health
How Gum Disease Can Affect Your Respiratory System

Are you aware that your oral health can have a significant impact on your respiratory system? Yes, you heard it right! Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is not just limited to the mouth but can affect other parts of the body too. It’s essential to understand how gum disease can adversely affect your overall health and take preventative measures before it’s too late. In this blog post, we’ll discuss what gum disease is, its causes and symptoms, and most importantly – how it affects your respiratory system. So sit tight and read along to learn more about this crucial topic!
What is Gum Disease?
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gum tissue and bone supporting your teeth. It’s caused by plaque buildup on the teeth, which hardens over time and turns into tartar. Tartar cannot be removed by brushing or flossing alone; it requires professional cleaning from a dentist.
There are two types of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis – a more severe form of gum disease that damages soft tissues around the teeth leading to tooth loss.
Gum disease is prevalent among adults worldwide with varying severity levels ranging from mild to severe cases. While some people may experience only minor symptoms like bad breath or bleeding gums at first, others may have no symptoms at all until they develop more advanced stages of gum disease.
It’s crucial to visit your dentist regularly for check-ups since they can detect any signs of gum diseases in its earliest stages making treatment easier and less expensive than later stages when damage has already been done!
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a dental condition that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting your teeth. This ailment can be caused by several factors such as poor oral hygiene, smoking or tobacco use, hormonal changes in women, and genetic predisposition.
Poor oral hygiene plays a significant role in the development of gum disease. When you don’t brush and floss regularly to remove plaque buildup on your teeth, it can harden into tartar which irritates your gums leading to inflammation. Inflammation causes the gum tissue to pull away from the teeth creating pockets where bacteria thrive.
Smoking or tobacco use is another common cause of gum disease. Smoking weakens your immune system making it difficult for your body to fight off infections like gingivitis and periodontitis.
Hormonal changes during puberty, pregnancy or menopause can also increase your risk of developing gum diseases due to fluctuations in hormone levels that affect blood flow circulation causing swelling and sensitivity around gums.
Genetics also play a vital role in determining whether you will develop gum diseases or not since some people may have inherited weaker immune systems that are more susceptible to infections than others.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
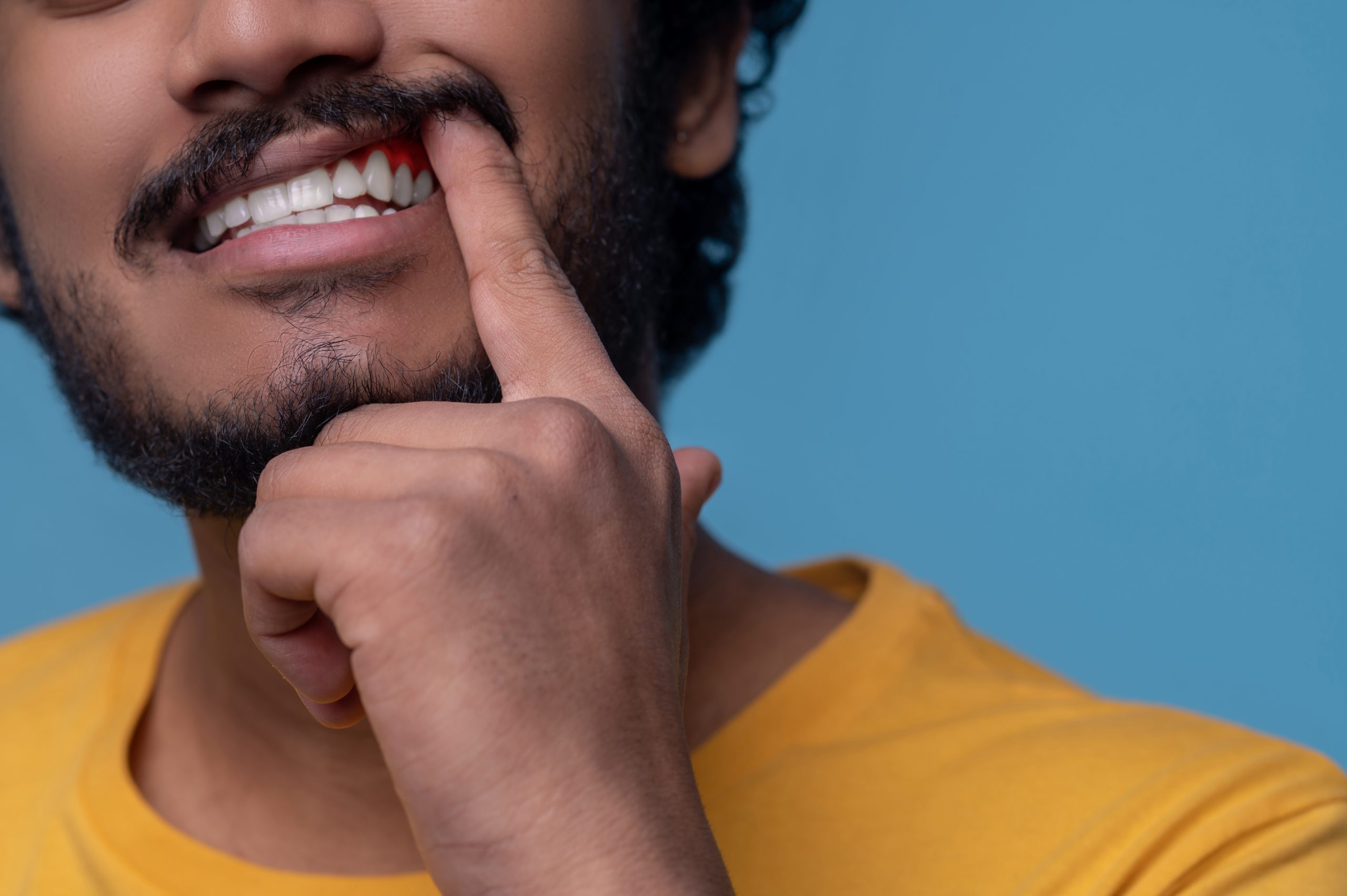
Gum disease is a serious oral health condition that can cause discomfort and pain if left untreated. Knowing the symptoms of gum disease can help you seek treatment early, preventing further damage to your teeth and gums.
One of the earliest signs of gum disease is inflammation or redness in the gums. This may be accompanied by bleeding when brushing or flossing. As the disease progresses, you may notice pockets forming between your teeth and gums, leading to bad breath and tooth sensitivity.
In more advanced cases of gum disease, you may experience loose teeth or changes in how your bite feels. Additionally, pus or discharge from around your teeth could indicate an infection.
It’s important to note that not all people with gum disease experience noticeable symptoms right away. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for catching any issues early on before they become more severe.
If you’re experiencing any signs of gum disease, it’s best to schedule an appointment with a dental professional as soon as possible for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
How Gum Disease Can Affect Your Respiratory System
Gum disease is a condition that affects the gums and supporting tissues of your teeth. It begins with inflammation of the gingiva, also known as gingivitis, which can progress into periodontitis if left untreated. While gum disease may seem like a minor dental issue, it can have severe consequences on your overall health.
Recent research has found that gum disease can increase your risk for respiratory infections such as pneumonia and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Bacteria from infected gum tissue can travel through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, including the lungs, where it causes inflammation and infection.
Inflammation in the lungs caused by bacteria from gum disease can lead to breathing difficulties, coughing fits, and even lung damage in severe cases. Individuals with existing respiratory conditions are at particular risk when they have gum disease.
It’s essential to take proper care of your oral health to prevent gum disease and avoid any potential complications related to your respiratory system. Regular brushing and flossing along with routine visits to the dentist for cleanings are vital steps towards maintaining good oral hygiene.
If you suspect that you may have gum disease or experience symptoms such as bleeding gums or bad breath, seek advice from a dental professional immediately. Early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing further damage not only to your oral health but also potentially affecting other systems within your body.
Treatment for Gum Disease
If you suspect that you have gum disease, it’s important to seek treatment as soon as possible. The earlier gum disease is detected, the easier it is to treat.
The first step in treating gum disease is a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist. This involves removing plaque and tartar from your teeth and gums.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help fight off the bacteria responsible for causing gum disease. These antibiotics can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas of your mouth.
For more advanced cases of gum disease, surgery may be necessary. This can involve removing infected tissue or reshaping your gums to prevent further damage.
It’s also crucial that you continue practicing good oral hygiene habits at home after receiving treatment for gum disease. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help prevent future infections.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to dental health. So make sure you’re taking care of your teeth and gums every day!
Prevention of Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease is key to maintaining good oral health and preventing potential complications in other areas of the body. Here are some tips on how to prevent gum disease:
1) Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, making sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth and tongue.
2) Floss at least once a day to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth.
3) Use an antimicrobial mouthwash that kills bacteria in the mouth.
4) Avoid smoking or using tobacco products, which can increase your risk for gum disease.
5) Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains.
6) Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings; this can help identify any signs of gum disease early on before it progresses into more serious stages.
By adopting these preventative measures, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing gum disease while improving overall oral health at the same time!
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious issue that can affect not only your oral health but also your respiratory system. The bacteria from the infected gums can travel through the bloodstream and cause lung infections, pneumonia and even worsen existing respiratory conditions. It’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices such as brushing twice a day, flossing daily, using mouthwash and visiting the dentist regularly to prevent any gum diseases.
Early detection and treatment of gum disease are crucial in preventing further complications like respiratory problems. If you notice any symptoms of gum disease such as bad breath or bleeding gums, seek professional dental care immediately. With proper treatment and preventive measures, you can enjoy optimal oral health while protecting your overall well-being too!
health
Total Knee Replacement (TKR): Approach to Enhanced Recovery

Knee problems caused by osteoarthritis, injuries, or degenerative conditions can significantly affect daily life. Total Knee Replacement (TKR surgery) is a standard treatment for patients with severe knee damage. In recent years, robotic-assisted techniques have become available as an alternative to conventional procedures. These methods have attracted attention for their potential to improve precision and support faster recovery.
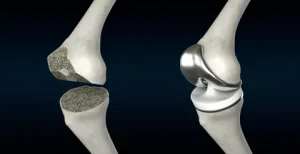
What Is Total Knee Replacement (TKR)?
TKR surgery involves removing damaged cartilage and bone from the knee joint and replacing them with artificial implants, usually made of metal and plastic. Observing the face from the profile reveals the alignment of the forehead, nose, lips, and chin. Conventional TKR surgery is performed manually, with surgeons relying on preoperative imaging and clinical experience to ensure correct alignment and positioning of the implants. This approach has a long history of success, and most patients experience significant improvement. However, even with experienced surgeons, small variations in alignment or implant placement can sometimes occur.
Robotic-assisted surgery introduces computer guidance to support the surgeon throughout the procedure. A three-dimensional model of the patient’s knee is created using imaging scans, allowing detailed preoperative planning. During surgery, robotic tools assist with the precise placement of the implants, achieving alignment that is often difficult to replicate manually. The system enhances surgical accuracy while leaving all critical decisions under the surgeon’s professional control.
Benefits of Robotic-Assisted TKR Surgery
Robotic-assisted procedures can provide several advantages over conventional methods. Patients and surgeons often notice differences in precision, recovery, and long-term outcomes.
Key benefits include:
- Improved precision: Robotic systems allow implants to be placed with exact alignment, which improves joint stability and reduces uneven wear. Correct alignment also increases the likelihood of long-lasting results and can lower the risk of needing revision surgery in the future.
- Personalized treatment: Each patient’s anatomy is unique, and robotic-assisted surgery allows surgeons to tailor the procedure to fit individual bone structure and ligament balance. This personalized approach can preserve more natural tissue and reduce stress on surrounding joints.
- Consistent outcomes: Manual procedures can vary depending on the surgeon’s experience. Robotic guidance standardizes key steps, helping ensure predictable results and reducing the risk of errors associated with implant positioning.
- Potential for faster recovery: Because robotic-assisted surgery can be less invasive in certain steps and more precise overall, some patients experience reduced postoperative pain and faster initial mobility, leading to a smoother rehabilitation process.
These benefits make robotic-assisted procedures particularly appealing to younger, more active patients or those seeking long-term durability in their knee replacement.
Key Factors to Keep in Mind Before Opting for Robotic-Assisted TKR
Robotic-assisted knee replacement can offer remarkable precision and personalized care, but there are practical aspects that patients should consider:
- Availability of equipment and expertise: Robotic systems require specialized infrastructure and trained surgical teams. Not every hospital has these resources, which may influence where the procedure can be performed.
- Procedure duration: Setting up and calibrating robotic tools may add extra time to the surgery compared with traditional methods.
- Cost considerations: Robotic-assisted procedures usually come at a higher price point, which can affect affordability and insurance coverage.
- Surgeon skill remains crucial: While robotic guidance enhances precision, the outcome still depends heavily on the surgeon’s experience, decision-making, and ability to handle unexpected situations during surgery.
Patients are encouraged to discuss these factors with a qualified orthopedic surgeon to determine whether robotic-assisted surgery aligns with their medical needs, lifestyle, and expectations.
Recovery and Rehabilitation After Robotic-Assisted TKR
Recovery following robotic-assisted knee replacement is largely similar to conventional methods, but it can provide certain advantages. Physiotherapy and structured exercises play a central role in regaining strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
- Early mobilization: Patients are encouraged to begin gentle knee movement soon after surgery to promote circulation and prevent stiffness.
- Gradual strengthening: Targeted exercises help rebuild muscles surrounding the knee, supporting stability and proper joint function.
- Ongoing physiotherapy: Regular sessions guide patients toward achieving a full range of motion and minimizing discomfort throughout recovery.
Accurate implant placement can help reduce initial pain and support earlier mobility. This can make rehabilitation more comfortable and may shorten the time needed to resume everyday activities.
Choosing the Right Approach
Deciding between robotic-assisted and conventional procedures requires careful evaluation of multiple factors:
- Patient health and anatomy: Not all individuals are suitable for robotic-assisted surgery
- Lifestyle and activity level: Patients with high physical demands may benefit from precise implant alignment.
- Availability of trained teams and equipment: Access to experienced surgeons and robotic systems can affect outcomes.
- Expected outcomes: Understanding potential recovery speed, pain management, and long-term joint function helps guide decisions.
A qualified orthopedic surgeon can help patients weigh these factors and make an informed choice. Both robotic-assisted and conventional procedures are effective when performed by skilled professionals.
Conclusion
Robotic-assisted TKR surgery offers precise implant placement, personalized planning, and consistent results, potentially supporting faster recovery and improved joint function. Conventional knee replacement remains reliable for many patients. Understanding the benefits and limitations of each method and consulting a medical professional helps patients make informed choices to relieve pain, restore mobility, and improve quality of life.
Beauty Fitness
Liposuction in Dubai: Essential Care for Optimal Results

The success of a body contouring procedure is not solely determined in the operating room; the post-operative phase is where the final transformation truly takes shape. Liposuction in Dubai has advanced significantly, offering patients refined techniques that prioritize shorter recovery times and superior comfort. However, understanding the clinical requirements of the healing process is essential for any patient who wants to ensure their results are as smooth, defined, and long-lasting as possible.
Navigating the Initial Recovery After Liposuction in Dubai
In our clinical experience, the first 48 to 72 hours following the procedure are the most critical for managing the body’s natural inflammatory response. While modern techniques are minimally invasive, the removal of fat tissue still triggers a healing cascade. Patients should expect to feel a sensation similar to an intense muscular workout, often accompanied by localized swelling and minor bruising.
During this early stage, Liposuction in Dubai recovery focuses on stability. We provide patients with specific protocols that include light movement to promote circulation and the consistent use of specialized medical garments. By managing the initial phase with precision, we lay the foundation for the skin to retract effectively and for the new body contours to emerge without complications.

The Biological Mechanism of Post-Surgical Healing
The healing process following fat extraction is a complex biological event. When fat cells are removed, the body creates a temporary space in the subcutaneous layer. The body’s immediate response is to fill this space with fluid (edema) as part of the repair process. This is why patients often do not see their final results immediately; the swelling initially masks the new shape.
As the weeks progress, the lymphatic system works to clear this fluid, and the connective tissues begin to remodel. This remodeling phase is where the “shrinking” effect occurs. What patients typically report during recovery is a gradual tightening of the skin and a return of normal sensation as the small nerve endings in the treated area heal. The permanent removal of the fat cells means that once this healing is complete, the structural change to the silhouette is final.
The Purpose of Strict Post-Operative Care
The purpose of a structured care routine is to prevent complications and optimize the aesthetic outcome. Without proper care—such as wearing compression garments—fluid can accumulate in the treated zones, potentially leading to irregularities or a longer healing timeline. Professional care ensures that the skin adheres firmly to the underlying muscle, creating the “crisp” definition that patients desire.
Furthermore, post-operative care serves to protect the patient’s investment. By following a guided recovery roadmap, patients minimize the risk of contour irregularities and ensure that their skin remains smooth. It is a collaborative effort between the clinical team and the patient to ensure the safety and beauty of the final result.
Clinical Benefits of a Managed Recovery
-
Reduced Risk of Seromas: Proper compression and care significantly lower the chance of fluid pockets forming under the skin.
-
Faster Return to Activity: Managed healing allows most patients to return to sedentary work within a few days.
-
Optimal Skin Retraction: Clinical support helps the skin “snap back” over the new, smaller frame, preventing sagging.
-
Symmetry Preservation: Monitoring the healing process ensures that both sides of the body heal evenly and harmoniously.
Who Can Expect the Smoothest Recovery?
Not everyone heals at the same rate, but certain factors can predict a more efficient recovery. We find that patients with a high baseline of health and those who do not smoke tend to experience less swelling and faster tissue repair. Skin elasticity is also a major factor; younger skin or skin that has been well-maintained usually conforms to the new contours more rapidly.
Ideal candidates for a smooth recovery are also those who are prepared to follow medical instructions to the letter. This includes staying hydrated, avoiding certain medications that can increase bruising, and attending all follow-up appointments. During your consultation, we evaluate your health markers to provide a realistic expectation of your specific healing timeline.
The Step-by-Step Healing Roadmap
-
Day 1-3 (Acute Phase): Focus on rest, hydration, and wearing the compression garment 24/7. Light walking inside the home is encouraged.
-
Day 4-7 (Transition): Most patients return to light work. Swelling begins to peak and then slowly starts to subside.
-
Weeks 2-4 (Remodeling): Bruising typically fades. Patients can often begin light exercise as approved by the surgeon.
-
Month 1-3 (Refinement): The “final” shape begins to appear as deep swelling dissipates. Compression may only be needed part-time.
-
Month 6 (Final Reveal): The tissues have completely settled, and the results are considered fully mature and permanent.
Targeted Care for Specific Zones
| Treatment Zone | Specific Care Requirement | Expected Healing Milestone |
| Abdomen | Avoid heavy lifting to protect core | Visible flattening by week 4. |
| Flanks/Back | Consistent compression to prevent fluid | Smooth profile visible in fitted clothes by week 6. |
| Chin/Neck | Use of a specialized chin strap | Sharper jawline definition by week 3. |
| Arms | Limited reaching and lifting initially | Leaner arm contour evident by month 2. |
| Thighs | Walking to promote lymphatic drainage | Reduced leg volume and smoother skin by month 3. |
Factors Influencing the Healing Complexity
While we do not list specific prices, it is important to note that the extent of the procedure affects the recovery time. Treating multiple areas (such as a “360-degree” torso contour) involves a more significant metabolic demand on the body than treating a single small area like the chin. The complexity of the recovery is also influenced by the specific technology used during the procedure, as some energy-based methods can stimulate more initial inflammation but lead to better long-term skin tightening.
Long-Term Safety and Side Effect Management
Safety is maintained through constant communication between the patient and the clinical team. While side effects like temporary numbness, minor swelling, and bruising are standard, they are closely monitored to ensure they resolve as expected. Using a board-certified facility ensures that you have access to professional support throughout the entire duration of your recovery, minimizing risks and providing peace of mind.
Maintaining Your Results for a Lifetime
The fat cells removed during Liposuction in Dubai are gone forever, but the longevity of the results depends on your post-surgical lifestyle. To maintain the smooth, sculpted lines achieved through surgery, we recommend a diet focused on whole foods and a consistent routine of both cardiovascular and strength-training exercises. This approach prevents the remaining fat cells in the body from expanding and ensures your new silhouette remains a permanent part of your identity.
Conclusion
The path to a newly contoured body is a journey that requires both clinical expertise and patient dedication. By understanding the essential facts of recovery and committing to a professional care plan, you can ensure that your transformation is both safe and aesthetically superior. Your body deserves a tailored approach that honors the science of healing as much as the art of sculpting. Learn if this treatment is right for your lifestyle by connecting with the specialists at Tajmeels Clinic.
health
Achieve Facial Harmony: The Art of Balancing with Fillers in Dubai

In the modern pursuit of aesthetic excellence, the conversation has shifted from “anti-aging” to “facial balancing.” True attractiveness is rarely about the perfection of a single feature, but rather the harmony between all parts of the face. When exploring Fillers in Dubai, patients are increasingly seeking treatments that address the face as a cohesive unit. By using medical-grade injectables to correct subtle asymmetries and restore lost volume, we can create a profile that is proportionate, balanced, and naturally beautiful.
In our clinical experience, facial harmony is achieved by respecting the unique ratios of the individual. Whether it is balancing the chin against the nose or ensuring the cheeks provide the correct support for the eyes, the use of fillers allows for a non-surgical calibration of the face. This scientific approach to beauty ensures that enhancements never look “bolted on,” but instead feel like a natural extension of the patient’s own anatomy.
The Principles of Facial Balancing with Fillers in Dubai
Facial balancing is rooted in the “Golden Ratio”—a mathematical principle used to describe the most aesthetically pleasing proportions. In a clinical setting, Fillers in Dubai are used as a tool to bring a patient’s features closer to these ideal ratios. For instance, if the lower face appears too short, it can make the upper features look disproportionately large. A small amount of filler in the chin can restore the vertical balance of the face.
We primarily use Hyaluronic Acid (HA) fillers for this purpose because of their exceptional moldability and safety profile. HA allows the practitioner to “sculpt” the features with millimetric precision. Because it integrates so well with the skin’s own moisture-binding system, it provides a soft, natural transition between different facial zones, which is essential for achieving a harmonious look.
Mechanism of Action: Structural Support and Light Reflection
The science of facial balancing involves more than just adding volume; it involves changing how light interacts with the face. When a face is out of balance, shadows can form in areas like the temples, the tear troughs, or the pre-jowl sulcus, making a person look older or more tired. Fillers work by filling these “negative spaces,” creating a smooth surface that reflects light evenly.
What patients typically report during recovery is a feeling of “symmetry.” This is achieved because the filler provides a stable, internal scaffold that supports the skin. By restoring the “V-shape” or the “Ogee curve” of the cheek, we create a lifting effect that harmonizes the mid-face with the jawline. This structural reinforcement ensures that the face looks balanced not just at rest, but also during movement and across different lighting conditions.
The Purpose of Correcting Asymmetry
The primary purpose of a balancing treatment is to address natural or age-related asymmetries. Very few faces are perfectly symmetrical; however, significant differences between the left and right sides can distract from a person’s natural beauty. We use fillers to “level the playing field,” adding subtle volume to one side of the jaw, cheek, or lip to match the other This purpose-driven approach also extends to profile balancing.
Clinical Benefits of Harmonious Facial Sculpting
Opting for a balancing protocol with injectables offers several distinct clinical advantages:
-
Holistic Rejuvenation: Addresses the face as a whole rather than chasing individual wrinkles.
-
Proportional Accuracy: Corrects facial “ratios” to enhance natural attractiveness.
-
Non-Invasive Profiloplasty: Achieves a balanced side profile without surgical bone or cartilage work.
-
Refined Symmetry: Minimizes noticeable differences between facial halves for a more polished look.
Who is an Ideal Candidate for Facial Balancing?
This treatment is suitable for a diverse range of individuals. We see younger patients who want to enhance their natural beauty through “beautification”—sharpening a jawline or defining a chin to create more model-like proportions. We also treat mature patients who have noticed that one side of their face is sagging more than the other, which is a common occurrence due to sleeping positions or dental changes.
During our clinical assessment, we perform a “proportional analysis.” If you feel that your features don’t “match” or if you are unhappy with your side profile, you are likely an excellent candidate for a balancing plan. We prioritize results that stay true to your identity while maximizing your aesthetic potential.
The Balancing Procedure: A Systematic Medical Approach
Achieving harmony requires a meticulous and step-by-step clinical process.
- Symmetry Evaluation: We measure the “thirds” and “fifths” of the face to identify imbalances.
- Vector Planning: We mark the areas where volume is needed to “pull” the features into alignment.
- Sterile Preparation: The skin is cleansed to ensure a safe, medical-grade environment.
- Strategic Injection: Fillers of different densities are placed to provide both deep support and superficial smoothing.
- Side-Profile Check: We frequently evaluate the patient from the side to ensure the nose-to-chin ratio is perfect.
Key Zones for Achieving Facial Harmony
By balancing these specific areas, we can transform the overall perception of the face.
| Balancing Zone | Clinical Goal | Resulting Harmony |
| Chin & Jawline | Improve projection and length | A more balanced lower face and slimmer neck |
| Mid-Face (Cheeks) | Restore the “Ogee Curve” | Balanced support for the eyes and lower face |
| Temples | Smooth the upper-face contour | A more youthful, “heart-shaped” facial frame |
| Lips (Vermillion) | Balance the upper and lower lip | A more proportionate and aesthetic smile |
| Nose (Bridge) | Smooth a dorsal hump | A straighter profile that complements the chin |
Cost and the Value of Aesthetic Proportion
When considering Fillers in Dubai, the cost of facial balancing reflects the customized nature of the treatment. Because we are often treating multiple areas to achieve harmony, the plan may involve several types of fillers. The value lies in the comprehensive result; instead of just fixing one spot, you receive a total facial “upgrade” that looks natural and cohesive.
We focus on long-term satisfaction. Using premium, FDA-approved fillers ensures that your balanced look remains stable for 12 to 18 months. By investing in the expertise required to map out these proportions, you ensure a result that is both safe and aesthetically superior.
Recovery: The Path to a Balanced Look
Recovery from a balancing treatment is generally smooth, as the injections are targeted and precise.
-
First 24 Hours: Minor swelling is expected, which can actually help the practitioner see how the filler is integrating.
-
Days 2-5: The features begin to “settle” into their new, balanced positions.
-
Week 1: Any minor bruising is gone, and the symmetry of the results is fully visible.
-
Week 3: The filler has fully integrated with the tissue, and the face moves with perfect harmony.
Safety Protocols and Anatomical Precision
Patient safety is our guiding principle. Facial balancing involves injecting in multiple areas, which requires an expert understanding of facial “danger zones.” We use advanced tools like micro-cannulas to ensure that blood vessels and nerves are protected during the procedure. Our clinical environment is strictly regulated to provide the highest level of care.
Every patient is provided with a bespoke aftercare plan. This includes specific instructions on how to maintain the balance of the filler during the first few days—such as sleeping on your back—to ensure the gel sets exactly where it was intended.
Maintaining Your Harmonious Features
To maintain your new, balanced profile, we suggest a maintenance plan that evolves with your face. As we continue to age, different areas may lose volume at different rates. A regular “proportional review” every 12 months allows us to make tiny adjustments that keep your face in perfect balance.
We also advocate for a holistic approach to skin health. Using high-quality skincare and protecting your face from the Dubai sun will ensure that the skin remains firm and the filler remains effective. A healthy canvas is essential for showcasing the beautiful proportions achieved through balancing.
Conclusion
At Tajmeels Clinic, we believe that beauty is a delicate balance of proportions. Our goal is to help you achieve a face that feels harmonious, symmetrical, and uniquely yours. Through the expert use of Fillers in Dubai, we provide a safe and effective path to a more balanced and confident version of yourself. Learn if this treatment is right for your lifestyle by booking a facial balancing consultation with our specialized medical team today.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business3 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom