Technology
Navigating Zero-Trust: The Rise of Generative AI in Cybersecurity

Navigating Zero-Trust: The Rise of Generative AI in Cybersecurity
Understanding Zero-Trust
Zero Trust is a contemporary security strategy that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It is based on the assumption that threats can originate from both inside and outside the network. This approach necessitates that all users, regardless of whether they are inside or outside an organization’s network, be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated for security configuration and posture before being granted or maintaining access to applications and data.
The Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new data based on existing data. It has a broad range of applications, including data retrieval and analysis, content generation, and summarization. In the realm of cybersecurity, generative AI can assist threat hunters with data retrieval for ongoing investigations and provide real-time insights that inform vulnerability management workflows.
Generative AI in Cybersecurity
The potential for generative AI to impact the cybersecurity space is immense. A generative AI model trained on vast amounts of historical cybersecurity data could identify patterns and trends, resulting in the ability to predict future threats. This allows cybersecurity professionals to anticipate threats before they materialize, maximizing the value of their existing security tools.
Zero-Trust and Generative AI: A Powerful Combination
When combined, Zero Trust and Generative AI offer a robust solution to modern cybersecurity challenges. Generative AI enhances the Zero Trust model by providing a deeper understanding of potential threats, enabling more effective authentication and authorization processes.

Image by https://contrank.com/
Comparative Table: Traditional vs. AI-Enhanced Cybersecurity
| Traditional Cybersecurity | AI-Enhanced Cybersecurity | |
|---|---|---|
| Threat Detection | Reactive: Responds to threats as they occur | Proactive: Anticipates threats before they materialize |
| Data Analysis | Manual: Requires human intervention for data analysis | Automated: Uses AI for data retrieval and analysis |
| Threat Response | Slower: Time-consuming manual threat response | Faster: AI enables rapid response to threats |
The advent of Generative AI and its integration with the Zero Trust model marks a significant milestone in the evolution of cybersecurity. This combination offers a robust solution to the complex challenges posed by the digital age, where threats are increasingly sophisticated and unpredictable.
Generative AI, with its ability to generate new data from existing data, brings a proactive approach to threat detection. It allows cybersecurity professionals to anticipate threats before they materialize, thereby maximizing the value of their existing security tools. This is a significant shift from the traditional reactive approach, which responds to threats as they occur.
The Zero Trust model, on the other hand, enhances security by operating on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” It assumes that threats can originate from both inside and outside the network, requiring all users to be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated for security configuration and posture.
When combined, these two powerful tools offer a comprehensive solution to modern cybersecurity challenges. Generative AI enhances the Zero Trust model by providing a deeper understanding of potential threats, enabling more effective authentication and authorization processes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the integration of Generative AI into the Zero Trust model not only represents a significant advancement in cybersecurity but also offers a promising solution to the complex cybersecurity challenges of the digital age. As we continue to navigate the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, the combination of Generative AI and Zero Trust will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of cybersecurity. It’s an exciting time to be part of this rapidly evolving field, and we look forward to seeing how these advancements will transform cybersecurity in the years to come.
Technology
Smart Home Technology Trends: Exploring the Latest Innovations
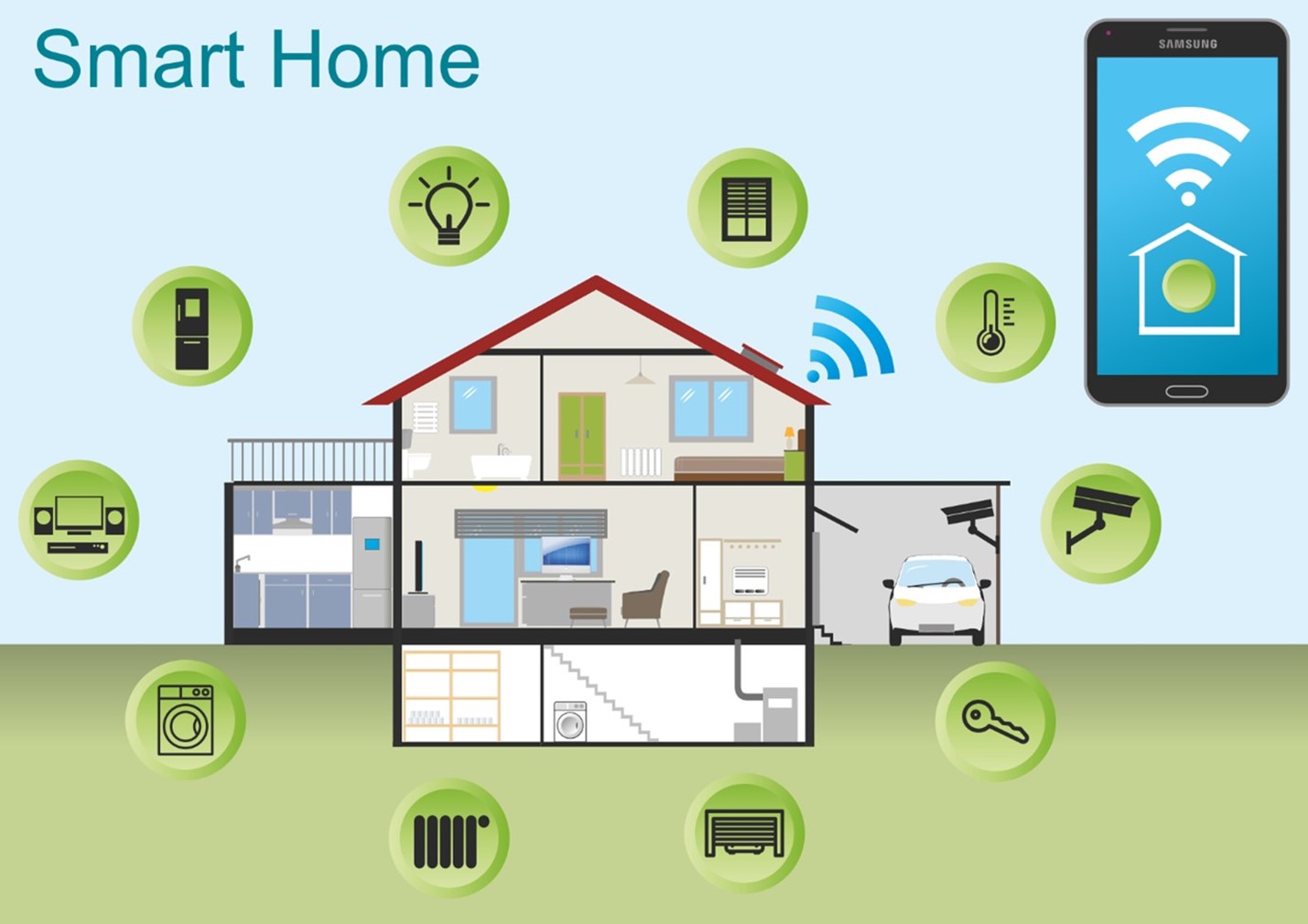
Introduction: The Author’s Perspective
As a tech aficionado with a passion for innovative home solutions, I’ve been fascinated by the evolution of smart home technology. This article dives into the latest trends and advancements that are reshaping how we live, interact, and experience our homes.
Understanding Smart Home Technology

Image by : Yandex
Smart home technology encompasses devices and systems that enhance convenience, security, and efficiency through automation and connectivity, transforming traditional living spaces into intelligent environments.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence
Exploring how AI-driven platforms and smart assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri enhance functionality, learning user preferences, and optimizing home management tasks.
Advancements in Voice Control Systems
Discussing the evolution of voice-activated controls for lighting, HVAC systems, entertainment devices, and appliances, offering hands-free convenience and accessibility.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability

Image by : Yandex
Highlighting smart technologies that monitor energy consumption, optimize heating and cooling systems, manage water usage, and promote eco-friendly practices within smart homes.
Enhanced Home Security Solutions
Image by : Yandex.com 2
Examining IoT-enabled security cameras, smart locks, doorbell cameras, and monitoring systems that enhance home security through real-time alerts, remote access, and integration with mobile devices.
Smart Appliances and IoT Integration

Image by : Yandex
Illustrating the integration of IoT in household appliances such as refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, and robotic vacuums, offering remote control and automated functionalities for enhanced efficiency.
Customization and Personalization
Showcasing how smart home technologies allow users to customize settings, schedules, and preferences tailored to individual lifestyles, enhancing comfort and usability.
Future Prospects and Emerging Technologies
Speculating on future trends such as augmented reality (AR) in home design, blockchain for secure IoT transactions, 5G connectivity for faster data transmission, and the potential for autonomous home management systems.
Conclusion
As smart home technology continues to advance, its integration into everyday life promises unprecedented levels of convenience, efficiency, and security. By embracing these trends and innovations, homeowners can transform their living spaces into connected ecosystems that adapt to their needs and preferences seamlessly.
Technology
Mastering Neural Networks in Machine Learning: Techniques and Applications

Introduction: The Author’s Perspective
As a seasoned data scientist specializing in machine learning and neural networks, I’ve witnessed firsthand their transformative impact on various industries. In this article, I aim to delve into the intricacies of neural networks, equipping you with the knowledge to harness their power effectively.
Headings:
- Understanding Neural Networks
- Types of Neural Networks
- Key Components of Neural Networks
- Training Neural Networks
- Advanced Techniques and Architectures
- Applications of Neural Networks
- Challenges and Considerations
- Future Trends in Neural Networks
Understanding Neural Networks

Image by : Yandex
Neural networks are a fundamental concept in machine learning inspired by the human brain’s structure and functioning. They enable computers to learn from data and perform tasks like classification, regression, and pattern recognition.
Types of Neural Networks
| Type | Description |
| Feedforward Neural Networks | Basic structure where information flows in one direction, useful for simple tasks. |
| Convolutional Neural Networks | Specialized for processing grid-like data, commonly used in image and video recognition. |
| Recurrent Neural Networks | Designed for sequence data, maintaining a state that allows them to remember past inputs. |
| Generative Adversarial Networks | Pairs of networks contesting with each other, often used for generating new content. |
Key Components of Neural Networks
Neurons, layers (input, hidden, output), weights, biases, activation functions (ReLU, sigmoid), and loss functions (cross-entropy, MSE) are crucial components that determine a neural network’s functionality and performance.
Training Neural Networks
Explaining the process of training neural networks using backpropagation, gradient descent, and techniques like regularization and dropout to improve generalization and prevent overfitting.
Advanced Techniques and Architectures
Discussing advanced architectures like deep neural networks (DNNs), recurrent neural networks (RNNs) with LSTM and GRU cells, attention mechanisms, and transfer learning for leveraging pre-trained models.
Applications of Neural Networks
Illustrating how neural networks are applied across various domains, including healthcare (diagnosis), finance (fraud detection), natural language processing (translation), and autonomous vehicles (image recognition).
Challenges and Considerations
Addressing challenges such as data scarcity, interpretability, computational resources, and ethical concerns surrounding AI and neural network applications.
Future Trends in Neural Networks
Exploring emerging trends such as explainable AI, neural architecture search, federated learning, and the integration of neural networks with other AI techniques for more robust and efficient solutions.
Conclusion
Neural networks continue to revolutionize machine learning by enabling sophisticated analysis and decision-making from complex data. Understanding their fundamentals, applications, and future directions is essential for any data scientist or AI enthusiast looking to stay ahead in this rapidly evolving field.
Technology
Blockchain technology Applications Beyond Bitcoin

Introduction:
As a blockchain enthusiast and advocate for decentralized technologies, I’ve witnessed the transformative potential of blockchain beyond its association with Bitcoin. This article explores various applications of blockchain technology, highlighting its versatility and impact across industries such as supply chain management, healthcare, finance, and more.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
Define blockchain technology and its underlying principles. Explain how blockchain consists of decentralized and immutable ledgers, secured through cryptographic hashing, that enable transparent and secure transactions without intermediaries.
Supply Chain Management
Examine blockchain‘s role in supply chain management. Discuss how blockchain enhances transparency, traceability, and efficiency by enabling real-time tracking of goods, reducing fraud, and ensuring compliance throughout the supply chain.
Smart Contracts and Automation
Explore the concept of smart contracts powered by blockchain. Highlight how smart contracts facilitate automated and self-executing agreements, enabling parties to transact securely and transparently without relying on intermediaries.
Healthcare Records and Data Security
Analyze blockchain applications in healthcare. Discuss how blockchain ensures secure and interoperable health records, facilitates patient data management, and enhances privacy through decentralized storage and access control.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Discuss the emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) powered by blockchain. Highlight how blockchain enables peer-to-peer lending, decentralized exchanges, liquidity pools, and automated financial services without traditional intermediaries.
Digital Identity Verification
Examine blockchain’s role in digital identity verification. Discuss how blockchain-based identity systems provide secure and verifiable digital identities, reducing identity theft and enabling seamless authentication across platforms.
Intellectual Property Rights
Explore blockchain applications in intellectual property rights. Discuss how blockchain can timestamp and authenticate digital creations, track ownership, and manage rights through smart contracts, enhancing copyright protection and royalties distribution.
Voting Systems and Governance
Discuss blockchain’s potential in enhancing voting systems and governance. Highlight how blockchain ensures transparency, tamper-proof voting records, and secure elections, fostering trust and participation in democratic processes.
Environmental and Social Impact
Address blockchain’s impact on environmental and social issues. Discuss initiatives like blockchain-based carbon credits, supply chain transparency for ethical sourcing, and charitable donations tracking, promoting sustainability and social responsibility.
Challenges and Considerations
Address the challenges and considerations associated with blockchain technology. Discuss scalability issues, regulatory frameworks, energy consumption concerns in proof-of-work systems, and the need for interoperability and standardization.
Informative Table: Key Blockchain Applications
| Application | Description | Examples |
| Supply Chain Management | Enhancing transparency and traceability | Food safety, luxury goods authentication |
| Smart Contracts | Automated, self-executing agreements | Real estate transactions, insurance claims |
| Healthcare Records | Secure and interoperable patient data | Electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Peer-to-peer lending, decentralized exchanges | Decentralized lending platforms, yield farming |
| Digital Identity Verification | Secure and verifiable digital identities | Self-sovereign identity, KYC processes |
Comparative Table: Traditional vs. Blockchain-based Systems
| Aspect | Traditional Systems | Blockchain-based Systems |
| Data Security | Centralized data storage | Decentralized, immutable ledger |
| Transaction Speed | Manual processing and settlement | Near-instantaneous transactions |
| Transparency | Limited transparency and auditability | Transparent, verifiable transactions |
| Trust | Intermediaries and third-party verification | Trustless, consensus-based verification |
| Compliance | Compliance through intermediaries | Automated compliance through smart contracts |
Conclusion: Embracing Blockchain’s Potential
Blockchain technology is poised to revolutionize multiple industries beyond its origins in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. From supply chain transparency and smart contracts to decentralized finance and secure healthcare records, blockchain offers innovative solutions to complex challenges.
As businesses and governments explore blockchain’s capabilities, addressing challenges and leveraging its benefits will pave the way for a more transparent, efficient, and inclusive future. Embracing blockchain’s potential today will shape tomorrow’s decentralized and interconnected world.
-
Business1 year ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business1 year ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business1 year ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business11 months ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health1 year ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports1 year ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment1 year ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance1 year ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom






























