health
Florida’s Leprosy Challenge: Scientists Discover Endemic Cases
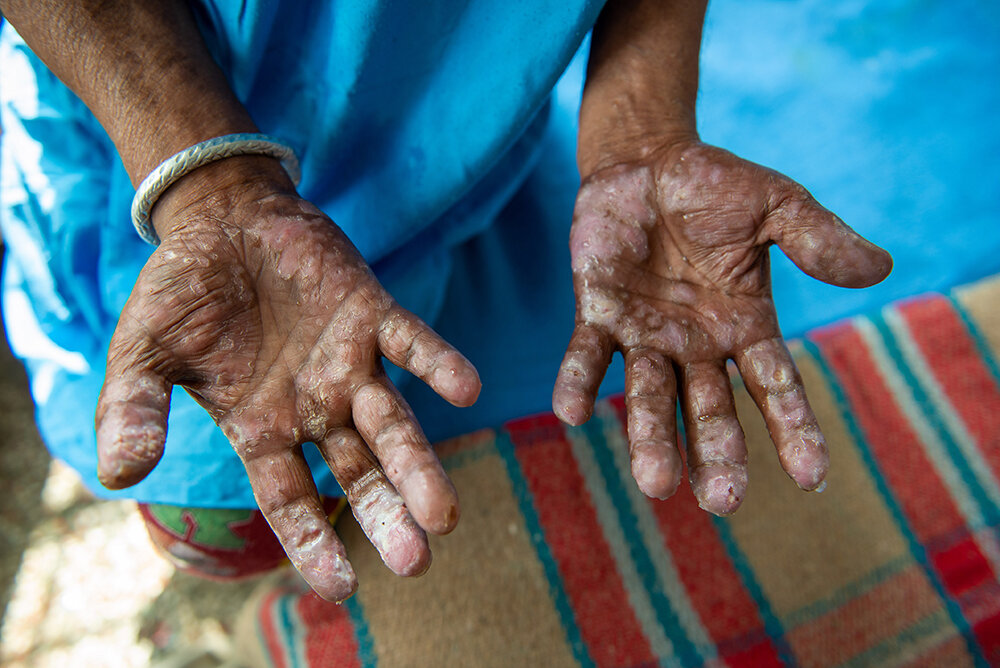

Introduction: Unraveling Florida’s Leprosy Challenge
In recent times, Florida has faced a growing leprosy challenge, raising concerns among scientists and healthcare professionals. In this article, we delve into the discovery of endemic leprosy cases in the state and the implications it poses for public health and society.
1. The Leprosy Outbreak: Tracing the Origins
Trace the origins of the leprosy outbreak in Florida. Understand how this once rare disease is now becoming more prevalent and the factors contributing to its spread.
2. Endemic Leprosy Cases: Uncovering the Extent
Scientists have been working to uncover the extent of endemic leprosy cases in Florida. Explore the data and statistics that shed light on the geographic distribution and demographics of those affected.
3. Diagnostic Challenges: Detecting Leprosy Early
Early detection is crucial for managing leprosy and preventing its transmission. Discover the challenges faced by healthcare professionals in diagnosing the disease and the efforts to improve diagnostic capabilities.

Image by: https://www.newvision.co.ug/category/health/constant-danger-life-after-leprosy-a-long-neg-152634
4. Socioeconomic Impacts: Addressing Stigma and Discrimination
Leprosy carries a historical stigma, and its resurgence in Florida raises concerns about discrimination and social challenges faced by those affected. Learn about the efforts to address stigma and support individuals living with leprosy.
5. Public Health Response: Containment and Prevention
Explore the public health response to the leprosy challenge in Florida. Discover the measures taken to contain the spread of the disease and prevent further cases through education, awareness, and targeted interventions.
6. Research and Innovation: Advancing Leprosy Management
Scientists and researchers are working tirelessly to advance leprosy management and treatment. Learn about the latest breakthroughs in research and the development of novel interventions to combat the disease.
7. Community Engagement: Empowering Communities
Community engagement plays a vital role in addressing Florida’s leprosy challenge. Explore the importance of community involvement in disease management and how it fosters a united front against leprosy.
Conclusion: Confronting Florida’s Leprosy Challenge
In conclusion, Florida’s leprosy challenge calls for a comprehensive and collaborative approach. As scientists discover endemic cases and public health response efforts intensify, addressing the resurgence of leprosy becomes a collective responsibility. By empowering communities, reducing stigma, and advancing research, we can confront this challenge and prevent further spread of the disease. Together, we stand against leprosy, aiming to ensure the well-being and health of all individuals in the state. Let us unite in our efforts to tackle Florida’s leprosy challenge and work towards a future where this once rare disease becomes a thing of the past.
Care
Pediatric Dentistry Idaho: Fear-Free, Tech-Driven Care in 2026

Choosing a pediatric dentist in Idaho Falls is one of the most significant healthcare decisions a parent in Southeast Idaho can make. In fact, as we move through 2026, dental providers in Bonneville County have shifted the landscape from traditional “drill-and-fill” methods to a more holistic, tech-integrated approach. As a result, modern parents are no longer just looking for a clinic; rather, they are looking for an experience that eliminates dental anxiety and sets their children on a path toward lifelong oral health.
To help with this decision, this comprehensive 1300-word guide breaks down the top-rated providers for 2026, the latest technological advancements in pediatric care, updated pricing, and essential tips for navigating children’s dentistry in the “208” area code.

1. Top-Rated Pediatric Practices in Idaho Falls (2026)
Based on clinical excellence, parent testimonials, and the adoption of “Fear-Free” protocols, these five practices are currently the gold standard in Idaho Falls:
Alligator Pediatric Dentistry & Orthodontics
Located conveniently for families across Idaho Falls and Ammon, Alligator Pediatric Dentistry remains a market leader in 2026. This year, they have further integrated behavioral psychology into their practice. As a result, the office is designed as a themed adventure, ensuring children associate the dentist with fun rather than pain.
- Why it stands out:
Most notably, they specialize in “first-visit” success. Additionally, they offer fully integrated orthodontic care, meaning your child can stay with the same trusted team from their first tooth all the way through their braces.
Sunny Smiles Pediatric Dentistry
Dr. Kailey Housley and her team are celebrated for their incredibly gentle approach. As a board-certified pediatric dentist, Dr. Housley focuses on the unique developmental needs of infants and toddlers.
- Why it stands out: Their “Age One” visit program is highly regarded, focusing on preventive education for parents and a non-threatening introduction for the child.
Baker Pediatric Dentistry
For families with children who have special healthcare needs, Dr. Thomas Baker is the premier choice. His staff is specifically trained in sensory-friendly communication and medical-grade safety protocols.
- Why it stands out: They offer customized sedation plans and an environment tailored to children with autism, ADHD, or physical disabilities.
Clubhouse Pediatric Dentistry
Known for its high-tech approach, Clubhouse Pediatric on Merlin Drive has become a favorite for tech-savvy parents. They employ the newest technology in digital imaging and laser dentistry.
- Why it stands out: They are leaders in “No-Drill” dentistry, utilizing water-based lasers to treat cavities without the need for traditional numbing shots in many cases.
Eagle Rock Dental Care
While a family-focused practice, their pediatric wing is exceptional. They offer the convenience of seeing the whole family in one location while maintaining a child-specific environment for the younger patients.
- Why it stands out: Their patient portal and scheduling flexibility make them the top choice for busy Idaho Falls families with multiple children.
2. 2026 Technology: A New Era of Painless Care
- AI-Assisted Cavity Detection: Artificial Intelligence software now scans digital X-rays to catch decay months before it’s visible to the human eye. This allows for simpler, cheaper preventive treatments.
- Hard-Tissue Lasers (WaterLase): These lasers remove decay using light and water. The result is often no vibration, no heat, and—most importantly—no needle required for the filling.
- 3D Intraoral Scanners: The days of “goopy” impression molds are gone. In 2026, digital scanners create a 3D model of your child’s mouth in seconds, which is essential for accurate growth monitoring and orthodontics.
3. 2026 Price Guide: Dental Costs in Idaho Falls
Understanding the financial side of healthcare is essential for Idaho families. Based on February 2026 market data, here are the estimated costs for pediatric services in the region:
Service
Estimated Cost (No Insurance)
With Insurance/Membership
Comprehensive New Patient Exam
$95 – $130
$0 (Preventive)
Child Prophy (Cleaning)
$85 – $115
$0 (Preventive)
BPA-Free Dental Sealants
$50 – $70 per tooth
$10 – $25
Tooth-Colored Filling
$215 – $305
$45 – $110
Space Maintainer
$350 – $500
$150 – $250
Nitrous Oxide (Laughing Gas)
$125 – $160
Usually Out-of-Pocket
Note: These are estimates for Southeast Idaho. Prices may vary based on the complexity of the case.
4. Why Specialization Matters: The Pediatric Advantage
Many parents ask if a general family dentist is sufficient. While many are capable, a specialized pediatric dentist in Idaho Falls provides three distinct advantages:
Here is the content revised with transition words to create a more logical and connected flow.
- Behavioral Expertise: Pediatric specialists undergo 2-3 years of additional residency focused on child psychology. As a result, they know how to de-escalate a tantrum and turn a scary situation into a learning moment.
- Growth Monitoring: Furthermore, they are experts in jaw development. For instance, catching a “crossbite” or “crowding” early can save you thousands in future orthodontic surgeries.
- Special Needs Training: Finally, pediatric offices are physically designed to accommodate different abilities, from wider hallways for wheelchairs to quiet rooms for sensory-sensitive children.
5. Prevention: The 2026 Focus
The trend in 2026 dentistry is “Prevention Over Restoration.” Leading Idaho Falls clinics are now emphasizing:
- Silver Diamine Fluoride (SDF): A breakthrough liquid that can stop a cavity without any drilling. It’s a “miracle” for young children who aren’t ready for a full filling.
- Nutritional Coaching: Dentists are now acting as nutritional consultants, helping parents identify “hidden sugars” in common Idaho snacks that lead to rapid enamel erosion.
- Saliva Testing: Advanced clinics can now test your child’s saliva to determine their “Caries Risk Profile,” identifying if they are genetically more prone to cavities.
6. Managing Dental Anxiety in 2026
If your child is terrified of the dentist, you are not alone. Idaho Falls clinics have evolved to handle this:
- “Happy Visits”: Short, 5-minute visits where the child just gets a sticker and rides in the chair. These are crucial for building trust.
- Sedation Safety: Offices like Clubhouse Pediatric or Alligator utilize board-certified anesthesiologists for complex cases, ensuring the highest safety standards for IV sedation or general anesthesia.
- Virtual Reality Distraction: VR headsets are now commonly used during cleanings, allowing children to watch their favorite shows while the dentist works.
7. Insurance & Savings for Idaho Families
With the cost of living rising, managing dental expenses in the “208” is vital.
-
PPO Networks: Delta Dental and Blue Cross of Idaho are widely accepted. In fact, most top-rated clinics in Idaho Falls are “In-Network,” which can save you up to 50% on major work.
-
In-House Membership Plans: However, if you are self-employed or without insurance, look for membership plans. For example, for a monthly fee of around $30–$40, you receive all preventive care and a 20% discount on all other procedures.
-
Medicaid (Healthy Connections): Finally, many Idaho Falls offices accept Idaho Medicaid. However, slots for new patients fill up quickly, so it is recommended to book 3-4 months in advance.
8. Conclusion: A Lifetime of Smiles
In 2026, Idaho Falls offers some of the best pediatric dental care in the Pacific Northwest. By choosing a specialist who embraces modern technology and emphasizes preventive care, you aren’t just getting a cleaning; you are investing in your child’s confidence and overall health.
Consumer Services
Remote Medical Documentation: Real-Time Scribes for Clinic

Medical documentation rarely feels like a problem at first. Notes get done. Charts are closed. The day moves on. But over time, something starts to shift. Providers stay late. Staff feel rushed. Errors creep in. What looks manageable on the surface slowly becomes a heavy operational burden. Many practices do not realize how costly in-house documentation truly is until it begins to affect time, revenue, and morale.
These costs are not always obvious. They do not always show up on balance sheets. Yet they impact clinics every single day.
Time That Quietly Slips Away
One of the biggest hidden costs is time. Providers often spend hours completing notes before clinic hours, during lunch breaks, or late at night. This time is unpaid and exhausting. It also shortens recovery time between workdays.
Staff members are affected too. Medical assistants and front-desk teams are frequently pulled away from their core duties to help with documentation tasks. This leads to delays, bottlenecks, and frustration for both patients and staff.
Over weeks and months, these lost hours add up. What could have been spent on patient care, scheduling, or follow-ups gets consumed by charting.

Burnout That Builds Slowly
Burnout does not always come from long patient lists. It often comes from what happens after the visits end. Constant documentation pressure drains focus and energy. Providers feel they are always catching up.
This stress affects performance and job satisfaction. Tired clinicians are more likely to make small documentation mistakes or feel disconnected during visits. Staff turnover becomes more common, which creates new costs in hiring and training.
Burnout is expensive, even if it does not appear on an invoice.
Direct Financial Costs You May Overlook
In-house documentation comes with visible expenses like salaries, benefits, training time, and equipment. But there are other costs that are easy to miss.
Here are a few that often go unnoticed:
- Overtime pay for staff helping with charts
- Delayed billing due to incomplete notes
- Lost revenue from fewer available appointment slots
- Costs of correcting documentation errors or addendums
- Training time for new staff when turnover occurs
Each item alone may seem minor. Together, they create a steady drain on clinic resources.
The Shift Toward Smarter Documentation Support
As documentation demands grow, many clinics begin looking for ways to reduce the pressure on in-house teams. Online medical documentation offers a practical alternative by allowing notes to be completed remotely within existing EHR systems, without disrupting daily workflows. This type of support helps providers stay focused on patient care while documentation is handled efficiently in the background.
This approach reduces after-hours charting and keeps documentation timely and accurate. Instead of stretching staff thin, clinics gain support that fits into current workflows without adding physical space or long-term staffing commitments.
This shift is less about changing how care is delivered and more about removing unnecessary strain from daily operations.
Accuracy and Compliance Risks
When documentation is rushed or delayed, accuracy suffers. Small errors can lead to billing issues, claim denials, or compliance concerns. Fixing these problems takes additional time and effort.
In-house teams often juggle multiple responsibilities. Documentation becomes one task among many. This increases the chance of missed details or inconsistent note quality.
Reliable documentation support helps maintain consistency and completeness, which protects both providers and practices in the long run.
Limited Flexibility as Patient Volume Changes
Patient volume is rarely steady. Some days are packed. Others are lighter. In-house documentation teams do not always scale well with these changes.
Hiring more staff for busy periods increases overhead. Keeping extra staff during slow periods wastes resources. This imbalance creates stress for managers and clinicians alike.
Remote documentation support offers flexibility. Clinics can adjust hours based on need without the pressure of permanent staffing decisions.
What Practices Often Miss
The true cost of in-house documentation is not just financial. It affects:
- Provider energy and focus
- Staff morale and retention
- Patient experience and wait times
- Workflow efficiency across the clinic
When these areas suffer, growth becomes harder. Practices spend more time managing problems instead of improving care.
Doing medical documentation in-house can feel familiar and safe. But familiarity often hides inefficiency. The hours spent charting late, the stress carried home, and the small operational losses all point to a larger issue. Over time, these challenges begin to affect how smoothly a clinic operates and how sustainable the workload feels for providers, often pulling focus away from direct patient engagement and quality of care.
This is where MVSPlus becomes a practical option. MVSPlus offers remote medical documentation support through trained virtual scribes who work within existing EHR systems. The service is designed to reduce documentation time, improve note accuracy, and support clinics without adding in-house staffing pressure. By handling the data entry in real-time, our scribes allow physicians to stay fully present during patient exams, ensuring a smoother clinical experience and higher quality records without workflow interruptions.
Beauty Fitness
Jawline Fillers in Dubai: Symmetry & Balance with Centric Aesthetic

Facial attractiveness is often mathematically linked to symmetry and proportion. While no face is perfectly identical on both sides, significant deviations in the lower face can disrupt the overall harmony of one’s features. Jawline fillers in Dubai have become the leading medical intervention for correcting these imbalances without the need for bone-shaving surgery or permanent implants.
By strategically adding volume to the weaker side of the mandible, practitioners can create a more uniform, balanced, and aesthetically pleasing profile that aligns with the rest of the facial features.
The Science of Asymmetry and Mandibular Correction
Most facial asymmetry stems from genetics, sleeping habits, or unilateral dental issues that affect bone development. When we perform jawline fillers in Dubai, we conduct a detailed “cephalometric” analysis to identify where the bone or soft tissue is lacking.
By using high-density dermal fillers, we can physically “build out” the recessed side of the jaw. This process involves placing the filler deep against the bone to mimic the missing skeletal structure, effectively leveling the jawline and ensuring that the chin sits perfectly in the midline of the face.
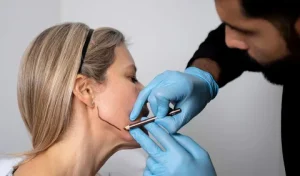
Clinical Experience with Symmetrical Sculpting
In our clinical experience, achieving symmetry requires a “dual-volume” approach. We rarely inject the same amount of filler on both sides of the face. Instead, we use a precise titration method, adding micro-droplets of filler to the deficient side until it mirrors the more dominant side.
This requires a keen medical eye and a deep understanding of facial vectors. What patients typically report during recovery is a subtle yet profound shift in how they look in photos, as the face appears more centered and the features more “in focus” due to the improved lower-face foundation.
The Purpose of Balancing the Lower Third of the Face
The primary reason to pursue Jawline fillers in Dubai for symmetry is to create a sense of “visual rest.” When the jaw is uneven, the eye is often drawn to the imbalance rather than the person’s gaze. By straightening the mandibular border, we create a clear, horizontal frame for the face.
This balance is particularly important for the “V-shape” or “U-shape” of the chin. A centered chin and an even jaw angle provide a structural anchor that makes the nose and eyes appear more symmetrical by association, leading to a more harmonious overall appearance.
Key Benefits of Symmetry-Focused Injectables
- Corrects Bone Imbalances: Compensates for natural skeletal variations between the left and right sides.
- Non-Surgical Realignment: Adjusts the visual “center” of the face without invasive bone work.
- Immediate Visual Harmony: Results are visible instantly, allowing for real-time adjustments.
- Boosts Photogenic Confidence: Creates a more balanced look from every angle, especially in profile.
Who is a Candidate for Symmetry Enhancement?
The ideal candidate is someone who notices that their jawline looks “different” on one side or whose chin appears slightly off-center. We also treat patients who have experienced soft-tissue loss on one side due to aging or weight fluctuations. During your consultation at Tajmeels Clinic, we use specialized lighting to map out the shadows of your face.
This helps us see exactly where the “hollows” are located. Candidates should have realistic expectations and understand that while we can significantly improve symmetry, the goal is “harmony” rather than clinical perfection.
The Procedure: A Precision Alignment Session
The treatment begins with a sterile preparation of the skin and the mapping of the facial midline. After a topical numbing agent is applied, we typically utilize a blunt-tipped cannula. In our clinical experience, the cannula is the superior tool for symmetry because it allows us to “sweep” the filler across the jawline, ensuring a smooth transition between the filler and the natural bone. We often have the patient sit upright during the final stages of the injection to check the symmetry against gravity, ensuring the balance remains perfect whether the patient is smiling or at rest.
Target Zones for Symmetrical Refinement
| Symmetry Zone | Clinical Goal | Aesthetic Result |
| Gonial Angle (Left/Right) | Evening out the back width | A balanced, chiseled look from both sides |
| Mandibular Body | Straightening an uneven line | A uniform border between the face and neck |
| Chin Apex (Center) | Re-centering the chin point | Improved facial alignment and “V” taper |
| Pre-Jowl Sulcus | Filling unilateral hollows | A seamless, smooth lower face transition |
Economic and Volume Factors for Balancing
The cost of a symmetry-focused treatment depends on the severity of the imbalance. Some patients may only need a single syringe to “touch up” one side, while others may require a full reconstruction of the jawline to bring both sides into alignment.
Because we use high-G-prime, structural fillers, the results of jawline fillers in Dubai are very durable, often lasting 12 to 18 months. Choosing an expert injector ensures that the product is used efficiently, focusing only on the areas that need correction to achieve the most natural and cost-effective outcome.
What to Expect During the Healing Phase
What patients typically report during recovery is a slight difference in “firmness” between the two sides for the first few days. This is normal as the side receiving more filler may experience slightly more swelling. This usually subsides within 72 hours, leaving the jawline looking even and balanced.
We recommend avoiding any “facial manipulation” like heavy massages for two weeks to ensure the filler stays in its precisely mapped location. Most patients return to their normal routine immediately, enjoying their new, symmetrical profile.
Medically Responsible Standards for Symmetrical Care
Safety and symmetry go hand-in-hand. An injector must be careful not to “over-correct,” as this can create a new form of imbalance. Our clinical protocols for jawline fillers in Dubai involve a “less is more” approach, where we can always add more filler in a follow-up session if needed.
We use only FDA-approved, high-quality biocompatible materials to ensure that your path to a balanced face is safe. Choosing a licensed clinic like Tajmeels Clinic ensures that your symmetry is handled by professionals who understand the intricate relationship between facial anatomy and aesthetics.
Maintaining Your Balanced Profile Long-Term
To maintain your new, symmetrical look, we suggest regular check-ups. As we age, we may lose more volume on one side than the other, so a minor “tweak” every 12 to 14 months can keep the balance intact. Additionally, maintaining good dental health is important, as tooth loss can affect the underlying bone structure of the jaw.
Using medical-grade skincare to keep the skin over the filler healthy and firm will ensure that your symmetrical results remain crisp and defined for years to come.
Conclusion: Finding Harmony in Your Features
Symmetry is the quiet foundation of a beautiful face. By addressing the imbalances in your jawline, you can unlock a new level of facial harmony that enhances your entire appearance.
At Tajmeels Clinic, we are dedicated to the art of balance, using medical science to refine your profile in a way that feels natural and true to you. We believe that a symmetrical jawline is the key to a more confident and balanced self-image.
Learn if this treatment is right for your lifestyle by scheduling a symmetry assessment with our expert medical team.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business3 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom































