Computer Electronic
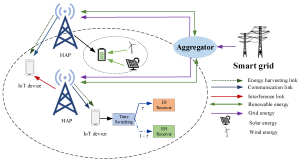
Securing the Future: Unveiling Security and Privacy Challenges in SWIPT-NOMA Networks
Computer Electronic
Streamlining Insurance Operations with Automated Policy Checking

Insurance runs on details. A single missed exclusion, an incorrect limit, or an outdated endorsement can quietly turn into a major issue months—or years—later. As insurance products become more complex and regulatory expectations continue to rise, organizations are under growing pressure to review policies faster without compromising accuracy. That’s where policy checking services are stepping in as a critical support system for insurers, brokers, and MGAs.
Rather than relying solely on manual review, many organizations are rethinking how policies are verified, validated, and monitored throughout their lifecycle.

Understanding the Role of Policy Checking
Before diving into technology, it’s important to clarify what is policy checking in insurance. At its core, policy checking is the process of reviewing insurance documents to ensure coverage terms, conditions, limits, and exclusions align with regulatory requirements, underwriting intent, and client expectations.
This process isn’t limited to initial issuance. Policies are checked during renewals, endorsements, audits, mergers, and claims preparation. The more policies an organization handles, the harder it becomes to maintain consistency through manual effort alone.
Why Manual Policy Reviews Fall Short
Traditional policy reviews depend heavily on human expertise—and while that expertise is valuable, it comes with limitations. Long documents, repetitive checks, and tight deadlines increase the likelihood of oversight. Even experienced reviewers can miss subtle inconsistencies when working at scale.
This is where policy checking automation starts to change the conversation. Automation doesn’t replace judgment; it supports it by handling repetitive validation tasks and highlighting exceptions that truly need attention.
How Automation Is Reshaping Policy Reviews
Modern systems built for automated policy checking for insurance use structured rules and intelligent data extraction to review policies far more quickly than manual methods. Instead of reading every page line by line, reviewers receive flagged insights that guide their focus.
Automation ensures policies are checked consistently, regardless of who is reviewing them or how busy the team is. That consistency alone reduces risk exposure significantly, especially for organizations managing large portfolios.
The Growing Influence of AI
Artificial intelligence has taken automation a step further. With ai insurance policy checking, systems can analyze language patterns, compare clauses across documents, and learn from historical review outcomes.
AI doesn’t just spot missing information—it recognizes context. It understands how specific clauses interact and where deviations might introduce risk. Over time, these systems become smarter, improving accuracy and reducing false positives.
Why Insurers Are Turning to Policy Checking Services
For many organizations, building and maintaining these systems internally isn’t practical. This has led to increased demand for specialized policy checking services that combine technology with insurance expertise.
These services offer flexibility. Whether an organization needs ongoing support or help during peak workloads, external teams can scale quickly without adding permanent overhead. More importantly, they bring standardized processes that reduce variability across reviews.
AI as a Support Tool, Not a Replacement
There’s a misconception that AI-driven tools eliminate the need for skilled reviewers. In reality, ai for policy checking works best when paired with human judgment. AI identifies patterns, flags issues, and accelerates reviews—but experienced professionals still make the final call.
This collaboration is what makes policy checking ai so effective. Reviewers spend less time searching for problems and more time evaluating their real-world impact.
Real-World Use Cases Where Automation Delivers Value
The benefits of automation become most visible in real operational scenarios. Some of the most common insurance policy checking automation use cases include portfolio audits, renewal reviews, compliance assessments, and pre-claim evaluations.
During renewals, for example, automation helps ensure coverage hasn’t drifted from original intent. During audits, it enables teams to review large volumes of policies quickly without cutting corners. These use cases aren’t theoretical—they’re becoming standard practice across the industry.
When Outsourcing Makes Strategic Sense
Not every organization wants to manage tools, rules, and models internally. In such cases, insurance policy checking services provide a practical alternative. These services combine automation with expert oversight, offering accuracy without complexity.
Outsourcing is especially useful during business transitions, rapid growth, or regulatory changes—periods when internal teams are already stretched thin. Instead of slowing down, organizations can maintain review quality and turnaround times.
The Importance of Consistent Policy Checking
Consistency is often overlooked, yet it’s one of the most valuable outcomes of automation and external services. Every policy goes through the same structured checking policy process, reducing subjective interpretation and improving audit readiness.
Over time, this consistency strengthens trust—not just internally, but with regulators and clients as well.
Looking Ahead
As insurance operations continue to modernize, policy checking will no longer be treated as a back-office task. It’s becoming a strategic function tied directly to risk management, compliance, and customer confidence.
Organizations that invest in smarter review processes today are better prepared for tomorrow’s challenges—whether that’s higher policy volumes, stricter regulations, or more complex products.
If you’re looking to strengthen accuracy, reduce risk, and modernize your policy review workflows, Exdion Insurance offers intelligent solutions designed to support scalable, technology-driven policy checking.
Computer Electronic
Transforming Connectivity: Bluetooth Low Energy BLE Technology
The Demand for Energy-Efficient Wireless Solutions
Today’s ecosystem is increasingly filled with battery-operated devices. These range from smartwatches that monitor heart rates to sensors that track temperatures in large warehouses. Even smart locks play a crucial role in securing our homes. In this landscape, users expect their devices to operate efficiently for months or even years. They want minimal need for battery replacements or recharging. This high demand puts tremendous pressure on wireless technology to provide optimal performance while using minimal energy.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) stands out as the preferred standard for these applications. It is specifically designed for low-duty-cycle communication. However, its role has expanded far beyond basic data transfer. Modern BLE devices are now expected to support secure pairing, cloud connectivity, seamless firmware updates, voice control, and compatibility with multiple communication standards. All of this must happen while prioritizing power efficiency.
To meet these demands, ultra-efficient BLE SoCs have made significant strides. They have enhanced the radio frequency (RF) layout, integrated on-chip security features, and optimized power usage. As a result, these SoCs can sustain a long operational life, even in challenging environments.
Characteristics of Ultra-Efficient BLE SoCs
The strength of an ultra-efficient BLE SoC does not rely on a single characteristic. Instead, it arises from a comprehensive optimization strategy. This strategy includes RF design, digital processing, memory management, and software controls. These SoCs employ low-leakage process nodes and advanced RF front ends to minimize power consumption during transmission while ensuring reliable connections.
On the digital side, these SoCs are typically built around low-power microcontroller architectures, often leveraging optimized RISC cores. This structure allows them to execute protocol stacks, implement security measures, and manage power states with exceptional accuracy. Features such as smart clock gating and deep sleep modes ensure that energy is used only when necessary, enabling continuous operation for over 10 hours on small coin-cell batteries or rechargeable batteries.
Multi-Protocol Support in a Connected Ecosystem
One notable advancement in modern BLE SoCs is the integration of native multi-protocol support. Today’s devices seldom work in isolation; they must connect with smart home systems, cloud platforms, mobile applications, and industrial control units. This necessity highlights the importance of interoperability across various standards. These include BLE 5.x, Matter, Thread, Zigbee, and proprietary 2.4 GHz protocols.
Next-generation BLE SoCs can incorporate multiple communication stacks into a single chip. This capability broadens their application across various ecosystems without the need for additional hardware. As a result, it reduces bill-of-material costs, simplifies product design, and accelerates certification processes.
For example, a single SoC may support BLE connections with smartphones while also enabling Thread networking for Matter-based smart home systems. This dynamic protocol switching, achieved with minimal power consumption, is a hallmark of today’s advanced BLE platforms.
Enhanced Security Features
In a world where billions of interconnected devices are common—spanning homes, factories, hospitals, and urban infrastructures—security concerns are critical. High-performance BLE SoCs incorporate hardware-based security engines to protect both data integrity and device identity.
Secure boot mechanisms ensure that only authorized firmware operates on the device. Built-in encryption accelerators prevent wireless communications from being intercepted or tampered with. Additionally, cryptographic credentials are securely stored in hardware key storage. This comprehensive security architecture fosters trust, which is essential for applications like smart door locks, medical devices, and connected industrial sensors, where data privacy is crucial.
Seamless Connectivity Across Applications
Ultra-efficient BLE SoCs enable seamless connections for a wide array of real-world applications. In smart homes, they facilitate the operation of lighting systems, thermostats, climate controls, and voice-activated devices with low latency and high reliability. The power efficiency of these devices means they can run for years on a single battery, significantly reducing maintenance efforts.
In wearables, these SoCs support continuous health monitoring, tracking heart rates and sleep patterns, all while providing all-day battery life within compact form factors. The balance of a robust radio and efficient processing units significantly enhances user experience.
In industrial contexts, BLE SoCs manage assets, predict maintenance needs, surveil equipment, and automate operations. Their ability to maintain constant communications even under high interference conditions makes them ideal for large-scale applications.
Additionally, in retail, advanced BLE SoCs power electronic shelf label (ESL) solutions, allowing retailers to adjust prices of countless items in real-time. This is a prime example of how low power consumption can converge with scalability and multi-protocol networking for a cohesive solution.
Optimizing RF Design for Reliable Performance
Even more advanced BLE SoCs incorporate high-sensitivity RF receivers, linear power amplifiers, and sophisticated filtering methods to ensure reliable operation under challenging conditions. Devices frequently utilize the same 2.4 GHz band as Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, and industrial machinery.
To manage this, BLE SoCs employ techniques such as adaptive frequency hopping, channel mapping, interference detection, and coexistence algorithms. These strategies promote stable connectivity and minimize the need for retransmissions, reducing power consumption and enhancing both data reliability and user satisfaction.
Enabling Large-Scale IoT Growth
The inherent scalability of ultra-efficient BLE SoCs proves invaluable for massive deployments. Whether managing a network of intelligent streetlights or implementing sensor networks within factories, these SoCs offer predictable long-term performance.
For solution providers and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), this translates to fewer maintenance costs, increased device uptime, expedited deployment timelines, and an overall improved total cost of ownership (TCO).
Future-Proofing Through Evolving Protocols
The BLE ecosystem is rapidly evolving. It is adapting to new standards like Matter and Thread while also advancing the capabilities of BLE technology. Through software upgrades and backward compatibility, ultra-efficient SoCs are designed to remain relevant for years. Their flexible architecture helps safeguard OEM investments and accelerates the time-to-market for next-generation devices.
Conclusion
Bluetooth Low Energy SoCs have emerged as a cornerstone of today’s interconnected systems. They facilitate seamless interactions across smart homes, wearables, ESLs, STBs, industrial automation, and IoT frameworks. By blending ultra-low power consumption with secure wireless connectivity, they offer high RF performance and support for multiple protocols.
These platforms are not just connection chips. They are the fundamental building blocks for the intelligent, energy-efficient, and secure devices of tomorrow. As the connected landscape continues to expand, their role will become increasingly critical. They will shape how we interact with technology in our daily lives.
Computer Electronic
Maximizing Business Success with Manpower Recruitment Services

In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations must continuously adapt to changing market demands, skill requirements, and workforce expectations. Whether it is scaling operations, managing seasonal workloads, or entering new markets, having the right talent in place is essential. This is where manpower recruitment services play a pivotal role. These services help businesses identify, attract, and retain skilled professionals while maintaining flexibility, efficiency, and cost control.
Manpower recruitment has transformed from a transactional hiring activity into a strategic function that supports organizational growth, productivity, and long-term sustainability.

The Evolution of Manpower Recruitment
Traditionally, manpower recruitment focused on filling vacant positions as quickly as possible. However, modern recruitment strategies emphasize talent quality, cultural fit, and future readiness. Organizations now require professionals who can adapt to new technologies, processes, and business models.
With rising competition for skilled talent, companies are increasingly partnering with specialized recruitment providers to gain access to wider talent pools and faster hiring solutions.
Why Organizations Choose a Manpower Recruitment Agency
A professional manpower recruitment agency acts as an extension of a company’s HR function. These agencies leverage industry expertise, recruitment technology, and established talent networks to source candidates who align with specific job requirements.
By working with recruitment specialists, businesses reduce hiring time, improve candidate quality, and minimize recruitment risks. This approach is especially beneficial for companies with limited internal recruitment resources or high-volume hiring needs.
The Strategic Role of a Manpower Staffing Agency
A reliable manpower staffing agency offers flexible workforce solutions that adapt to changing business requirements. Staffing agencies provide talent for permanent roles, temporary assignments, and contract-based positions, allowing organizations to maintain agility without long-term commitments.
This flexibility is crucial for industries experiencing fluctuating demand, project-driven work, or rapid expansion. Staffing agencies help organizations remain responsive while optimizing workforce costs.
End-to-End Manpower Staffing Services
Modern manpower staffing services cover the entire employment lifecycle. These services include candidate sourcing, screening, interviewing, background verification, onboarding, payroll management, and compliance handling.
By outsourcing these responsibilities, businesses can focus on core operations and strategic priorities while ensuring a seamless hiring experience for both employers and candidates.
Industry-Focused Recruitment Solutions
Many organizations prefer partnering with a specialized man power staffing agency that understands their industry’s unique workforce challenges. Different sectors such as manufacturing, IT, healthcare, logistics, construction, and retail require distinct skill sets and compliance standards.
Industry-focused staffing partners bring domain expertise that ensures candidates are job-ready, reducing training time and improving overall productivity.
The Value of Manpower Job Placement Consultants
Manpower job placement consultants play a crucial role in bridging the gap between employers and job seekers. Their consultative approach involves understanding candidate skills, career goals, and employer expectations.
By focusing on long-term compatibility rather than short-term placement, placement consultants help organizations build stable teams while supporting candidate career growth.
How Manpower Agencies Enable Workforce Scalability
Professional manpower agencies provide businesses with the ability to scale their workforce efficiently. Whether expanding operations, launching new projects, or managing seasonal demand, agencies offer quick access to qualified talent.
This scalability allows organizations to respond to market changes without the financial and operational burden of permanent hiring.
Integrated Staffing and Recruitment Expertise
A full-service manpower staffing & recruitment agency combines staffing flexibility with strategic recruitment planning. This integrated approach ensures organizations can address immediate hiring needs while building a talent pipeline for future growth.
Such agencies offer workforce analytics, hiring forecasts, and talent insights that support informed decision-making and long-term workforce planning.
Choosing the Right Manpower Provider Company
Selecting the right manpower provider company is critical for achieving hiring success. Businesses should evaluate providers based on industry experience, recruitment capabilities, compliance expertise, and service reliability.
A trusted manpower provider delivers consistent talent quality, transparent processes, and proactive support, becoming a long-term partner rather than just a service vendor.
Benefits of Partnering With Manpower Recruitment Services
Organizations that leverage professional manpower recruitment solutions gain multiple advantages:
- Faster hiring turnaround times
- Access to a wider and pre-screened talent pool
- Reduced recruitment and administrative costs
- Compliance and payroll risk mitigation
- Improved workforce flexibility and scalability
- Enhanced employee retention through better role matching
These benefits help businesses maintain operational stability while pursuing growth opportunities.
Manpower Recruitment in a Competitive Talent Market
As competition for skilled professionals intensifies, companies must adopt smarter hiring strategies. Manpower recruitment services enable organizations to stay ahead by leveraging recruitment expertise, market insights, and scalable hiring models.
By aligning recruitment strategies with business objectives, companies can build resilient teams that drive innovation, efficiency, and long-term success.
Conclusion
In an era where workforce agility and talent quality define business performance, manpower recruitment services have become indispensable. From sourcing skilled professionals to managing complex staffing requirements, these services empower organizations to operate efficiently and adapt to change with confidence.
By partnering with experienced manpower recruitment specialists, businesses can streamline hiring, reduce risks, and focus on growth. If you’re looking for a trusted recruitment partner to support your workforce needs, G&S Consulting offers expert manpower recruitment solutions designed to help organizations succeed in a competitive market.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom