Technology Explained
How Social Media Is Changing the News Industry

In the digital age, the news industry is undergoing a seismic shift, largely driven by the rise of social media. Platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok have not only changed how news is consumed but also how it is produced and disseminated. This article delves into the multifaceted impact of social media on the news industry, exploring both the opportunities and challenges it presents.
Democratization of News
One of the most significant impacts of social media on the news industry is the democratization of news. Traditional news outlets like newspapers, television, and radio were once the gatekeepers of information. Today, social media platforms have leveled the playing field, allowing anyone with internet access to share news and information. This democratization has led to a more diverse array of voices and perspectives, making the news landscape more inclusive.
Citizen Journalism
The rise of citizen journalism is a direct consequence of social media’s influence. Ordinary people can now report on events as they happen, often providing real-time updates and firsthand accounts that traditional media outlets may not have immediate access to. This has been particularly evident during crises and significant events, such as natural disasters, protests, and political upheavals. Citizen journalists can sometimes offer a raw, unfiltered view of events, adding a layer of authenticity to news reporting.
Speed and Accessibility
Social media has dramatically increased the speed at which news is disseminated. Breaking news can spread like wildfire, reaching millions of people within minutes. This immediacy is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it allows people to stay informed about current events almost instantaneously. On the other hand, the rush to share information quickly can sometimes lead to the spread of misinformation.
Real-Time Updates
Platforms like Twitter have become go-to sources for real-time updates. News organizations and journalists use these platforms to provide live coverage of events, offering minute-by-minute updates that keep the public informed. This has changed the expectations of news consumers, who now demand instant access to information.
Accessibility
Social media has also made news more accessible to a global audience. People from different parts of the world can access news from various sources, breaking down geographical barriers. This global accessibility has fostered a more interconnected world, where people are more aware of international events and issues.
Challenges and Ethical Concerns
While social media has brought numerous benefits to the news industry, it also presents several challenges and ethical concerns. The rapid dissemination of information can sometimes lead to the spread of fake news and misinformation. The lack of editorial oversight on social media platforms means that false information can spread unchecked, potentially causing harm.
Misinformation and Fake News
The spread of misinformation is one of the most pressing issues facing the news industry today. Social media platforms are rife with false information, ranging from harmless rumors to dangerous conspiracy theories. The challenge for news organizations is to debunk misinformation while maintaining credibility. This has led to an increased focus on fact-checking and the development of tools and algorithms to identify and flag false information.
Echo Chambers
Another concern is the creation of echo chambers, where people are exposed only to information that aligns with their existing beliefs. Social media algorithms often prioritize content that users are likely to engage with, which can lead to the reinforcement of existing biases and the polarization of public opinion. This has significant implications for the news industry, as it becomes more challenging to present balanced and unbiased reporting.
The Role of Algorithms
Algorithms play a crucial role in determining what news content users see on social media. These algorithms are designed to maximize engagement, often prioritizing sensational or emotionally charged content. While this can increase user engagement, it can also skew the news landscape, making it more difficult for important but less sensational stories to gain traction.
Personalization
On the positive side, algorithms allow for personalized news feeds, tailoring content to individual preferences and interests. This can enhance the user experience by providing relevant and engaging content. However, the downside is that it can contribute to the aforementioned echo chambers, limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints.
The Business Model
The traditional business model of the news industry has been upended by social media. Advertising revenue, once the lifeblood of newspapers and television networks, has shifted to social media platforms. This has forced news organizations to adapt, exploring new revenue streams such as subscriptions, memberships, and sponsored content.
Monetization Strategies
Many news organizations have turned to paywalls and subscription models to generate revenue. While this can provide a steady income stream, it also limits access to information, potentially widening the gap between those who can afford to pay for news and those who cannot. Sponsored content and native advertising have also become more prevalent, blurring the lines between editorial content and advertising.
Collaboration and Partnerships
In response to these challenges, some news organizations are forming partnerships with social media platforms. These collaborations can provide financial support and increased visibility, but they also raise questions about editorial independence and the influence of tech companies on the news industry.
The Future of News
As social media continues to evolve, so too will its impact on the news industry. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and augmented reality are likely to further transform how news is produced and consumed. AI-powered news bots, for example, can generate news articles and provide real-time updates, while augmented reality can offer immersive news experiences.
Adaptation and Innovation
The key to navigating this ever-changing landscape is adaptation and innovation. News organizations must be agile, embracing new technologies and exploring innovative ways to engage with audiences. This may involve experimenting with new formats, such as podcasts, video content, and interactive storytelling.
Trust and Credibility
In an era of misinformation and fake news, trust and credibility are more important than ever. News organizations must prioritize transparency, accuracy, and ethical journalism to maintain the trust of their audiences. This may involve greater collaboration with fact-checking organizations and increased efforts to educate the public about media literacy.
Conclusion
Social media has undoubtedly transformed the news industry, bringing both opportunities and challenges. It has democratized news, increased speed and accessibility, and forced news organizations to rethink their business models. However, it has also given rise to misinformation, echo chambers, and ethical concerns. As the news industry continues to evolve, the key to success will be adaptation, innovation, and a steadfast commitment to trust and credibility. By navigating these complexities, the news industry can harness the power of social media to inform, engage, and empower audiences around the world.
Technology
AI-Integrated Zillow Clone App Development
Digital Development
Boldify for Facebook: Quick Bold Text in Seconds

Scroll through Facebook for just five minutes and you’ll notice something: most posts look exactly the same. Plain text blends into the feed, making it easy for users to scroll past without noticing important messages. In a crowded social media environment, visual formatting plays a major role in grabbing attention and increasing engagement. This is where Boldify, a powerful bold text generator, makes a difference. Instead of struggling with plain, unformatted posts, Boldify allows you to create eye-catching Facebook bold text instantly. In this article, you’ll learn why bold text matters, how Boldify works, and how you can use it to stand out on Facebook within seconds.
Why Bold Text Matters on Facebook (User Engagement Psychology)
Facebook is a fast-moving platform. Users scroll quickly, often stopping only when something visually stands out. Bold text works because it creates contrast. When certain words appear heavier or more prominent, the brain processes them faster.
Here’s why bold text improves engagement:
- It grabs attention in crowded feeds.
- It improves readability and scan ability.
- It highlights key messages instantly.
Bold formatting is especially powerful in:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Facebook groups
If you’re building a brand or growing a personal profile, bold text strengthens your identity. It emphasizes important announcements, promotions, or calls to action, making your message harder to ignore.
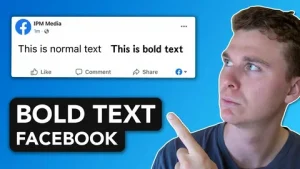
The Challenge: Facebook Doesn’t Offer Built-In Bold Formatting
One of the biggest frustrations for users is that Facebook does not provide built-in bold formatting for regular posts. Unlike word processors, you cannot simply select text and click “Bold.”
That’s why many people search for:
- how to bold text on Facebook
- Facebook bold text generator
- bold letters for Facebook
Without a proper tool, users are left copying complicated codes or trying ineffective formatting tricks. This creates a clear need for a reliable and easy-to-use bold font generator.
What Is Boldify?
Boldify is an online bold text generator designed to help users create stylish bold letters instantly. Instead of modifying Facebook’s formatting, Boldify uses Unicode-based bold fonts that are fully compatible with social media platforms.
Here’s what makes Boldify simple and powerful:
- No installation required
- Works directly in your browser
- Free and instant access
- Compatible with Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and WhatsApp
Because it uses special Unicode characters, the bold text appears naturally once pasted into Facebook posts, comments, bios, or Messenger chats. This makes Boldify a practical and beginner-friendly solution for anyone looking to create bold text online.
How Boldify Helps You Create Bold Facebook Text in Seconds
Using Boldify is straightforward and requires no technical knowledge. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Enter Your Text
Open Boldify and type your message into the input box. This could be a status update, promotional message, announcement, or bio line.
Example:
New Blog Post Live
Limited Time Offer
Join Our Community Today
Step 2: Automatic Bold Conversion
As soon as you enter your text, Boldify automatically converts it into multiple bold font styles. Within seconds, you’ll see several variations generated instantly.
Step 3: Copy and Paste to Facebook
Choose the bold style you like, click the copy button, and paste it directly into:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Messenger chats
That’s it. In just a few seconds, your plain text becomes visually powerful Facebook bold text.
Key Features That Make Boldify Stand Out
There are many tools online, but Boldify offers specific advantages that make it reliable and user-friendly.
1. One-Click Copy Feature
No need to manually select text. Just click and copy instantly.
2. Multiple Bold Style Variations
Get access to different bold styles to match your tone and branding.
3. Mobile-Friendly Interface
Boldify works smoothly on smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
4. No Login Required
You don’t need to create an account. Just open and start using.
5. Fast Performance
Text conversion happens instantly without delays.
6. Clean and Simple Design
The interface is distraction-free, making it easy for beginners to use.
These features make Boldify more than just a basic bold letters generator—it becomes a practical social media enhancement tool.
Practical Ways to Use Bold Text on Facebook
Now that you know how to generate bold text, let’s explore practical ways to use it effectively.
Highlight Important Announcements
SALE TODAY ONLY
Registration Closes Tonight
Bold formatting ensures these messages get noticed quickly.
Strengthen Call-to-Actions
Instead of writing:
Join us now
Write:
JOIN US NOW
It creates urgency and clarity.
Emphasize Keywords in Posts
Highlight important parts of your message to guide the reader’s attention.
Improve Facebook Bios
Use bold text to make your profession, tagline, or brand name stand out.
Stand Out in Facebook Groups
When commenting in large groups, bold text increases visibility and improves response rates.
SEO & Branding Benefits of Using Bold Text
While bold text doesn’t directly change Facebook’s algorithm, it improves how users interact with your content.
Here’s how it benefits branding and visibility:
- Improves readability
- Encourages longer post engagement
- Strengthens personal or business branding
- Creates structured content hierarchy
- Makes posts look professional
When your content looks organized and visually appealing, users are more likely to stop scrolling and engage.
Tips for Using Bold Text Effectively
Bold text is powerful—but only when used strategically.
- Don’t overuse bold formatting.
- Highlight only key phrases or calls-to-action.
- Combine bold text with emojis carefully.
- Maintain readability and spacing.
Too much bold text can reduce its impact. The goal is to enhance clarity, not overwhelm the reader.
Conclusion
Standing out on Facebook is no longer optional—it’s necessary. Since Facebook doesn’t offer built-in bold formatting for posts, tools like Boldify provide a fast and effective solution.
Consumer Services
Right Software Development Partner in India for Your 2026 Startup

Starting a startup in 2026 feels exciting, but also confusing. You have an idea, maybe even a small team, yet one big question always appears first: who will build your product? Most founders are not programmers. They need reliable custom software development services to turn their idea into a real app, website, or platform.
India has become one of the most trusted places for startups to build software. Why? Because you get skilled engineers, global experience, and affordable pricing in one place. From fintech apps in Dubai to healthcare software used in Europe and the US, many young companies rely on Indian development partners.
In this article, we will understand how startups should choose a development partner and explore ten reliable Indian companies that provide custom software development services suitable for early-stage businesses.
How to Choose the Right Development Partner
Before hiring any company, a founder should understand what they actually need. A startup does not require a huge corporate vendor. It needs guidance and flexibility.
Here is a simple decision checklist-
- Do they build MVPs for startups or only big enterprise projects?
- Do they help with product planning or just coding?
- Do they offer cloud setup on AWS or Google Cloud?
- Can they explain technical ideas in simple English?
- Do they support your product after launch?
A good provider of custom software development services acts like a technical cofounder. They tell you what features to delay, how to save cost, and how to launch faster. For example, many fintech startups first build only login, wallet, and payment features. They add analytics later. This approach saves both time and money.

Top 10 Software Development Companies in India for Startups
Below are ten reliable companies suitable for startup founders. Each offers custom software development and flexible engagement.
1. AppSquadz
AppSquadz focuses on startup MVP development and scalable digital products. They provide mobile app development, SaaS platforms, cloud solutions, and custom software development services based on business needs. Many education and healthcare startups choose them for UI/UX guidance and post-launch support.
2. Konstant Infosolutions
Known for mobile applications, especially ecommerce and booking apps. Startups launching marketplace platforms often use their affordable software development services. They have experience with payment integrations and real time chat systems.
3. TatvaSoft
This custom application development company works with startups building web platforms and dashboards. They are strong in NET and React technologies. Several SaaS products serving the logistics industry were built by their teams.
4. PixelCrayons
Popular among international founders from the UK and Dubai. They offer dedicated developer hiring. Many early stage companies choose them when they need quick product development without hiring an internal team.
5. OpenXcell
A good option for AI and blockchain based startups. If your idea includes automation, chatbots, or analytics tools, they provide custom software development services with consulting support.
6. Radixweb
This firm helps startups scale after launch. Suppose your app suddenly gets 50000 users. They help migrate it to AWS and optimize performance. That makes them useful for growing SaaS businesses.
7. MindInventory
Strong in UI and UX design. Many founders do not realize how important user experience is. This company focuses on making apps easy to use, which improves customer retention.
8. Hidden Brains
A long established custom software development provider that works with fintech and healthcare software projects. They also build ERP systems for startups entering manufacturing.
9. Net Solutions
Useful for ecommerce startups. They have experience with Shopify and headless commerce platforms. Many D2C brands launching online stores work with them.
10. SPEC INDIA
They focus on data driven platforms and analytics dashboards. Startups handling large customer data sets or reporting tools benefit from their expertise.
Why Startups Prefer India in 2026
A few years ago startups hired freelancers. Today they prefer a custom application development company. The reason is simple: startups now build complex products. Think about apps using AI, payment gateways, cloud storage, and real time chat. One freelancer cannot manage everything. India offers three big advantages:
First, cost. A startup in the United States may spend $120000 to build an MVP. In India the same project can often be done for $15000 to $30000 using affordable software development services.
Second, cloud knowledge. Many Indian teams work daily with AWS and Google Cloud. They know how to make scalable systems. This means your app will not crash when 100 users become 10000 users.
Third, startup understanding. Indian companies now follow agile methods. They release small updates weekly instead of waiting six months.
You might ask: Is cheaper always lower quality? No. Many Indian developers build SaaS products used worldwide. Cost is lower mainly because operating expenses are lower, not because skill is lower.
Conclusion
Choosing the right development partner in 2026 is not just a technical decision — it’s a strategic one. For early-stage startups, the company you hire will directly influence your product quality, launch speed, scalability, and even investor confidence.
India continues to be a preferred destination because it offers a strong balance of cost efficiency, technical expertise, and startup-focused execution. However, the real advantage does not come from geography alone , it comes from selecting a partner who understands MVP thinking, agile development, cloud scalability, and long-term product growth.
FAQs
1. Why do startups prefer hiring Indian software development companies?
Startups prefer Indian companies because they offer a strong balance of cost efficiency, technical expertise, and scalable development practices. Many firms in India have global experience working with startups from the US, Europe, and the Middle East, making them comfortable with international standards and agile workflows.
2. How much does it cost to build an MVP in India?
The cost of building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) in India typically ranges between $15,000 and $30,000, depending on complexity, features, and technology stack. More advanced platforms involving AI, fintech integrations, or complex dashboards may cost more.
3. How long does it take to develop a startup MVP?
Most startup MVPs take 8 to 16 weeks to develop. Simple apps with limited features can launch faster, while SaaS platforms or fintech products may require additional time for backend development, security setup, and testing.
4. Should startups hire freelancers or a development company?
Freelancers may work for very small projects, but modern startup products often require backend development, UI/UX design, cloud setup, testing, and ongoing support. A development company provides a structured team, project management, and long-term maintenance — reducing risk for early-stage founders.
5. What should startups look for before signing a development contract?
Before signing, startups should check:
- Portfolio of similar startup projects
- Clear pricing structure
- Post-launch support policy
- Ownership of source code
- Experience with cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business3 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom