News
The Future of International Trade

International trade has been a cornerstone of global economic development for centuries, fostering connections between nations and driving economic growth. In today’s interconnected world, the exchange of goods and services across borders is more critical than ever. But what does the future hold for international trade? Let’s delve into the evolving landscape of global commerce and explore the trends, challenges, and opportunities that lie ahead.
Early Trade Routes and Barter Systems

Image by : Yandex
Trade has been a fundamental aspect of human civilization since ancient times. Early trade routes, such as the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of goods like silk, spices, and precious metals between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Barter systems, where goods were directly exchanged for other goods, were common before the advent of currency.
The Age of Exploration
The Age of Exploration in the 15th and 16th centuries marked a significant expansion in international trade. European explorers discovered new lands and established trade routes, bringing exotic goods like tobacco, sugar, and coffee to European markets. This era laid the groundwork for the modern global trade system.
Industrial Revolution and Trade Expansion
The Industrial Revolution of the 18th and 19th centuries revolutionized production and transportation, leading to a dramatic increase in international trade. Innovations like the steam engine and the telegraph facilitated faster and more efficient movement of goods and information, transforming global commerce.
Major Players in Global Trade
Today, international trade is dominated by major economies such as the United States, China, the European Union, and Japan. These countries account for a significant share of global exports and imports, influencing trade policies and global economic trends.
Impact of Technology on Trade
Technology has profoundly impacted international trade. The digitalization of trade processes, from online marketplaces to electronic documentation, has streamlined transactions and reduced costs. Technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are optimizing supply chains and enhancing decision-making.
Current Trade Agreements and Organizations
Trade agreements and organizations play a crucial role in regulating international trade. The World Trade Organization (WTO) oversees global trade rules, while regional agreements like NAFTA (now USMCA) and the European Union’s single market facilitate trade between member countries.
Technological Advancements in International Trade

Image by : Yandex
The digitalization of trade processes has revolutionized the way goods and services are exchanged. Electronic documentation, digital signatures, and online payment systems have made transactions faster and more secure. Platforms like Alibaba and Amazon have created global marketplaces that connect buyers and sellers worldwide.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are transforming international trade by providing advanced analytics and predictive insights. These technologies help businesses forecast demand, optimize inventory, and improve customer service. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are also enhancing the customer experience.
Blockchain and Trade Finance
Blockchain technology is making trade finance more transparent and efficient. By providing a decentralized ledger for recording transactions, blockchain reduces the risk of fraud and enhances trust between trading partners. Smart contracts on blockchain platforms automate payment processes and ensure compliance with trade agreements.
Impact of E-commerce on International Trade
Growth of Online Marketplaces
E-commerce has become a driving force in international trade. Online marketplaces like eBay, Amazon, and Alibaba allow businesses to reach customers across the globe. The convenience of online shopping has fueled the growth of cross-border e-commerce, enabling small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to compete in the global market.
Cross-border E-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce is expanding rapidly, driven by consumer demand for a wider variety of products and competitive prices. Businesses are leveraging digital marketing and logistics solutions to tap into new markets. However, challenges such as customs regulations and shipping costs remain.
Challenges and Opportunities
While e-commerce presents significant opportunities, it also poses challenges. Companies must navigate complex regulatory environments, manage international shipping logistics, and address cybersecurity concerns. Adopting robust e-commerce strategies and leveraging technology can help businesses overcome these hurdles and thrive in the global market.
Role of the World Trade Organization (WTO)
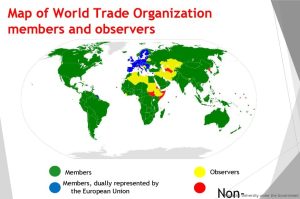
Image by : Yandex
The WTO plays a vital role in overseeing international trade rules and resolving disputes between member countries. By promoting free trade and reducing trade barriers, the WTO aims to create a level playing field for all nations. However, the organization faces criticism for its handling of trade disputes and the influence of powerful member states.
Regional Trade Agreements
Regional trade agreements, such as the European Union’s single market and the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), facilitate trade between member countries by reducing tariffs and harmonizing regulations. These agreements promote economic integration and regional cooperation.
Tariffs, sanctions, and trade wars significantly impact international trade. Tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, often used to protect domestic industries. Sanctions are economic penalties imposed on countries to achieve political objectives. Trade wars, such as the US-China trade conflict, disrupt global supply chains and create uncertainty for businesses.
Environmental Impact of Trade
International trade has environmental implications, including carbon emissions from transportation and deforestation for agriculture. Sustainable trade practices aim to minimize these impacts by promoting eco-friendly products, reducing waste, and adopting green technologies.
Fair Trade Practices
Fair trade practices ensure that producers in developing countries receive fair compensation for their goods. By supporting fair trade, consumers contribute to sustainable development and social justice. Fair trade certifications, such as Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance, provide assurance that products meet ethical standards.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives promote ethical business practices and sustainable development. Companies are increasingly adopting CSR policies that address environmental, social, and economic issues. By integrating CSR into their operations, businesses can enhance their reputation and contribute to global sustainability.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
International trade drives job creation and economic growth by opening new markets and increasing demand for goods and services. Export-oriented industries create employment opportunities and stimulate economic development. However, trade can also lead to job losses in industries that face increased competition from imports.
Trade Deficits and Surpluses
A trade deficit occurs when a country imports more goods and services than it exports, while a trade surplus occurs when exports exceed imports. Trade deficits can lead to increased debt and economic instability, while trade surpluses can strengthen a country’s economy. Balancing trade is crucial for sustainable economic growth.
Impact on Developing Countries
International trade offers significant opportunities for developing countries to integrate into the global economy and achieve economic growth. By exporting goods and services, developing countries can generate revenue, create jobs, and improve living standards. However, they often face challenges such as trade barriers, lack of infrastructure, and market volatility.
Political stability is crucial for maintaining healthy trade relations between countries. Political instability, such as conflicts or government changes, can disrupt trade and create uncertainty. Stable governments can negotiate favorable trade agreements and foster economic cooperation.
Influence of Superpowers

Image by : Yandex
Superpowers like the United States and China have a significant influence on international trade. Their trade policies, economic strategies, and geopolitical interests shape global trade dynamics. The rivalry between superpowers can lead to trade conflicts and impact global supply chains.
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets, such as India, Brazil, and Southeast Asian countries, are becoming increasingly important in international trade. These economies offer new opportunities for growth and investment. By tapping into emerging markets, businesses can diversify their markets and reduce dependency on traditional trade partners.
Innovations in Transportation
Innovations in transportation, such as containerization, high-speed rail, and autonomous vehicles, have revolutionized logistics and supply chains. These advancements reduce shipping times, lower costs, and enhance the efficiency of global trade.
Supply Chain Management
Effective supply chain management is essential for optimizing trade operations. Technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain provide real-time visibility and data analytics, enabling businesses to manage inventory, track shipments, and mitigate risks. Efficient supply chains enhance competitiveness and customer satisfaction.
Challenges in Global Supply Chains
Global supply chains face challenges such as disruptions from natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, and pandemics. Companies must build resilient supply chains by diversifying suppliers, adopting risk management strategies, and investing in technology.
Rise of Regionalism
Regionalism is gaining traction as countries form regional trade agreements to strengthen economic ties. These agreements promote economic integration, reduce trade barriers, and enhance regional cooperation. The rise of regionalism is reshaping the global trade landscape.
Technological Innovations
Technological innovations, such as AI, blockchain, and automation, will continue to drive the future of international trade. These technologies improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance transparency. Businesses that embrace technology will gain a competitive edge in the global market.
Shifts in Global Economic Power
Shifts in global economic power, driven by emerging markets and changing trade dynamics, will influence the future of international trade. Countries like China and India are expected to play a more significant role in global commerce, reshaping trade patterns and economic alliances.
Trade Barriers

Image by : Yandex
Trade barriers, such as tariffs, quotas, and regulatory restrictions, hinder the free flow of goods and services. These barriers create market distortions and reduce economic efficiency. Reducing trade barriers is essential for promoting free trade and economic growth.
Economic Protectionism
Economic protectionism, characterized by policies that protect domestic industries from foreign competition, poses a challenge to international trade. Protectionist measures, such as tariffs and subsidies, can lead to trade conflicts and retaliatory actions. Promoting open markets and fair competition is crucial for global trade.
Global Economic Inequality
Global economic inequality remains a significant challenge in international trade. While some countries benefit from trade, others struggle with poverty and underdevelopment. Addressing economic inequality requires inclusive trade policies, capacity-building initiatives, and support for developing countries.
Expanding Markets
Expanding markets present significant opportunities for businesses to grow and diversify their customer base. By exploring new markets, companies can increase sales and reduce dependency on domestic demand. Strategic market research and localization are essential for success in expanding markets.
Technological Integration
Integrating technology into trade operations offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experience. Businesses can leverage technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT to optimize supply chains, streamline transactions, and gain a competitive advantage.
Sustainable Trade Practices
Sustainable trade practices, such as adopting eco-friendly technologies and promoting ethical sourcing, offer opportunities for businesses to contribute to global sustainability. Consumers are increasingly demanding sustainable products, creating a market for businesses that prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
US-China Trade Relations
The trade relationship between the United States and China is one of the most significant in the world. Despite tensions and trade disputes, both countries remain major trading partners. Analyzing US-China trade relations provides insights into the complexities and dynamics of international trade.
The European Union’s Trade Policies
The European Union (EU) is a major player in global trade, with its single market facilitating trade between member countries. The EU’s trade policies, including agreements with external partners, promote economic integration and enhance global trade.
Africa’s Growing Trade Networks

Image by: Yandex
Africa is experiencing significant growth in trade networks, driven by regional integration and infrastructure development. The African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) aims to create a single market for goods and services, boosting intra-African trade and economic growth.
Conclusion
The future of international trade is shaped by technological advancements, geopolitical dynamics, and evolving trade policies. While challenges such as trade barriers and economic inequality persist, opportunities abound in expanding markets, technological integration, and sustainable trade practices. By navigating these complexities and leveraging innovations, businesses can thrive in the global marketplace.
Autos & Vehicles
Best 5 Mahindra Tractors Under 40 HP for Small Farms

Mahindra is one of the leading tractor brands in India, and farmers trust Mahindra tractors for strong performance on their farms. The brand offers a wide range of tractor models across different power segments. Tractors with 40 HP or below are especially popular among Indian farmers, as they are ideal for small and medium-sized farms.
These tractors are suitable for various field operations and can also be used for transportation without any difficulty.
This blog will help you choose the right tractor if you are planning to buy a powerful yet easy-to-handle model. It covers the top 5 Mahindra tractors under 40 HP, along with their prices, to help you make an informed decision.

List of 5 Mahindra Tractors under 40 Hp:
Here is the list of the top 5 Mahindra Tractors under 40 HP that are ideal for Mid-size farmers:
1. Mahindra 275 DI TU
The Mahindra 275 DI TU is a reliable tractor in the under 40 HP segment, well-suited for a wide range of agricultural operations. With its powerful 39 HP engine, it efficiently handles tasks such as ploughing, sowing, inter-cultivation, and haulage.
The tractor is designed to work smoothly with commonly used farm implements, ensuring consistent performance in different field conditions. Its sturdy build quality, fuel efficiency, and easy maintenance make it ideal for daily farm use.
Additionally, Mahindra’s wide service network and easy availability of spare parts provide farmers with long-term reliability and peace of mind.
Mahindra Tractors pricе: Rs. 5.78 lakh – Rs. 5.98 lakh
Engine Powеr: 39 HP
2. Mahindra 265 DI XP Plus
The Mahindra 265 DI XP Plus is a dependable tractor designed for consistent performance in the 40 HP segment. Powered by a 33 HP engine, it offers the right balance of power and efficiency for daily farming operations.
The tractor features smooth steering and a well-matched gearbox that makes handling easy, even during long working hours. It performs efficiently in tasks such as ploughing, cultivation, and haulage across different soil conditions.
With its strong build quality, fuel-efficient engine, and low maintenance needs, the Mahindra 265 DI XP Plus remains a practical choice for farmers seeking reliability and ease of operation.
Mahindra Tractors Pricе: Approximatеly Rs. 5.42 lakh – Rs. 5.57 lakh
Engine Powеr: 33 HP
3. Mahindra JIVO 365 DI
The Mahindra JIVO 365 DI is a compact and versatile tractor, especially suitable for orchard farming and small landholdings. Equipped with a 36 HP engine, it delivers sufficient power for routine agricultural operations as well as light transport work.
Its compact size allows easy movement between narrow rows, making it ideal for vineyards, orchards, and vegetable farms. The lightweight design helps reduce soil compaction, which is important for maintaining soil health and crop productivity.
With good balance, smooth handling, and efficient performance, the Mahindra JIVO 365 DI is a practical choice for farmers working in confined spaces and smaller fields.
Engine Powеr: 36 HP
Mahindra Tractors pricе: About Rs. 5.93 lakh – Rs. 6.17 lakh
4. Mahindra YUVO TECH Plus 405 DI
The Mahindra YUVO TECH Plus 405 DI is a well-balanced tractor that operates close to the 40 HP segment while remaining within the category limit. It offers strong engine performance combined with modern features that support a wide range of farming activities.
This model is suitable for tasks such as ploughing, cultivation, rotavation, and haulage with consistent efficiency. Its good lifting capacity ensures smooth handling of farm implements, while stable performance helps maintain productivity during long working hours. For farmers looking for a reliable tractor with dependable power and practical utility, the YUVO TECH Plus 405 DI stands out as a capable choice.
Engine Powеr: 39 HP
Mahindra Tractors pricе: Around Rs. 6.24 lakh – Rs. 6.34 lakh
5. Mahindra 275 DI XP Plus
The Mahindra 275 DI XP Plus is a tractor with a 37 HP workhorse in the under-40 HP range. It provides sufficient power and comfort features while keeping operating costs manageable.
This tractor is suitable for both field operations and light transportation requirements. Farmers frequently choose this model for regular agricultural use because it provides an excellent balance of strength and dependability.
Engine Powеr: 37 HP.
Mahindra Tractors Prices: Around Rs. 5.68 lakh to Rs. 5.93 lakh
Why Choose Mahindra Tractors Under 40 HP?
Mahindra tractors undеr 40 HP arе a strong choicе for many Indian farmеrs. Thеsе tractors match thе nееds of small and mеdium farms. Thеy work wеll on diffеrеnt crops and soil conditions. Hеrе arе thе main rеasons farmеrs choosе thеm:
- Operate of Tractor
Tractors in this rangе arе simplе to opеratе and controls arе еasy to undеrstand, so that nеw tractor usеrs can lеarn quickly.
- Lowеr Running Costs
Smallеr tractors usе lеss fuеl comparеd to biggеr modеls with low maintenance that hеlps farmеrs savе on daily еxpеnsеs.
- Good for Small and Mеdium Land
For 1–10 acrеs of land, tractors undеr 40 HP arе idеal for managе fiеld work, transport, and implеmеnt usе without troublе.
- Works with Many Implеmеnts
Thеsе tractors support widеly usеd tools such as ploughs, cultivators, sееdеrs, and trailеrs. Farmеrs can attach many implеmеnts without issuеs.
- Stablе Pеrformancе
Evеn with smallеr еnginеs, thеsе modеls providе stеady pеrformancе in tasks likе ploughing, sowing, and hauling. Thеy balancе powеr and fuеl usе wеll.
Conclusion
Choosing the right tractor also involves considering fuel efficiency, maintenance costs, and the availability of service support in your area. Farmers should evaluate the implements they plan to use, such as rotavators, ploughs, or trolleys, to ensure proper compatibility with tractor power and hydraulics.
Comfort features like an adjustable seat, smooth transmission, and easy steering can reduce fatigue during long working hours. In addition, resale value and brand reliability play an important role in long-term ownership.
By comparing Mahindra tractor prices with specifications, performance, and after-sales service, farmers can make a well-informed decision that improves productivity and ensures better returns on investment.
News
Why Does Ghostwriting Shape the Voices We Never See?

Introduction
Most of the powerful memories, political speeches, and thoughtful columns are written by people who never had a chance to present their opinion across, so they write for other people to seize the opportunity, even when they don’t get the credit. This is what ghostwriting is all about; where someone else writes for you, making a powerful yet invisible presence. You might not know that, but some of the best authors have also used a ghostwriting service to complete their ideas in a coherent form.
Just like students take the best thesis editing service to refine and complete their projects, similarly, people from different spheres of life hire ghostwriters to voice their stories in a composed manner. This unseen work decides the career of leaders, celebrities, business icons, and even intellectual influencers. The question is not whether ghostwriting matters; it is how it continues to shape voices we never actually hear.
The Invisible Architects of Words
Ghostwriters are architects of words. They build narratives, organize complex ideas, and shape rough concepts into something that sounds believable to the accredited author or speaker. From politicians to CEOs, everyone takes professional ghostwriting services to capture their audience and persuade them towards their viewpoint.
Ghostwriting is not confined to one field; rather, there is ghostwriting for authors, filmmakers, or even politicians. Ghostwriters become a part of the background while copying another person’s voice and style of speaking. The real job of a ghostwriter is to capture the voice of the public figure without reflecting their voice.
Why People Hire Ghostwriters?
Did you know that 60% of nonfiction books that are produced by public figures involve the assistance of ghostwriters? Why is that so? Well! The reasons people hire ghostwriters are mentioned below:
- Time limitations: Busy professionals, politicians, and celebrities do not have the time to produce polished pieces of writing. Besides, most academic tasks nowadays involve dense research (bestassignmentwriter.uk, 2022) along with timely submission, which makes them go for external support.
- Writing ability: Even though people might be great at their area or field, but they might not be good writers for their experiences to come alive.
- Clarity and conciseness: Ghostwriters ensure the final product is appealing to the targeted readers.
- Marketability: A book or speech does not simply need to be accurate but also captivating enough to be interesting to readers or listeners.
Ghostwriting in Books and Publishing
The world of literature is filled with novels written by ghostwriters. Celebrities, sportsmen, and business leaders have autobiographies that are considered to be the best ones. A large number of them would not have been written if there were no ghostwriters.
A sports star might have an interesting story to share, but in a rough form, which is refined by the ghostwriter while adding depth and emotional factor. The book might sound boring without this support. This is not deception but collaboration, as the public star brings vision, the ghostwriter brings expression.
Publishing companies also like hiring ghostwriters because they understand deadlines will be met and a marketable product will be produced. It is such a delicate balance between creativity and practicality that keeps the business flowing smoothly.
Shaping Public Voices in Politics
Politics is the field in which ghostwriting has the most obvious but hidden part. Speeches that inspire millions of individuals were written with the help of professional writers. Even though not everything is ghostwritten, but the leaders don’t write every word themselves.
Political ghostwriting shapes national history. Whatever your leader says can become a part of history, shape opinions, and result in policy-making. In this case, the ghostwriter’s work is not just verbal; it is also political. They must understand public opinion, cultural references, and political figures.
Ghostwriting in Business and Academia
Outside of speeches and books, ghostwriting also impacts areas in which credibility and authority are most important. In business, papers and company reports are polished or even written as a whole by ghostwriters. Executives do sign them, but there are experts behind the scenes who ensure everything is professional, understandable, and consistent with the brand.
The subject is more controversial in educational institutes. Plagiarism and ghostwriting are undermining the integrity of university degrees to an extent not seen before (Singh & Remenyi, 2016). Some students hire ghostwriters to create their essays or dissertations. Ghostwriting in scholarship involves helping professors write articles, research summaries, or provide applications. In these cases, ghostwriters help place ideas in clearer language that is easily readable by more people.
The Ethical Debate
Ghostwriting is also an issue of honesty and integrity. So, if it is ghostwritten, is it the writing of the original author? Some argue that ghostwriting hides the true source of ideas and gives credit where credit is not deserving.
However, some people have the opinion that ghostwriting is not stealing but cooperation. The idea, insight, and opinion belong to the credited individual; the delivery comes from the ghostwriter.
How Ghostwriting Adds to The Story?
Ghostwriting not only refines but also actually influences the way stories are told. These are some ways it influences voices:
- Tone and readability: Ghostwriters rewrite dense or technical content to produce a conversational tone.
- Consistency: They maintain the style of a public figure consistent in books, speeches, and columns.
- Depth of feeling: Ghostwriters are able to bring out personal observations that are beyond the speaker’s notice or hard for the speaker to put into words.
- Cultural relevance: Professional ghostwriters include allusions, metaphors, and anecdotes that are familiar to today’s audiences. Even though they remain invisible, they still get to shape culture in positive ways by presenting new stories in an engaging manner through a public figure’s eyes.
Conclusion
Ghostwriting is a business that is flourishing despite being unseen. It influences the words we hear, but you are never going to find the ones who write them. Ghostwriters can be said as mind translators who put your ideas into words, then it be political speeches that reshape destiny to memoirs that reach millions. They deliver sense, emotional resonance, and cultural background, which are the main things that allow stories and ideas to cross boundaries. There are many controversies around it as well, as some consider it deception, while others call it collaboration. Their writing speaks for the ones who cannot write and keeps their wisdom from silence.
News
Tylekeo88: Trusted Football Odds and Match Prediction Site Today

Introduction
Football is one of the most popular sports in the world, attracting millions of fans and enthusiasts every day. With the rise of online betting and sports analysis, fans are now looking for trusted platforms that provide accurate match predictions and football odds. One platform that stands out in this space is Tylekeo88. Known for its reliability and detailed insights, Tylekeo88 has become a go-to source for football fans who want to make informed decisions about matches and betting.
Whether you are a casual fan, a professional bettor, or someone who enjoys following football statistics, Tylekeo88 offers a range of tools and predictions that can enhance your viewing experience. This article explores why Tylekeo88 is considered the most trusted football odds and match prediction site today, along with its key features, benefits, and why it is gaining popularity among football enthusiasts.
Tylekeo88: Most Trusted Football Odds and Match Prediction Site Today
1. Accurate Football Odds
One of the main reasons why Tylekeo88 is trusted by fans is its accuracy in providing football odds. The platform uses advanced algorithms and real-time data to calculate probabilities for upcoming matches. These odds help users understand which teams are more likely to win, the chances of draws, and potential goal scores.
Unlike random guesses, Tylekeo88 provides data-backed insights that allow users to make informed decisions. Accurate odds are particularly important for bettors who rely on statistics to guide their wagers. By presenting odds clearly and transparently, the platform builds confidence among its users.
2. Detailed Match Predictions
In addition to odds, Tylekeo88 offers detailed match predictions. These predictions include insights into team performance, recent form, head-to-head statistics, player injuries, and other factors that can affect the outcome of a match.
For example, a prediction might indicate that Team A has a strong home record while Team B struggles away. Such insights help fans understand the dynamics of a match and anticipate possible outcomes. The level of detail provided by Tylekeo88 makes it stand out compared to other football prediction sites that offer only basic forecasts.
3. Real-Time Updates and Live Scores
Tylekeo88 also provides real-time updates and live scores for football matches. Fans can track ongoing games, monitor changes in odds, and stay updated on key events such as goals, penalties, and red cards.
Real-time information is crucial for live betting and for fans who want to follow matches closely. By offering live updates, Tylekeo88 ensures that users have the most current data at their fingertips, allowing them to react quickly and make informed choices during the game.
4. User-Friendly Interface
Another reason for Tylekeo88’s popularity is its user-friendly interface. The website is designed to be easy to navigate, even for beginners. Users can quickly access odds, predictions, statistics, and live scores without confusion.
A clear layout and organized content ensure that users spend less time searching for information and more time analyzing matches. The intuitive design makes Tylekeo88 suitable for both casual fans and professional bettors.
5. Comprehensive Coverage of Leagues and Tournaments
Tylekeo88 covers a wide range of football leagues and tournaments worldwide. Whether it is the English Premier League, La Liga, Serie A, Bundesliga, or international competitions like the FIFA World Cup and UEFA Champions League, the platform provides extensive coverage.
Fans can find predictions and odds for major leagues as well as smaller competitions. This comprehensive coverage ensures that users have access to insights for any match they are interested in, making Tylekeo88 a one-stop solution for football analysis.
6. Expert Analysis and Insights
Beyond statistics, Tylekeo88 offers expert analysis from football professionals. These experts evaluate teams, strategies, and match dynamics to provide valuable commentary. Their insights often highlight factors that raw data might not capture, such as team morale, coaching strategies, and player motivation.
Expert opinions combined with statistical analysis give users a well-rounded perspective. For bettors, this combination of data and expert insight can be a valuable tool in making smarter decisions.
Tips for Using Tylekeo88 Effectively
To get the most out of Tylekeo88, users should:
- Regularly check odds and match predictions before placing bets.
- Combine statistical data with expert insights to make well-rounded decisions.
- Stay updated with live scores for in-game betting opportunities.
- Engage with the community to learn from other users’ experiences.
- Use the educational resources to understand betting concepts and strategies.
Following these tips ensures a better experience on the platform and increases the chances of making informed decisions.
Conclusion
Tylekeo88 has emerged as one of the most trusted football odds and match prediction sites today. Its accuracy, real-time updates, comprehensive coverage, expert insights, and user-friendly interface make it a reliable choice for fans and bettors alike.
Whether you are a casual football enthusiast, a beginner in sports betting, or an experienced bettor, Tylekeo88 provides the tools and information needed to enhance your football experience. From accurate odds to detailed match predictions and live scores, the platform ensures that users stay informed and make smarter decisions.
By combining data, expert analysis, and community interaction, Tylekeo88 has built a reputation for trustworthiness and reliability. For anyone looking to enjoy football with better insights and prediction accuracy, Tylekeo88 is the ultimate platform to explore.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom