health
Understanding Obesity: Causes, Risks, and Treatment Options

Introduction
Understanding Obesity , a pervasive health issue, demands an in-depth examination encompassing its definition, underlying causes, associated risks, and the spectrum of treatment options available. This extensive exploration aims to provide a nuanced understanding of this multifaceted health concern.
Defining Obesity
1. Body Mass Index (BMI)
- Widespread Metric: BMI, a prevalent measure, designates obesity when exceeding 30. However, limitations exist, especially concerning individuals with high muscle mass.
2. Waist Circumference
- Refining Accuracy: Recognizing the limitations of BMI, waist circumference emerges as a valuable supplementary metric, particularly in individuals with notable muscle mass.

Image by: yandex.com
Risks of Obesity
1. Health Risks
- Myriad Consequences: Obesity is a precursor to severe health issues, including type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, cancer, and stroke.
2. Psychological Impact
- Beyond Physical Health: The repercussions extend to psychological realms, contributing to conditions such as depression and low self-esteem.
Causes of Obesity
1. Caloric Imbalance
- Core Determinant: The fundamental cause is an imbalance between calories consumed and expended, primarily driven by excess calorie intake.
2. Modern Lifestyles
- Sedentary Trends: Modern living, characterized by sedentary habits and the consumption of calorie-dense foods, amplifies the prevalence of obesity.
3. Underlying Health Conditions
- Secondary Contributors: Conditions like an underactive thyroid may contribute, although environmental factors play a substantial role.

Image by: yandex.com
Treating Obesity
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Cornerstone of Treatment: Embracing a balanced, calorie-controlled diet coupled with regular exercise forms the foundation of effective obesity management.
2. Psychological Support
- Behavioral Shifts: Trained healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in addressing behavioral aspects, offering support to reshape attitudes towards food.
3. Medications
- Orlistat Usage: In specific cases, medications like orlistat, mitigating fat absorption, are recommended as adjuncts to lifestyle modifications.
4. Surgery
- Ultimate Intervention: Surgical procedures, such as gastric bypass, are reserved for extreme cases when conventional approaches prove inadequate.
Other Obesity-Related Problems
1. Daily Challenges
- Impact on Daily Life: Obesity manifests in various challenges, including breathlessness, joint pain, and increased fatigue.
2. Serious Health Conditions
- Extensive Health Implications: Obesity elevates the risk of conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and various cancers.
3. Reduced Life Expectancy
- Significant Impact: The collective toll of obesity contributes to a reduced life expectancy, underlining its gravity.
Causes of Obesity in Detail
Poor Diet
1. Gradual Development
- Culmination of Choices: Obesity evolves gradually, influenced by poor dietary choices, especially the consumption of processed and high-calorie foods.
2. Alcohol Consumption
- Caloric Impact: Excessive alcohol intake significantly contributes to overall calorie consumption, contributing to weight gain.
Lack of Physical Activity
1. Modern Lifestyles
- Inactive Routines: Sedentary jobs and reliance on transportation contribute to insufficient physical activity, exacerbating the obesity epidemic.
2. Guidelines
- Activity Recommendations: Adhering to guidelines recommending at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly is crucial.

Image by: yandex.com
Genetics
1. Environmental Factors
- Dominance of Environment: While genetics may play a role, environmental factors and learned behaviors during childhood significantly contribute to obesity.
Medical Reasons
1. Underactive Thyroid
- Metabolic Influence: Conditions like hypothyroidism can affect metabolism, potentially contributing to weight gain.
2. Medications
- Medication-Induced Weight Gain: Certain medications, including corticosteroids and antidepressants, are linked to weight gain.
Diagnosing Obesity
1. BMI Limitations
- Critical Assessment: Acknowledging BMI limitations, especially in muscular individuals, prompts consideration of supplementary metrics like waist circumference.
2. GP Assessment
- Holistic Evaluation: General Practitioner (GP) visits involve a comprehensive assessment, encompassing lifestyle, underlying causes, and potential health risks.
Treating Obesity
1. GP Guidance
- Informed Recommendations: Seeking guidance from a GP is essential for safe weight loss, with an emphasis on a comprehensive approach involving diet, exercise, and support services.
2. Diet Guidelines
- Balanced Nutritional Intake: A healthy diet incorporates a variety of food groups, with attention to calorie intake and limitation of high-salt foods.
3. Exercise Recommendations
- Physical Activity Integration: Engaging in regular physical activity is indispensable for effective weight management, aligning with recommendations for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly.
4. Other Useful Strategies
- Comprehensive Support: Setting realistic goals, involving family and friends, and psychological support contribute synergistically to successful weight loss.

Image by: yandex.com
Avoiding Weight Regain
1. Caloric Needs
- Dynamic Adjustments: As weight decreases, ongoing attention to caloric needs is imperative to prevent weight regain.
2. Physical Activity
- Maintenance Role: Increased physical activity plays a pivotal role in preserving weight loss achievements.
Medication
1. Orlistat
- Prescribed Intervention: Orlistat, a medication reducing fat absorption, is recommended in conjunction with a balanced low-fat diet and lifestyle changes.
2. Side Effects
- Balancing Act: Common side effects, such as fatty stools, urge for bowel movements, and stomach pain, underscore the importance of adherence to a low-fat diet.
Photo by: unsplash.com
Surgery
1. Bariatric Surgery
- Ultimate Measure: Bariatric surgery is considered for severe obesity cases, contingent on specific criteria, including BMI and associated health conditions.
2. NHS Criteria
- Healthcare System Considerations: Bariatric surgery availability on the NHS aligns with specific eligibility criteria, ensuring judicious use of this intervention.
Image by: yandex.com
Treating Obesity in Children
1. Diet and Activity Improvement
- Holistic Approach: Addressing childhood obesity involves improving diet, increasing physical activity, and implementing behavior change strategies.
2. Medical Intervention
- Rare Consideration: Medical intervention, including orlistat use in severe cases, is considered exceptionally, with surgery generally not recommended for children.
3. Family Involvement
- Collaborative Effort: Family and GP involvement is integral to addressing childhood obesity, emphasizing the importance of a collaborative approach.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this comprehensive exploration of obesity unveils the intricate tapestry of factors contributing to its prevalence. By understanding its causes, evaluating associated risks, and embracing multifaceted treatment approaches, we pave the way for effective long-term management, promoting not only weight loss but overall health and well-being.
Care
Embracing Wearable Health Technology for Health Management
From smartwatches to fitness trackers, wearable technology has gained immense popularity. These devices provide insights into your body, enabling you to take preventive measures before minor issues escalate into serious health concerns.

What Are Wearable Health Devices?
Wearable health devices are electronic gadgets that you can wear on your body. Examples include fitness trackers, smartwatches, and specialized health monitors. These devices gather data related to your activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health metrics.
Equipped with advanced sensors, wearable devices track various aspects of your health, such as heart rate, movement, and even blood oxygen levels. The data collected is relayed to your mobile device in an easily digestible format, eliminating the need for extensive medical knowledge to understand your health status.
The Importance of Wearables in Health Monitoring
Wearable health devices play a crucial role in early symptom detection and overall health management. Here’s why they’re essential:
- Daily Monitoring: Unlike traditional check-ups, wearables provide continuous health monitoring. This ongoing observation means you can detect changes in your health before they necessitate a doctor’s visit.
- Encouraging Healthy Habits: Wearables help users establish and maintain healthy routines by providing feedback and motivation.
- Timely Alerts: These devices alert you to potential health concerns as soon as they arise, allowing for immediate action.
- Promoting Physical Activity: Regular reminders and progress tracking motivate users to stay active, contributing to improved health over time.
Much like machines require regular maintenance to function optimally, our bodies also benefit from consistent health monitoring. Wearable devices assist in this ongoing maintenance by keeping track of essential health metrics.
Key Health Metrics Monitored by Wearables
1. Heart Rate and Cardiovascular Health
Wearables monitor your heart rate throughout the day. If your heart rate strays from its normal range, the device will notify you, which is particularly beneficial for those with heart conditions or high-stress jobs. Some advanced devices can even detect irregular heartbeats, serving as an early warning sign for more severe issues.
2. Physical Activity Tracking
Most wearables track metrics such as step count, calories burned, and active minutes throughout the day. Visualizing your daily movement can be a powerful motivator. Small changes in daily activity can lead to significant long-term health benefits.
3. Sleep Quality Assessment
Sleep is often overlooked but is crucial for overall health. Wearables can track total sleep time, deep and light sleep cycles, and interruptions. By analyzing this data, users can tweak their bedtime routines and improve their sleep quality.
4. Stress Monitoring
Some advanced wearables measure stress levels through heart rate variability and breathing patterns. When stress levels rise, these devices often provide guided breathing exercises or suggest short breaks, which can be invaluable for those in demanding work environments.
5. Blood Oxygen and Vital Signs
Many modern wearables also monitor blood oxygen levels and skin temperature. These metrics can offer quick insights into respiratory health, potential infections, or fatigue levels. While they cannot replace traditional medical tests, they can provide important preliminary information.
Benefits of Wearable Technology in Daily Life
Wearables provide more than just raw data. They enhance personal health awareness and understanding, leading to numerous benefits:
- Increased Health Awareness: Users develop a deeper understanding of their health status and trends.
- Motivation to Stay Active: The mere act of tracking physical activity encourages individuals to be more active.
- Early Health Warnings: They can signal potential health issues before they escalate.
- Support for Long-term Health Goals: Wearables help users align their daily habits with their long-term health objectives.
For many who regularly wear these devices, seeing incremental improvements in their health is a huge motivator.
Wearables for Different Demographics
Wearable health technology can benefit people across various age groups and lifestyles:
- Young Adults: Often utilize wearables for fitness tracking and athletic performance.
- Office Workers: Use these devices to monitor physical activity and combat sedentary behavior.
- Older Adults: Frequently wear them to track heart rates and sleep patterns, enhancing health management.
- Patients: Use wearables as part of recovery plans for chronic conditions, facilitating closer monitoring of their health status.
Healthcare providers can also access data from wearables, offering a more comprehensive view of a patient’s habits between check-ups.
Limitations of Wearable Devices
Despite their advantages, wearable devices are not without shortcomings. Some potential drawbacks include:
- Data Accuracy: Wearables may not always provide precise measurements.
- Battery Life: Keeping these devices charged can be an added chore.
- Information Overload: Too much data can lead to anxiety over health concerns that may not require immediate attention.
- Not a Replacement for Doctors: While wearables provide valuable insights, they should supplement—not replace—professional medical advice.
Wearables should be seen as tools that complement your healthcare rather than definitive decision-makers.
The Future of Wearable Health Technology
The advancement of wearable technology is rapid and promising. Future innovations may include:
- Devices with enhanced disease detection capabilities.
- Non-invasive diabetes testers that measure blood sugar levels painlessly.
- Seamless data transfers directly from wearable devices to healthcare providers.
- Tailored health advice based on individual biometrics.
As technology evolves, wearables will become more sophisticated, smaller, and even more integral to everyday health management.
Conclusion
Wearable health devices have revolutionized how we approach health management. Rather than waiting for health issues to arise, individuals can monitor their well-being daily, making informed choices to maintain their health. These devices foster awareness, motivation, and early detection—transforming the way we think about our health.
By integrating wearable technology into daily life, individuals can cultivate a balanced and healthier lifestyle. More than mere gadgets, wearables serve as silent, constant companions on your health journey, guiding every step toward better health.
Business
Root Canal Treatment in Lahore: Expert Care for Your Teeth
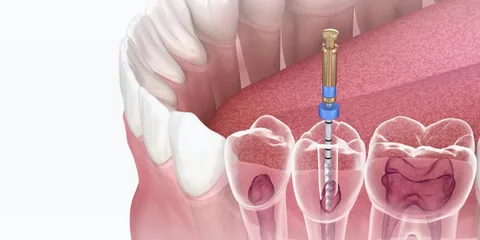
Advanced Root Canal Care in Lahore
Root canal problems are common in Lahore due to delayed dental visits and high sugar intake. Root Canal Treatment in Lahore is not just about pain relief; it is about saving your natural tooth with precision and long-term planning.
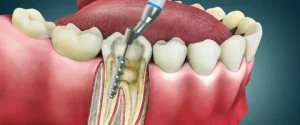
Why Root Canal Treatment Is Often the Best Option
When the tooth pulp becomes infected, extraction is not always the right answer. Saving the natural tooth helps maintain bite balance and jaw health. Root Canal Treatment in Lahore focuses on removing infection while keeping the original tooth structure intact, which is critical for long-term oral stability.
Signs That Indicate You Need a Root Canal
Many patients ignore early symptoms and visit only when pain becomes severe. Based on clinical experience, the most reliable indicators include:
- Deep, lingering tooth pain
- Sensitivity to hot or cold lasting more than 10 seconds
- Swelling near the affected tooth
- Darkening of the tooth
Early diagnosis allows Root Canal Treatment in Lahore to be completed in fewer visits with better outcomes.
Step-by-Step Root Canal Procedure Explained
This treatment is not a guess-based process. Each step is planned carefully to ensure success.
- Digital imaging to locate infected canals
- Local anesthesia for pain-free treatment
- Removal of infected pulp using rotary instruments
- Thorough canal disinfection
- Sealing with a biocompatible material
This structured approach makes Root Canal Treatment in Lahore predictable and safe.
Expertise Built on 23 Years of Dental Practice
Experience matters in endodontic care. Over 23 years, complex root anatomies, retreatment cases, and failed past procedures have been successfully managed. This level of exposure allows better judgment during Root Canal Treatment in Lahore, especially in molars with curved or hidden canals.
Technology That Improves Treatment Success
Modern dentistry is technology-driven. Advanced clinics use:
- Rotary endodontic systems
- Apex locators for accurate canal length
- Digital radiography with minimal radiation
- Magnification tools for precision
These tools significantly increase the success rate of Root Canal Treatment in Lahore.
Pain Management and Patient Comfort
Many patients fear pain due to outdated myths. In reality, the procedure is more comfortable than tooth extraction. Proper anesthesia, gentle techniques, and post-care planning ensure Root Canal Treatment in Lahore is a smooth experience even for anxious patients.
Post-Treatment Care for Long-Term Results
A root canal-treated tooth needs protection to last many years. After the procedure:
- A dental crown is usually recommended
- Oral hygiene must be maintained
- Regular follow-ups help detect early issues
With correct care, Root Canal Treatment in Lahore can preserve a tooth for decades.
Cost Factors and Treatment Planning
Costs vary depending on tooth type and infection severity. Molars require more time and expertise. Transparent consultation ensures patients understand the value behind Root Canal Treatment in Lahore, rather than focusing only on price.
Why Patients Trust Ideal Smile Dentistry
At Ideal Smile Dentistry, treatment decisions are based on clinical evidence, not shortcuts. Patients benefit from ethical diagnosis, advanced tools, and long-term planning rather than temporary fixes. This approach has built trust across Lahore’s dental community.
Why Experience Matters in Root Canal Dentistry
Dentistry is not just technical; it is judgment-based. After 23 years in dental surgery and clinical practice, patterns become clear. Knowing when to treat, retreat, or refer is what ensures patient safety and success. An experienced dentist can quickly assess complex cases, anticipate potential complications, and tailor treatments effectively.
This level of experience cannot be replaced by shortcuts or rushed procedures. Each patient’s unique anatomy and history warrant careful consideration and personalized care, which only comes from years of practicing and refining one’s skills.
Choosing the Right Dental Clinic in Lahore
Patients should look for:
- Experienced dental surgeons
- Modern diagnostic tools
- Clear treatment explanations
- Transparent pricing
- Long-term follow-up care
At Ideal Smile Dentistry, patient trust is built through experience, not marketing promises.
Frequently Asked Questions About Root Canal Treatment in Lahore
Is root canal treatment safe?
Yes, it is a routine and scientifically proven dental procedure with a high success rate.
How many visits are required?
Most cases are completed in one or two visits, depending on infection severity.
Will I need a crown after treatment?
In most cases, yes. A crown protects the treated tooth from fracture.
Can a failed root canal be retreated?
Yes, retreatment is possible and often successful with proper expertise.
Internal Resources for Patients
For related services, patients can explore:
- Tooth pain diagnosis guide
- Dental crowns and caps services
- Emergency dental care in Lahore
These resources help patients understand treatment options beyond Root Canal Treatment in Lahore.
Summary
Root canal treatment saves natural teeth, relieves pain, and restores oral health. With 23 years of surgical experience, advanced tools, and ethical care, patients in Lahore can expect reliable, long-lasting results when the procedure is done correctly.
Care
Natural Headache Relief: The Massage Therapy Solution

Headaches disrupt everything. They break your focus at work. Even ruin your sleep. They strain time with family and friends. Many people immediately choose pain medicine. It feels quick and easy. However, medicine often just masks the pain. It rarely solves the underlying problem. The pain usually returns.
Maybe you want a different solution. You might seek an approach that helps your body heal. Massage therapy is now a powerful option. It specifically targets tight muscles and stress patterns. These issues commonly cause headaches. Correctly applied, massage can reduce your pain naturally.
This guide explains exactly how headache massage works. Learn why it offers a reliable path to long-term relief.

How Massage Reduces Pain Naturally
Massage supports your body’s own healing process. It does not just cover symptoms. Let’s explore the key mechanisms.
First, it releases muscle tension.
Tight neck and shoulder muscles often trigger pain. Desk jobs and phone use strain these areas. This tension presses directly on nerves. Then, pain signals shoot to your head. Massage applies steady, deliberate pressure. It loosens these specific muscles. Reduced tension decreases nerve pressure. You will feel less stiffness. Fewer pain signals will fire. Regular sessions keep muscles relaxed longer. This directly prevents many headaches from starting.
Next, it improves blood circulation.
Tight muscles restrict healthy blood flow. Your head and neck then get less oxygen. Poor circulation can intensify headache pain. Massage gently manipulates soft tissue. This action encourages better blood flow. Improved circulation helps tissues heal and recover. Many people feel immediate warmth and ease in their neck afterward. Better blood flow can lower both the intensity and duration of headaches over time.
Additionally, it calms your nervous system.
Stress is a major headache trigger. It keeps your body in a tense “fight or flight” state. Your breathing becomes shallow. Muscles tighten unconsciously. This buildup often explodes into a headache. Massage triggers your relaxation response. It shifts your nervous system into a “rest and digest” state. Your muscles unwind. Your breathing deepens. This breaks the stress-pain cycle. You gain a tool to manage tension before it becomes a headache.
Also, it corrects posture problems
Your posture directly impacts headaches. Forward head posture (like looking at a screen) strains your neck muscles. This strain builds slowly but surely. It creates perfect conditions for chronic pain. Massage targets these overworked postural muscles. It releases the tight areas that pull your skeleton out of line. As your posture improves, mechanical strain on your neck decreases. This leads to fewer headaches and more daily comfort.
Critically, it offers sustainable relief
Medicine has its place for acute crises. However, long-term reliance poses problems. These include side effects and medication-overuse headaches. Massage provides a different, sustainable path. It builds body awareness and supports natural function. You can use it regularly without negative consequences. Many people combine it with stretching and stress management. This creates a holistic, proactive routine.
What to Expect from a Session
A professional headache massage is highly targeted. It is not a general relaxation session. First, your therapist will ask detailed questions. They will want to understand your pain patterns, daily activities, and medical history. This assessment guides their hands-on work.
The treatment typically focuses on your upper body. Key areas include your suboccipital muscles (skull base), neck, shoulders, and upper back. Therapists use specific techniques like myofascial release and trigger point therapy. They apply precise pressure to release muscle “knots” and tight fascia. The pressure is firm but should not cause sharp pain. Communication with your therapist is essential. Always tell them if the pressure is too much.
A session usually lasts between 30 to 60 minutes. Afterwards, you might feel deeply relaxed. Some mild soreness is possible, similar to post-exercise feeling. This normally fades within a day. Drink plenty of water. This helps flush metabolic waste released from your muscles.
Building a Long-Term Strategy
For chronic headaches, consistency matters. One massage might offer temporary relief. A series of sessions creates lasting change. It retrains tense muscles and resets poor posture. Many people start with weekly sessions. They then move to bi-weekly or monthly maintenance.
Your therapist can also give you tools for home. They may teach you simple neck stretches or self-massage techniques. They might advise on desk ergonomics or stress-reduction practices. This empowers you to take control between appointments.
Making the Choice for Your Health
Headaches can control your life, but you have options. If your pain stems from tension, stress, or posture, massage addresses these roots directly. It is a practical, drug-free method to reduce pain frequency and severity.
Choose a qualified professional. Look for a licensed massage therapist experienced in clinical or therapeutic work. Be clear about your headache history and goals.
Commit to a plan. Partner with your therapist. Give the process a few sessions to work. Combine hands-on care with the lifestyle changes they recommend.
Ultimately, this approach is about more than pain relief. It is about reclaiming your focus, your sleep, and your daily joy. It is an investment in a life with fewer interruptions and more comfort. Take the step toward lasting relief. Your body—and your calm, clear head—will thank you.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom































