.
1. One-Click Copy Feature
No need to manually select text. Just click and copy instantly.
2. Multiple Bold Style Variations
Get access to different bold styles to match your tone and branding.
3. Mobile-Friendly Interface
Boldify works smoothly on smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
4. No Login Required
You don’t need to create an account. Just open and start using.
5. Fast Performance
Text conversion happens instantly without delays.
6. Clean and Simple Design
The interface is distraction-free, making it easy for beginners to use.
These features make Boldify more than just a basic bold letters generator—it becomes a practical social media enhancement tool.
Practical Ways to Use Bold Text on Facebook
Now that you know how to generate bold text, let’s explore practical ways to use it effectively.
Highlight Important Announcements
SALE TODAY ONLY
Registration Closes Tonight
Bold formatting ensures these messages get noticed quickly.
Strengthen Call-to-Actions
Instead of writing:
Join us now
Write:
JOIN US NOW
It creates urgency and clarity.
Emphasize Keywords in Posts
Highlight important parts of your message to guide the reader’s attention.
Improve Facebook Bios
Use bold text to make your profession, tagline, or brand name stand out.
Stand Out in Facebook Groups
When commenting in large groups, bold text increases visibility and improves response rates.
SEO & Branding Benefits of Using Bold Text
While bold text doesn’t directly change Facebook’s algorithm, it improves how users interact with your content.
Here’s how it benefits branding and visibility:
- Improves readability
- Encourages longer post engagement
- Strengthens personal or business branding
- Creates structured content hierarchy
- Makes posts look professional
When your content looks organized and visually appealing, users are more likely to stop scrolling and engage.
Tips for Using Bold Text Effectively
Bold text is powerful—but only when used strategically.
- Don’t overuse bold formatting.
- Highlight only key phrases or calls-to-action.
- Combine bold text with emojis carefully.
- Maintain readability and spacing.
Too much bold text can reduce its impact. The goal is to enhance clarity, not overwhelm the reader.
Conclusion
Standing out on Facebook is no longer optional—it’s necessary. Since Facebook doesn’t offer built-in bold formatting for posts, tools like Boldify provide a fast and effective solution.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business3 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom