Technology Explained
The Role of AI in Predictive Maintenance
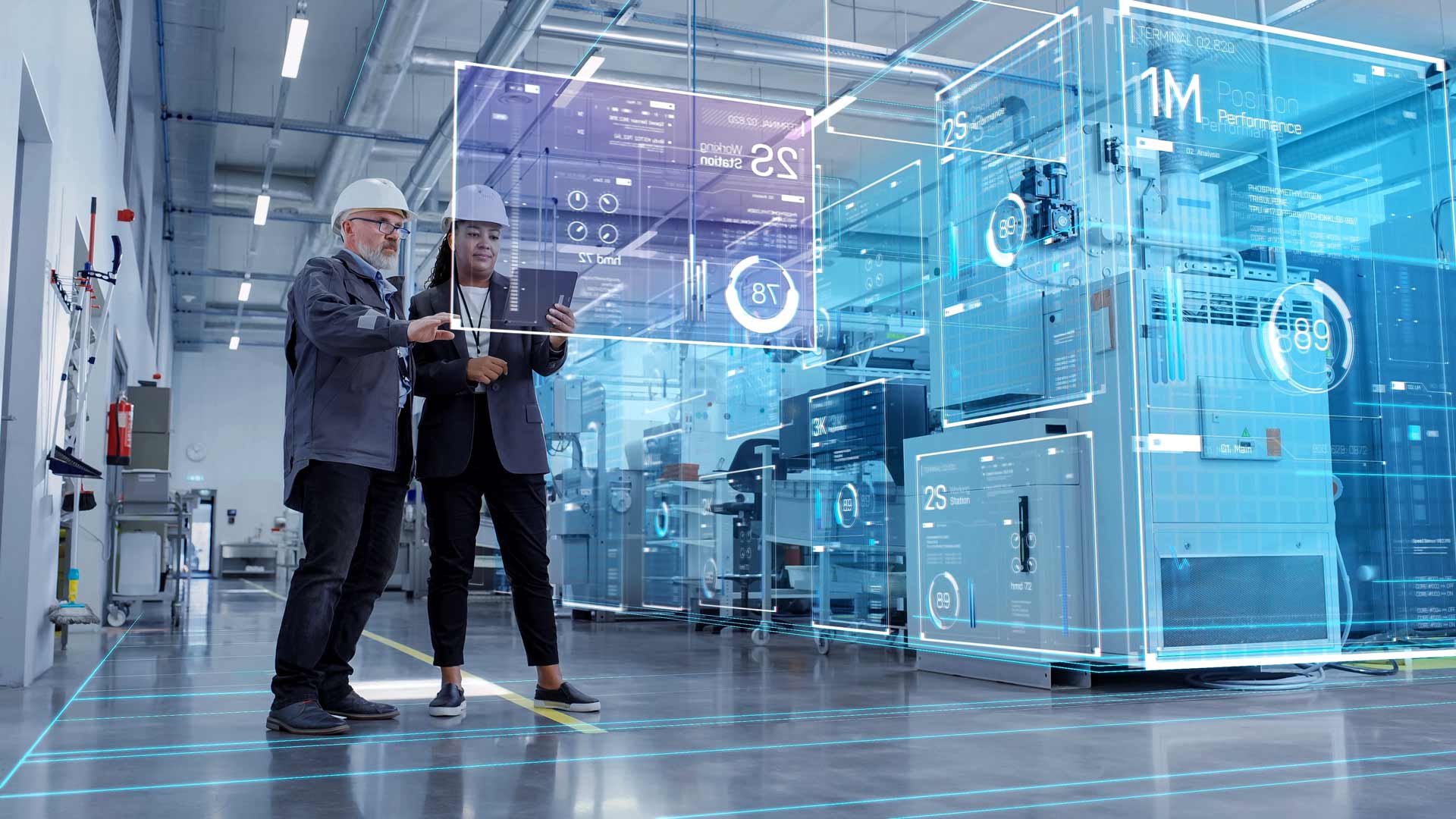

In the modern industrial landscape, the maintenance of machinery and equipment is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Traditional maintenance strategies, such as reactive and preventive maintenance, have been the norm for many years. However, these approaches often fall short of optimizing machinery performance and minimizing downtime. Enter Predictive Maintenance (PdM), a game-changing strategy powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) that promises to revolutionize the way industries manage their assets.
Understanding Predictive Maintenance

Image by : Yandex
Predictive Maintenance is a proactive maintenance strategy that uses data analysis tools and techniques to detect anomalies in equipment and predict when maintenance should be performed. This approach aims to prevent unexpected equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules, thus enhancing the overall efficiency of operations.
Key Components of Predictive Maintenance
1. Data Collection: Sensors and IoT devices are used to collect real-time data from equipment.
2. Data Processing: The collected data is processed and analyzed to identify patterns and trends.
3. Predictive Algorithms: Machine learning algorithms are used to predict potential failures and recommend maintenance actions.
4. Maintenance Scheduling: Based on the predictions, maintenance activities are scheduled to minimize downtime and maximize equipment lifespan.
The Role of AI in Predictive Maintenance
Artificial Intelligence plays a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of Predictive Maintenance. By leveraging AI technologies, industries can achieve more accurate predictions, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce operational costs.
AI-Powered Data Analysis
AI algorithms, particularly machine learning and deep learning models, are adept at analyzing large volumes of data to identify patterns and trends that may not be apparent through traditional analysis methods. These algorithms can process data from various sources, including sensors, historical maintenance records, and operational logs, to provide insights into equipment health and performance.
Predictive Modeling
One of the core applications of AI in Predictive Maintenance is the development of predictive models. These models use historical data to predict future equipment failures and maintenance needs. By continuously learning from new data, AI models can improve their accuracy over time, leading to more reliable predictions.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
AI enables real-time monitoring of equipment by continuously analyzing data from sensors and IoT devices. When the AI system detects anomalies or deviations from normal operating conditions, it can trigger alerts, allowing maintenance teams to take proactive measures before a failure occurs. This real-time capability is essential for preventing unexpected downtime and costly repairs.
Optimization of Maintenance Schedules
AI can optimize maintenance schedules by determining the most opportune times for maintenance activities. By predicting when equipment is likely to fail, AI can help schedule maintenance during periods of low operational impact, thereby minimizing disruptions to production. This optimization also extends the lifespan of equipment by ensuring that maintenance is performed only when necessary.
Cost Reduction
One of the significant benefits of AI-driven Predictive Maintenance is cost reduction. By preventing unexpected equipment failures and optimizing maintenance schedules, industries can reduce repair costs, minimize downtime, and extend the lifespan of their assets. Additionally, AI can help identify inefficiencies in maintenance processes, leading to further cost savings.
Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing sector, Predictive Maintenance powered by AI has been instrumental in reducing downtime and improving production efficiency. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze data from machinery to predict when components such as bearings or motors are likely to fail. By scheduling maintenance activities based on these predictions, manufacturers can avoid costly production halts and ensure smooth operations.
Energy Sector
The energy sector, particularly in power generation and distribution, relies heavily on Predictive Maintenance to ensure the reliability of critical infrastructure. AI-driven Predictive Maintenance systems can monitor the health of turbines, transformers, and other equipment, predicting failures and optimizing maintenance schedules. This approach not only enhances the reliability of energy supply but also reduces operational costs.
Transportation and Logistics

Image by : Yandex
In transportation and logistics, Predictive Maintenance is used to monitor the health of vehicles and infrastructure. AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors installed on trucks, trains, and aircraft to predict maintenance needs and prevent breakdowns. This proactive approach ensures the timely delivery of goods and services while reducing maintenance costs.
Healthcare Industry
In the healthcare sector, Predictive Maintenance is applied to medical equipment such as MRI machines, ventilators, and diagnostic devices. AI algorithms can predict when these critical devices are likely to fail, allowing for timely maintenance and minimizing the risk of equipment downtime. This ensures the continuous availability of essential medical services and improves patient care.
Challenges and Future Directions
Data Quality and Integration
One of the primary challenges in implementing AI-driven Predictive Maintenance is ensuring the quality and integration of data from various sources. Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate predictions and suboptimal maintenance decisions. Industries must invest in robust data collection and integration frameworks to overcome this challenge.
Model Interpretability
While AI algorithms can provide accurate predictions, their decision-making processes are often complex and difficult to interpret. This lack of transparency can be a barrier to the adoption of AI-driven Predictive Maintenance. Developing interpretable models and providing clear explanations for maintenance recommendations can help build trust in AI systems.
Scalability
Scaling AI-driven Predictive Maintenance solutions to large and diverse industrial environments can be challenging. Industries must ensure that their AI systems can handle the volume and variety of data generated by numerous assets. Scalable cloud-based solutions and edge computing can address this challenge by providing the necessary computational power and flexibility.
Future Directions
The future of AI in Predictive Maintenance holds exciting possibilities. Advances in AI technologies, such as reinforcement learning and natural language processing, can further enhance the accuracy and effectiveness of Predictive Maintenance systems. Additionally, the integration of AI with other emerging technologies, such as blockchain and augmented reality, can provide new opportunities for improving maintenance processes and decision-making.
Conclusion
Predictive Maintenance, powered by Artificial Intelligence, is transforming the way industries manage their assets. By leveraging AI technologies, industries can achieve more accurate predictions, optimize maintenance schedules, and reduce operational costs. As AI continues to evolve, its role in Predictive Maintenance will become increasingly critical, driving further improvements in operational efficiency and asset management. Embracing AI-driven Predictive Maintenance is not just a competitive advantage but a necessity for industries aiming to thrive in the digital age.
Consumer Services
Right Software Development Partner in India for Your 2026 Startup

Starting a startup in 2026 feels exciting, but also confusing. You have an idea, maybe even a small team, yet one big question always appears first: who will build your product? Most founders are not programmers. They need reliable custom software development services to turn their idea into a real app, website, or platform.
India has become one of the most trusted places for startups to build software. Why? Because you get skilled engineers, global experience, and affordable pricing in one place. From fintech apps in Dubai to healthcare software used in Europe and the US, many young companies rely on Indian development partners.
In this article, we will understand how startups should choose a development partner and explore ten reliable Indian companies that provide custom software development services suitable for early-stage businesses.
How to Choose the Right Development Partner
Before hiring any company, a founder should understand what they actually need. A startup does not require a huge corporate vendor. It needs guidance and flexibility.
Here is a simple decision checklist-
- Do they build MVPs for startups or only big enterprise projects?
- Do they help with product planning or just coding?
- Do they offer cloud setup on AWS or Google Cloud?
- Can they explain technical ideas in simple English?
- Do they support your product after launch?
A good provider of custom software development services acts like a technical cofounder. They tell you what features to delay, how to save cost, and how to launch faster. For example, many fintech startups first build only login, wallet, and payment features. They add analytics later. This approach saves both time and money.

Top 10 Software Development Companies in India for Startups
Below are ten reliable companies suitable for startup founders. Each offers custom software development and flexible engagement.
1. AppSquadz
AppSquadz focuses on startup MVP development and scalable digital products. They provide mobile app development, SaaS platforms, cloud solutions, and custom software development services based on business needs. Many education and healthcare startups choose them for UI/UX guidance and post-launch support.
2. Konstant Infosolutions
Known for mobile applications, especially ecommerce and booking apps. Startups launching marketplace platforms often use their affordable software development services. They have experience with payment integrations and real time chat systems.
3. TatvaSoft
This custom application development company works with startups building web platforms and dashboards. They are strong in NET and React technologies. Several SaaS products serving the logistics industry were built by their teams.
4. PixelCrayons
Popular among international founders from the UK and Dubai. They offer dedicated developer hiring. Many early stage companies choose them when they need quick product development without hiring an internal team.
5. OpenXcell
A good option for AI and blockchain based startups. If your idea includes automation, chatbots, or analytics tools, they provide custom software development services with consulting support.
6. Radixweb
This firm helps startups scale after launch. Suppose your app suddenly gets 50000 users. They help migrate it to AWS and optimize performance. That makes them useful for growing SaaS businesses.
7. MindInventory
Strong in UI and UX design. Many founders do not realize how important user experience is. This company focuses on making apps easy to use, which improves customer retention.
8. Hidden Brains
A long established custom software development provider that works with fintech and healthcare software projects. They also build ERP systems for startups entering manufacturing.
9. Net Solutions
Useful for ecommerce startups. They have experience with Shopify and headless commerce platforms. Many D2C brands launching online stores work with them.
10. SPEC INDIA
They focus on data driven platforms and analytics dashboards. Startups handling large customer data sets or reporting tools benefit from their expertise.
Why Startups Prefer India in 2026
A few years ago startups hired freelancers. Today they prefer a custom application development company. The reason is simple: startups now build complex products. Think about apps using AI, payment gateways, cloud storage, and real time chat. One freelancer cannot manage everything. India offers three big advantages:
First, cost. A startup in the United States may spend $120000 to build an MVP. In India the same project can often be done for $15000 to $30000 using affordable software development services.
Second, cloud knowledge. Many Indian teams work daily with AWS and Google Cloud. They know how to make scalable systems. This means your app will not crash when 100 users become 10000 users.
Third, startup understanding. Indian companies now follow agile methods. They release small updates weekly instead of waiting six months.
You might ask: Is cheaper always lower quality? No. Many Indian developers build SaaS products used worldwide. Cost is lower mainly because operating expenses are lower, not because skill is lower.
Conclusion
Choosing the right development partner in 2026 is not just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. For early-stage startups, the company you hire will directly influence your product quality, launch speed, scalability, and even investor confidence.
India continues to be a preferred destination because it offers a strong balance of cost efficiency, technical expertise, and startup-focused execution. However, the real advantage does not come from geography alone , it comes from selecting a partner who understands MVP thinking, agile development, cloud scalability, and long-term product growth.
FAQs
1. Why do startups prefer hiring Indian software development companies?
Startups prefer Indian companies because they offer a strong balance of cost efficiency, technical expertise, and scalable development practices. Many firms in India have global experience working with startups from the US, Europe, and the Middle East, making them comfortable with international standards and agile workflows.
2. How much does it cost to build an MVP in India?
The cost of building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in India typically ranges between $15,000 and $30,000, depending on complexity, features, and technology stack. More advanced platforms involving AI, fintech integrations, or complex dashboards may cost more.
3. How long does it take to develop a startup MVP?
Most startup MVPs take 8 to 16 weeks to develop. Simple apps with limited features can launch faster, while SaaS platforms or fintech products may require additional time for backend development, security setup, and testing.
4. Should startups hire freelancers or a development company?
Freelancers may work for very small projects, but modern startup products often require backend development, UI/UX design, cloud setup, testing, and ongoing support. A development company provides a structured team, project management, and long-term maintenance — reducing risk for early-stage founders.
5. What should startups look for before signing a development contract?
Before signing, startups should check:
- Portfolio of similar startup projects
- Clear pricing structure
- Post-launch support policy
- Ownership of source code
- Experience with cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud
Digital Development
Vhsgjqm: Understanding Abstract Identifiers in the Digital Age
Costumer Services
SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails: A Comprehensive Guide

Introduction
If you’re facing problems with SBCGlobal email not receiving emails, you’re not alone. Many users experience email delivery issues caused by server settings, outdated configurations, or account security errors. This guide will walk you through why your SBCGlobal email might not be receiving messages, how to fix it step-by-step, and when to contact professional suppor for advanced troubleshooting.
What Is SBCGlobal Email?
SBCGlobal.net is a legacy email service originally provided by Southwestern Bell Corporation, which later merged with AT&T. Even though new SBCGlobal accounts are no longer being created, millions of users still access their SBCGlobal email through AT&T’s Yahoo Mail platform.
However, because SBCGlobal operates on older infrastructure and server settings, users sometimes experience email syncing, login, or receiving issues especially when using third-party apps or outdated settings.

Common Reasons SBCGlobal Email Is Not Receiving Emails
Before you start troubleshooting, it’s important to identify what might be causing the issue. Below are the most frequent culprits behind SBCGlobal email receiving problems:
- Incorrect Email Settings: If your incoming (IMAP/POP3) or outgoing (SMTP) settings are incorrect, emails won’t load properly.
- Server Outages: Temporary outages or server maintenance by AT&T or Yahoo may interrupt incoming mail delivery.
- Storage Limit Reached: When your mailbox exceeds its storage limit, new emails are automatically rejected.
- Spam or Filter Rules: Overly strict filters or incorrect spam settings might send legitimate emails to the Junk or Trash folder.
- Browser Cache or App Glitches: Cached data and outdated email apps can disrupt syncing or message retrieval.
- Blocked Senders or Blacklisted IPs: Accidentally blocking a sender or being on a spam blacklist may prevent messages from reaching your inbox.
- Security or Account Lock Issues: Suspicious login attempts or password errors can cause temporary account restrictions.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails
Let’s go through a series of troubleshooting steps to help you restore your email flow. You can perform these solutions on both desktop and mobile platforms.
1. Check SBCGlobal Email Server Status
- Sometimes, the issue isn’t on your end.
- Go to Downdetector or AT&T’s official website to see if SBCGlobal or AT&T Mail is down.
If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait until the service is restored.
2. Verify Your Internet Connection
Ensure your device has a stable and fast internet connection. Poor connectivity can stop your email client from syncing or fetching new messages.
3. Update Incoming and Outgoing Mail Server Settings
Outdated or incorrect settings are the most common reason SBCGlobal email stops receiving messages. Here are the correct configurations:
Common Reasons SBCGlobal Email Is Not Receiving Emails
Before you start troubleshooting, it’s important to identify what might be causing the issue. Below are the most frequent culprits behind SBCGlobal email receiving problems:
- Incorrect Email Settings: If your incoming (IMAP/POP3) or outgoing (SMTP) settings are incorrect, emails won’t load properly.
- Server Outages: Temporary outages or server maintenance by AT&T or Yahoo may interrupt incoming mail delivery.
- Storage Limit Reached: When your mailbox exceeds its storage limit, new emails are automatically rejected.
- Spam or Filter Rules: Overly strict filters or incorrect spam settings might send legitimate emails to the Junk or Trash folder.
- Browser Cache or App Glitches: Cached data and outdated email apps can disrupt syncing or message retrieval.
- Blocked Senders or Blacklisted IPs: Accidentally blocking a sender or being on a spam blacklist may prevent messages from reaching your inbox.
- Security or Account Lock Issues: Suspicious login attempts or password errors can cause temporary account restrictions.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Fix SBCGlobal Email Not Receiving Emails
Let’s go through a series of troubleshooting steps to help you restore your email flow. You can perform these solutions on both desktop and mobile platforms.
1. Check SBCGlobal Email Server Status
- Sometimes, the issue isn’t on your end.
- Go to Downdetector or AT&T’s official website to see if SBCGlobal or AT&T Mail is down.
If there’s an outage, you’ll need to wait until the service is restored.
2. Verify Your Internet Connection
Ensure your device has a stable and fast internet connection. Poor connectivity can stop your email client from syncing or fetching new messages.
3. Update Incoming and Outgoing Mail Server Settings
Outdated or incorrect settings are the most common reason SBCGlobal email stops receiving messages. Here are the correct configurations:
- Server:
imap.mail.att.net - Port: 993
- Encryption: SSL
- Username: Your full SBCGlobal email address
- Password: Your email password
Outgoing Mail (SMTP) Server:
- Server:
smtp.mail.att.net - Port: 465 or 587
- Encryption: SSL/TLS
- Requires Authentication: Yes
If you’re using POP3, use:
- Incoming server:
inbound.att.net, Port 995 (SSL required) - Outgoing server:
outbound.att.net, Port 465 (SSL required)
Double-check these settings in your email client (Outlook, Apple Mail, Thunderbird, etc.) to make sure they match.
4. Review Spam and Junk Folder
- Sometimes, legitimate emails end up in the Spam or Junk folder. Open these folders and mark any wrongly filtered emails as “Not Spam.”
- Also, check your Filters and Blocked Addresses under email settings to ensure no important addresses are being redirected or blocked.
5. Clear Browser Cache or Update Your App
If you access SBCGlobal email through a browser:
- Clear your cache, cookies, and browsing history.
- Try opening email in incognito/private mode to rule out extensions or ad blockers causing problems.
If you use the Yahoo Mail App or Outlook, ensure the app is updated to the latest version. Outdated apps may not sync with the latest server configurations.
6. Check Mailbox Storage Limit
- SBCGlobal email accounts have a maximum storage quota.
- Delete unnecessary emails from your inbox, sent, and trash folders.
- After clearing space, refresh your inbox or restart your email client — new emails should start appearing.
7. Reset or Re-Add Your SBCGlobal Account
- If none of the above methods work, try removing your SBCGlobal account from your email client and re-adding it with the correct settings.
- This refreshes the connection and often resolves syncing or server timeout issues.
8. Reset Your Password
If you suspect your account might have been compromised or temporarily locked, resetting your password is a smart step.
- Visit the AT&T Password Reset page.
- Follow the on-screen steps to verify your identity.
- Set a strong, unique password and re-login to your email account.
9. Disable Security Software Temporarily
- Firewall or antivirus software can sometimes block email servers.
- Temporarily disable them (only if you’re confident about your network security) and check if you start receiving emails again.
10. Contact SBCGlobal Email Support
- If you’ve followed all the steps and your SBCGlobal email is still not receiving messages, the issue might be server-side or linked to account configuration.
- In that case, it’s best to contact SBCGlobal email support for expert help.
You can reach certified technicians.
They can assist with:
- Account recovery and login errors
- Server synchronization issues
- Email migration or backup
- Advanced spam and security settings
Having professional help ensures your account is restored quickly without losing any important messages or data.
Tips to Prevent Future SBCGlobal Email Problems
- Update Passwords Regularly: Keep your email account secure and avoid login lockouts.
- Use a Reliable Email App: Apps like Outlook or Apple Mail handle IMAP connections more efficiently.
- Backup Emails Periodically: Regular backups protect your messages from unexpected sync failures.
- Keep Storage Under Control: Delete old attachments and large files frequently.
- Monitor Account Activity: Check for unusual login attempts from unknown locations.
Final Thoughts
Facing issues like SBCGlobal email not receiving emails can be frustrating, especially when you rely on your email for important communications. However, most problems can be resolved by verifying server settings, clearing browser cache, managing storage, or resetting passwords.
If you continue to face challenges, don’t hesitate to reach out to expert SBCGlobal email support for personalized assistance. A few minutes of professional troubleshooting can save hours of frustration and get your SBCGlobalemail running smoothly again.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom