News
The Impact of Geopolitical Tensions on International Trade

The Impact of Geopolitical Tensions on International Trade
In an increasingly interconnected world, international trade serves as the lifeblood of the global economy. However, geopolitical tensions can significantly impact the flow of goods, services, and capital across borders. Understanding the multifaceted effects of these tensions is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and stakeholders who navigate the complex terrain of global commerce.
The Nature of Geopolitical Tensions
Geopolitical tensions refer to conflicts or frictions between nations arising from political, economic, military, or cultural disputes. These tensions can manifest in various forms, including trade wars, sanctions, military confrontations, and diplomatic standoffs. The consequences of such tensions often ripple through international trade channels, affecting economies worldwide.
Trade Wars and Tariffs
One of the most direct ways geopolitical tensions impact international trade is through trade wars and the imposition of tariffs. A notable example is the trade war between the United States and China, which began in 2018. Both countries imposed tariffs on billions of dollars’ worth of goods, disrupting supply chains and increasing costs for businesses and consumers.
Trade wars can lead to a decline in trade volumes, as higher tariffs make goods more expensive and less competitive. This, in turn, can result in reduced economic growth and increased uncertainty in global markets. Companies may also seek to diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks, leading to shifts in trade patterns and new alliances.
Sanctions and Embargoes
Sanctions and embargoes are another tool used in geopolitical conflicts, with profound implications for international trade. Sanctions can target specific countries, industries, or individuals, restricting their ability to engage in global commerce. For instance, sanctions imposed on Iran have severely limited its oil exports, a critical source of revenue for the country.
Sanctions can disrupt global supply chains, as companies must navigate complex regulatory landscapes to ensure compliance. This can lead to delays, increased costs, and reduced access to essential goods and services. Additionally, businesses may face reputational risks if they are perceived as violating sanctions, further complicating their operations.

Picture by: Yandex.com
Impact on Global Supply Chains
Geopolitical tensions can disrupt global supply chains, leading to delays, increased costs, and reduced efficiency. For example, the COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in global supply chains, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions. The pandemic highlighted the risks of over-reliance on specific regions for critical components, prompting companies to rethink their supply chain strategies.
In response to geopolitical tensions, businesses may seek to diversify their suppliers, relocate production facilities, or invest in technology to enhance supply chain resilience. While these measures can mitigate risks, they also require significant investments and may take time to implement fully.
Geopolitical tensions can also impact currency markets and financial stability. When tensions escalate, investors may seek safe-haven assets, leading to currency fluctuations. For example, during periods of heightened geopolitical risk, the US dollar and gold often appreciate as investors seek stability.
Currency fluctuations can affect international trade by altering the relative prices of goods and services. A stronger domestic currency can make exports more expensive and less competitive, while a weaker currency can boost export competitiveness but increase the cost of imports. Businesses engaged in international trade must carefully manage currency risks to protect their profitability.
Shifts in Trade Alliances
Geopolitical tensions can lead to shifts in trade alliances and the formation of new economic blocs. Countries may seek to strengthen ties with allies and reduce dependence on adversaries. For instance, the European Union has sought to deepen trade relations with countries in Asia and Latin America to diversify its trade partners and reduce reliance on traditional markets.
These shifts can create new opportunities for businesses but also require adaptation to different regulatory environments and market dynamics. Companies must stay informed about evolving trade policies and be agile in responding to changing geopolitical landscapes.
Technological and Cybersecurity Risks
Technological advancements have transformed international trade, but they also introduce new risks in the context of geopolitical tensions. Cybersecurity threats, intellectual property theft, and technology transfer restrictions are critical concerns for businesses operating in the global market.
Geopolitical tensions can exacerbate these risks, as countries may engage in cyber espionage or impose restrictions on technology exports. Businesses must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and stay vigilant against emerging threats to protect their intellectual property and sensitive data.
The Role of Multilateral Institutions
Multilateral institutions, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of geopolitical tensions on international trade. These institutions provide frameworks for resolving trade disputes, promoting transparency, and fostering cooperation among nations.
However, the effectiveness of multilateral institutions can be challenged by geopolitical tensions. For instance, the WTO has faced criticism for its inability to resolve some high-profile trade disputes, leading to calls for reform. Strengthening these institutions and ensuring their relevance in a changing geopolitical landscape is essential for maintaining a stable and predictable global trading system.
Conclusion
Geopolitical tensions have far-reaching implications for international trade, affecting everything from tariffs and sanctions to supply chains and currency markets. Businesses, policymakers, and stakeholders must navigate these challenges by staying informed, diversifying their strategies, and investing in resilience.
While geopolitical tensions are an inherent part of the global landscape, their impact on international trade can be managed through proactive measures and international cooperation. By understanding the complexities of these tensions and their effects on trade, stakeholders can better prepare for and adapt to a dynamic and interconnected world.
News
Tidy and Tough: How a Garden Hose Reel Improves Workflow
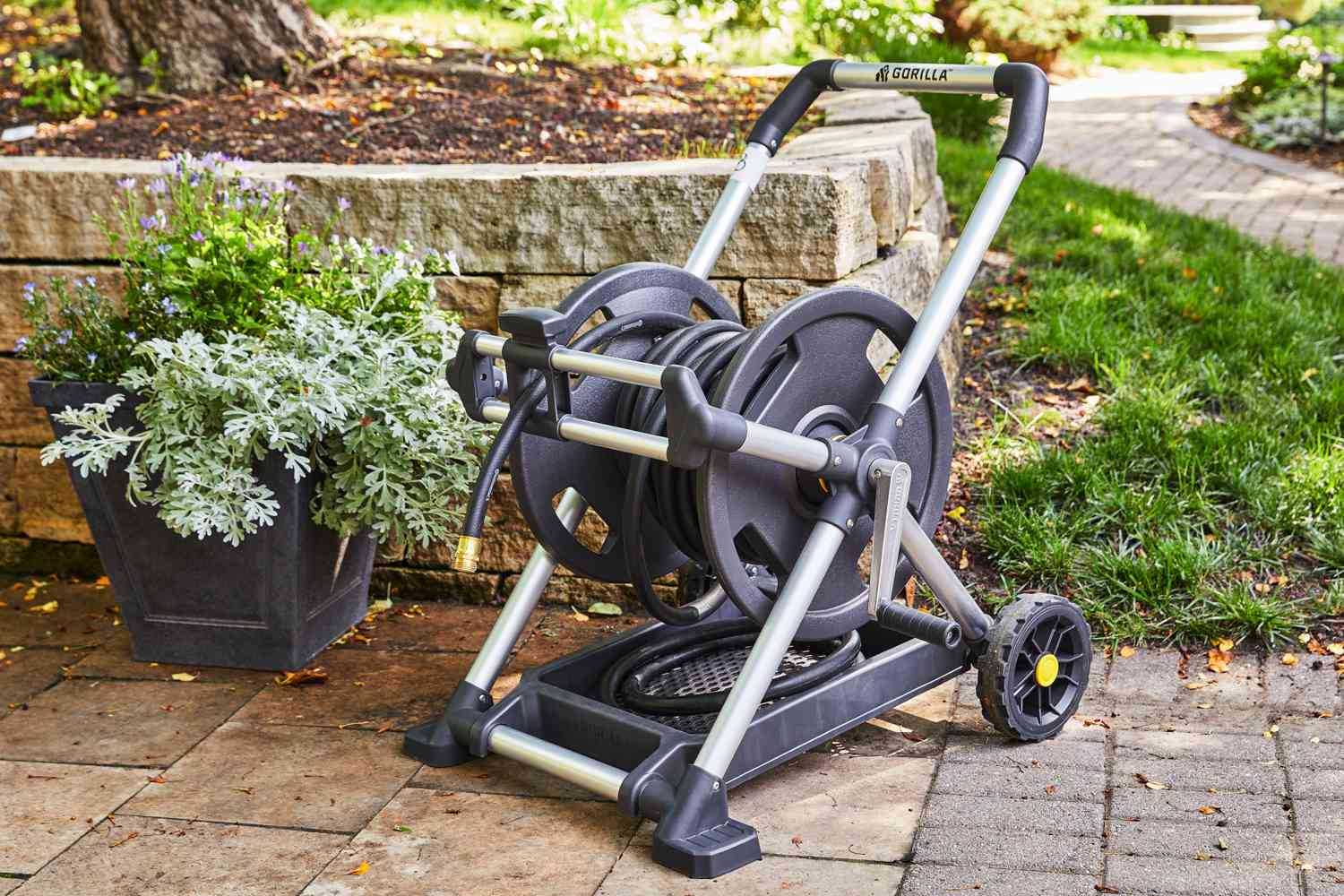

A tangled garden hose can make your outdoor space look messy and slow you down. It kinks, snags, and gets in the way. Luckily, for those who are frustrated by these issues, a garden hose reel can help. Designed to store and manage hoses efficiently, a hose reel keeps your outdoor space organized and your watering tasks running smoothly.
It doesn’t matter if you manage a small garden or maintain a larger landscape; having the right tools makes a big difference. A hose reel is one of those tools that people often overlook until they get one.
What Does a Garden Hose Reel Actually Do?
At its most basic, a hose reel stores your hose. Good reels protect the hose from sun damage, prevent sharp bends that lead to leaks, and clear your paths of trip hazards.
Most reels wind the hose using a manual crank, spring-loaded mechanism, or motorized rewind. They come in wall-mounted, freestanding, and cart-style designs. Some even have built-in storage compartments for nozzles and connectors.
Top Reasons to Use a Hose Reel
There’s a reason you’ll find a hose reel in most well-kept gardens or yards. Here’s what makes them such a brilliant addition:
1. Keeps Things Organized
A reel eliminates hose clutter. You won’t have to untangle or unwind a mess every time you water. It also gives your outdoor space a more polished, maintained look.
2. Extends Hose Life
When left on the ground, hoses are exposed to sharp edges, UV rays, and foot traffic. A hose reel protects it, preventing cracks and wear.
3. Saves Time and Energy
With a reel, you’re not wasting time dragging a hose across the yard or fighting with kinks. Pull it out, use it, reel it back in. Simple.
4. Improves Safety
A coiled hose on the ground is a tripping hazard. This is especially important if kids or older adults move through the garden frequently.
5. Reduces Water Waste
A damaged or kinked hose leaks water. Keeping the hose in good condition helps deliver a consistent flow and avoids waste.
Types of Garden Hose Reels
Different reels suit different setups. Here’s a quick look at the most common options:
- Wall-Mounted Reels: Ideal for fixed spots near a spigot. Great for smaller yards or patios.
- Hose Reel Carts: Mobile and versatile, these roll around larger spaces and often have extra storage.
- Retractable Hose Reels: These automatically retract with a spring-loaded mechanism. They are great for quick, no-fuss storage.
- Stationary Freestanding Reels:These can be placed anywhere in the yard and are best for gardens without nearby walls or posts.
How to Choose the Right Hose Reel
A few key factors help determine what kind of reel you need:
- Hose Length: Make sure the reel can handle the full length of your hose. Check the reel’s capacity before buying.
- Material: Look for rust-resistant metals or heavy-duty plastic. Reels designed for outdoor use should withstand sunlight and rain.
- Mounting Location: If you will be wall-mounting, make sure you have a secure surface near your water supply.
- Ease of Use: Features like swivel bases, comfortable handles, and auto-rewind systems can make a big difference.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Most hose reels come with clear instructions and all necessary hardware. For wall-mounted models:
- Use anchors for added stability if mounting to drywall or masonry.
- Place it at a comfortable height so you don’t have to bend or stretch awkwardly.
For ongoing care:
- Drain the hose before winter to avoid freezing and cracking.
- Check moving parts occasionally and apply lubricant if needed.
- Wipe down metal parts to prevent rust buildup.
Choosing the Right Hose Reel for Your Garden
When selecting your garden hose reel, keep these factors in mind:
A. Hose Length and Diameter
- Ensure the reel capacity matches your hose length (e.g., 50, 75, or 100 feet) and diameter (commonly 5/8″ or 3/4″).
B. Material and Durability
- Steel Reels: Heavy-duty and long-lasting, often powder-coated to resist rust.
- Plastic Reels: Lightweight and budget-friendly but less durable.
- Aluminum Reels: Rust-proof and sturdy, balancing weight and strength.
C. Mounting Options
- Wall-mounted for permanent setups.
- Freestanding or portable carts for flexible layouts.
- Retractable reels that mount under eaves or in sheds.
D. Ease of Use
- Test the winding mechanism—look for smooth-crank handles or reliable auto-retract motors.
- Check for integrated guides that help the hose spool evenly.
E. Additional Features
- Swivel Connector: Prevents hose twisting at the reel.
- Built-in Nozzle Holder: Keeps your watering tools within reach.
- Locking Mechanism: Holds the hose at a fixed length.
Choosing quality over price often results in fewer headaches and better long-term performance.
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Installing a Wall-Mounted Reel
- Find a Solid Surface: Concrete or sturdy wood studs are ideal.
- Use Proper Anchors: Masonry anchors for brick walls, heavy-duty wood screws for timber.
- Position at Waist Height: Easier to wind and unwind without bending.
- Check Water Source Proximity: Keep the reel close to your spigot to reduce plumbing modifications.
Maintaining Your Reel
- Winter Storage: Drain the hose and reel before freezing weather. Store indoors or cover with weatherproof tarps.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply silicone spray to bearings and swivels annually.
- Inspect for Wear: Check the hose for cracks and the reel for rust or loose bolts every season.
Proper upkeep ensures your reel remains tough and reliable year after year.
Real-Life Success Stories
Suburban Garden Transformation
Homeowner Sarah replaced her old plastic reel with a steel wall-mounted model. She reports:
- 50% less time spent on watering chores.
- Zero hose tangles for an entire season.
- Fewer backaches from winding—she now enjoys gardening more.
Community Garden Upgrade
A neighborhood community garden installed portable hose carts across plots. Results include:
- Improved plant health due to consistent watering.
- Visitors praising the tidy pathways.
- Volunteers noticing fewer trip incidents, even during busy planting days.
Pairing Your Reel with the Right Accessories
To get the most from your reel, consider using it alongside quality connectors, spray nozzles, and quick-release fittings. Some hose reels include these extras, but most can be added to customize your watering setup.
Final Thoughts
A hose reel turns an everyday tool into a more efficient part of your outdoor setup. It protects your hose, keeps your space neat, and streamlines watering tasks. Once you’ve used one, it’s hard to return to storing your hose the old way. For anyone who values simplicity, longevity, and order in the garden, a hose reel is an easy upgrade that pays off daily.ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ ㅤ
News
Online Betting ID is the First Step to Smarter Cricket Betting

Introduction
The online betting industry in India is growing rapidly, especially around cricket events like the IPL. With easy access to platforms and real-time match engagement, online betting has become a favorite pastime for thousands. But while many focus on odds, tips, and platform reviews, most forget the most important starting point — having a verified online betting ID.
Whether you’re a beginner testing the waters or an experienced bettor looking to scale, the first step to safe and seamless betting is getting the right online cricket ID from a trusted provider. This article will walk you through why it matters, what to look for in a provider, how to get your ID instantly through WhatsApp, and the trends shaping online cricket betting in 2025.
What is an Online Betting ID?
An online betting ID is a personal login credential that grants you access to top-tier betting exchanges like Lord Exchange, Diamond Exchange, Lotus365, and more. It acts as your entry pass into the world of real-time sports betting.
With a verified ID, you can:
- Place bets during live cricket, football, tennis, and kabaddi matches
- Manage your wallet with easy deposits and withdrawals
- Access multiple betting panels through one account
- Enjoy live odds and special bonus offers
Betting IDs are typically platform-specific and can be generated through a cricket ID provider. These IDs ensure secure access, personal tracking, and protection from fake panels or scam sites.
Why Online Cricket ID is Crucial
A online cricket ID is designed specifically for cricket betting. While general gaming IDs work across multiple sports and games, cricket-specific IDs are tailored for the nuances of cricket matches. This includes access to features like ball-by-ball betting, player performance-based odds, and toss or session predictions.
If you’re someone who primarily enjoys betting on cricket — whether IPL, World Cup, or domestic leagues — getting a dedicated cricket ID makes the process smoother and more personalized. It enhances your overall user experience and ensures that you’re not overpaying or getting restricted by general gaming limits.
Choosing the Right Cricket ID Provider
There are dozens of options available online, but not all of them are safe or genuine. Many bettors end up losing money or getting banned from platforms due to fake IDs or unauthorized providers.
That’s why choosing a verified cricket ID provider is essential. A good provider will:
- Activate your ID quickly (often within minutes)
- Offer real-time customer support via WhatsApp or Telegram
- Provide access to top platforms like Lord Exchange, Lotus365, and Diamond
- Be transparent about deposit limits, payout speeds, and bonus policies
You should also check if the provider has an active website, real client testimonials, and a strong online reputation. Platforms like KGF777 Exchange offer all of this with a smooth onboarding experience and complete security.
How to Get Your Betting ID via WhatsApp
One of the fastest and most popular methods of ID activation today is through a betting ID WhatsApp number. It’s fast, direct, and avoids unnecessary formalities.
Follow these steps:
- Visit KGF777 Exchange
- Click the WhatsApp icon or scan the QR code
- Message “Need a cricket ID” to the support team
- Submit basic info (like preferred platform and deposit amount)
- Get your ID credentials, and start betting within minutes
This method is especially helpful for mobile-first users and those who prefer personal communication over forms and tickets.
Online Betting Trends in 2025
In 2025, online betting is no longer limited to basic platforms or shady Telegram groups. The industry is shifting toward professional platforms, fast onboarding, and better user security.
Here are some trends shaping the space:
- Real-time dashboards with multiple live matches
- Mobile-first design with low data consumption
- In-app WhatsApp or Telegram support for immediate assistance
- Secure wallet integrations for UPI, Paytm, GPay, and bank transfers
- Responsible betting features to control daily limits and session time
All these features are available only when you access betting platforms through a verified online betting ID.
Safety and Legal Awareness
While betting in India operates in a grey legal space, having a verified ID with secure platforms reduces risk. Always make sure the platform you use has:
- HTTPS encryption
- Fast and clean UI
- Withdrawal transparency
- No hidden commission cuts
Using a secure cricket ID provider helps protect your personal data and funds from third-party misuse. Never share your betting ID with unknown agents or random groups.
Conclusion
In the world of online betting, your ID is more than just a login — it’s your access to a trusted, secure, and flexible experience. With the growth of cricket betting in India, starting with a verified online cricket ID is the smartest move you can make.
Choose a reliable cricket ID provider, get your login instantly through a betting ID WhatsApp number, and play with confidence across all major platforms.
Visit KGF777 Exchange now and activate your betting ID in minutes.
Author Bio
Ritu Das is a digital marketer and SEO strategist with expertise in the iGaming and sports entertainment space. She works with brands like KGF777 Exchange to create SEO-driven content and link-building strategies that increase traffic and improve online visibility.
News
What Are the Hidden Costs of Living as a Student in Dundee?
Dundee, often called Scotland’s “City of Discovery,” is gaining popularity among international students for its welcoming community, compact layout, and rich academic heritage. Home to two main universities—University of Dundee and Abertay University—the city blends affordability with quality education. With stunning views over the River Tay, a buzzing arts scene, and everything within walking distance, Dundee is an attractive choice for students looking for value and convenience in the UK.
What Is the Average Cost of Living in Dundee for Students?
While Dundee is known to be more affordable than cities like Edinburgh or London, students should still plan their monthly budgets carefully.
Here’s an approximate monthly breakdown of essential expenses:
- Rent: £400–£700 depending on the area and amenities
- Food & Groceries: £150–£250
- Transport: £30–£50 (most places are walkable)
- Utilities & Internet: £40–£100
- Phone Bill: £10–£25
- Entertainment & Eating Out: £60–£100
These costs can fluctuate based on lifestyle choices and personal spending habits.
What Hidden Housing Costs Should You Watch Out For?
Rent isn’t the only cost to consider when choosing where to live. Many students get caught off guard by hidden housing costs that aren’t always mentioned upfront. Understanding these can help you avoid nasty surprises.
Common hidden housing charges include:
- Utility Bills (Gas, Water, Electricity): Not always included in rent
- Council Tax: Full-time students are usually exempt but must apply for it
- Internet Setup Fees: Can cost £30–£50 upfront
- TV Licence: Required if you watch live TV or BBC iPlayer—costs ~£159/year
- Maintenance Charges: In some private flats or shared housing
- Deposit and Admin Fees: Can be one month’s rent or more, depending on the landlord
- Cleaning Costs: End-of-tenancy cleaning may be deducted from your deposit
Before signing a lease, ask for a full breakdown of costs and what is included to avoid unexpected financial strain.
Which Type of Accommodation Is Best for International Students?
When it comes to choosing where to live, options in Dundee vary from university-managed halls to private rentals.
Here’s a quick comparison:
| Type of Accommodation | Pros |
| University Halls | Safe, close to campus, great for meeting people |
| Private Halls | Modern amenities, often all-inclusive |
| Shared Houses/Flats | More independence, potential savings |
| Homestays | Cultural immersion, meals often included |
Many international students prefer student accommodation Dundee providers that offer flexible contracts and inclusive rent packages—helping reduce the stress of multiple monthly bills.
Where Should You Live in Dundee for the Best Student Experience?
The area you choose can significantly impact your living experience and budget.
Top student-friendly neighbourhoods in Dundee:
- West End: Close to the University of Dundee, lively student vibe
- City Centre: Great for nightlife and quick access to amenities
- Hilltown: More affordable but slightly farther from university buildings
- Broughty Ferry: A bit posher and more scenic—ideal for quiet living
Always consider commute time, safety, and what’s included in the rent before finalising a location.
What Unexpected Costs Can Affect Your Monthly Budget?
Aside from rent and groceries, students often overlook other small but frequent expenses that add up over time.
Extra costs to consider:
- Course Materials: Books, printing, software subscriptions
- Laundry: £3–£6 per load in halls or laundrettes
- Social Events & Societies: Membership fees and event tickets
- Takeaways & Coffee Runs: Weekly indulgences can inflate your budget
- Seasonal Clothing: Warm clothing for the Scottish winter
- Travel Back Home: Flight tickets during breaks or emergencies
These expenses may seem minor individually, but when added together, they can noticeably impact your overall cost of living Dundee budget.
What Smart Tips Can Help You Save Money in Dundee?
Being budget-conscious doesn’t mean missing out on the full student experience. In fact, with a few practical habits and smart choices, you can enjoy your university life to the fullest while still keeping your finances in check. Creating a realistic budget, tracking your spending, and prioritizing essential expenses can go a long way in helping you stay on top of your finances. Look out for student discounts, cook meals at home, and use public transport to cut down on daily costs. By making thoughtful decisions, you can live comfortably, stay social, and make the most of your student years without overspending.
Top student saving strategies:
- Use Student Discounts: TOTUM card, UNiDAYS, and local deals
- Cook at Home: More economical and healthier
- Split Bills: Share costs for groceries and streaming subscriptions
- Use Dundee’s Walking Paths: Cut down on transport costs
- Shop Second-Hand: Thrift stores for furniture and clothes
- Track Your Spending: Use budgeting apps like Monzo or Revolut
Conclusion: Is Dundee Affordable for International Students?
Dundee is undoubtedly one of the more affordable cities for students in the UK—but affordability comes with planning. Knowing about the hidden costs upfront helps you avoid financial pitfalls and makes your student journey smoother and stress-free. From budgeting for utilities to picking the right neighbourhood, a little homework goes a long way in ensuring you get the most out of your experience in this vibrant Scottish city.
-
Business2 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business2 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business2 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health2 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports2 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment2 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance2 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom
































