Technology
Apple MacBook Maker Expands Production with New Plant in Vietnam

Apple Maker Production with in Vietnam
Vietnam has become one of the world’s top destinations for tech manufacturing in recent years, and Apple has been no exception. In a move that will surely shake up the industry, Apple is expanding its production of MacBooks with a brand new plant in Vietnam. The decision to expand here wasn’t made lightly – Vietnam’s pool of skilled workers and favorable business conditions make it an attractive option for many global companies. But what does this mean for the Vietnamese economy? And how will it impact MacBook production as a whole? We’ll take a closer look at these questions and more in this article about Apple Maker Production with in Vietnam!
The Company
Apple has been a household name for decades, known for its innovative products and sleek designs. The company was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs, Steve Wozniak, and Ronald Wayne, with the goal of developing personal computers that were both user-friendly and accessible to the average consumer.
Since then, Apple has continued to push the boundaries of technology with products like the iPod, iPhone, iPad, and MacBook. Today, it’s one of the largest tech companies in the world with a market value nearing $2 trillion.
In recent years, Apple has been focused on expanding its manufacturing capabilities around the globe. Vietnam is just one example of this – but it’s an important one. By opening up new production plants here, Apple will be able to tap into a skilled workforce while keeping costs low.
Apple remains committed to innovation and growth as it continues to produce some of the most popular electronic devices on the planet.
The Product
The MacBook is Apple’s flagship laptop computer that has gained immense popularity over the years. The sleek design, powerful performance, and user-friendly interface have made it a top choice for professionals, students, and casual users alike.
The MacBook comes in various sizes ranging from 12 inches to 16 inches with different specifications based on the user’s requirements. Some of its notable features include Retina display, Touch ID, Force Touch trackpad, and long battery life.
Apple constantly upgrades the MacBook line by incorporating new technologies such as M1 chipsets that deliver exceptional speed and efficiency while reducing power consumption. It also supports advanced security features like Secure Enclave technology to ensure data privacy.
MacBooks are known for their seamless integration with other Apple devices through iCloud services. This allows users to access their files across multiple devices easily.
The MacBook stands out among its competitors due to its premium build quality, excellent performance capabilities, innovative features and functionalities all designed for an unparalleled user experience.
The Location
Vietnam has become an increasingly popular location for tech giants like Apple to manufacture their products. The country’s strategic geographic location, low labor costs, and favorable investment policies make it an ideal destination for companies looking to expand their production capacities.
Apple’s manufacturing plant in Vietnam is located in Bac Ninh province, which is about 30 kilometers northeast of Hanoi. This province is known for its strong industrial base and skilled workforce, making it a perfect fit for high-tech manufacturing operations.
The facility spans over 50 hectares and boasts state-of-the-art equipment that can produce up to 10 million units per year. It employs around 22,000 workers who are trained rigorously on the latest technology and production processes.
The proximity of this plant to major shipping ports ensures that products can be shipped quickly and efficiently to markets worldwide. Additionally, Vietnam’s stable political climate makes it a safe destination for foreign investors such as Apple.
The location of Apple’s manufacturing plant in Vietnam provides numerous advantages such as a skilled workforce, modern infrastructure facilities, cost-effectiveness among others – all contributing towards ensuring efficient production processes with quality results every time!
The People
Apple’s manufacturing in Vietnam has a significant impact on the people of the country. Not only does it provide employment opportunities, but it also boosts their economy. As Apple expands its production and opens a new plant in Vietnam, more jobs will be created for locals.
The workers who are part of Apple’s production in Vietnam have received training to ensure that they meet the company’s high standards when it comes to quality control. This means that not just anyone can work for Apple; they need to have skills and expertise that match what is required by the company.
Moreover, working with such an established brand like Apple provides Vietnamese employees with valuable experience and knowledge about technology innovation and advancements. They get a chance to learn from some of the best minds in tech which can help them advance further in their careers.
Apple has also made sure that all workers involved in their manufacturing processes receive fair wages and treatment as per international labor laws. Being treated well at work means happier employees, which ultimately leads to better productivity levels – something every company strives towards.
Apple’s decision to manufacture products in Vietnam has had a positive impact on the people of this country by providing them with job opportunities as well as access to valuable experience and knowledge gained from working with one of the most innovative companies globally.
The Process
The process of producing Apple products in Vietnam involves multiple stages, each one critical to ensure the quality and consistency that consumers expect from the brand.
The first stage is sourcing materials, where Apple works with suppliers to obtain high-quality components needed for production. These materials are then transported to the manufacturing facility in Vietnam.
Once at the plant, assembly begins. Workers carefully assemble each MacBook by hand, ensuring that every component is installed correctly and efficiently. Quality control measures are taken throughout this process to catch any issues early on.
After assembly, rigorous testing takes place to identify any defects or malfunctions before packaging and shipping out for distribution worldwide. This testing ensures that every MacBook meets Apple’s strict standards of quality and reliability.
In addition to these processes, there are also environmental considerations taken into account during production such as energy-efficient facilities and waste reduction efforts.
It is clear that the production process for Apple products is a complex but well-planned system designed for efficiency without sacrificing quality or sustainability measures along the way.
The Future
The Future of Apple’s Manufacturing in Vietnam is looking bright. As one of the largest tech companies in the world, Apple has always been known for being at the forefront of innovation and technology. With their new plant expansion in Vietnam, they are continuing to push boundaries and explore new opportunities.
The company is constantly looking for ways to improve their products and production processes. This means that we can expect to see even more advanced MacBook models being produced right here in Vietnam.
In addition to this, it’s likely that Apple will continue investing heavily into research and development within the country. This could potentially lead to new job opportunities for Vietnamese citizens as well as further growth for the local economy.
As a result, we may also see other major tech companies following suit by expanding their manufacturing presence in Vietnam. This would create a domino effect where more jobs are created and businesses thrive.
The future looks promising not only for Apple but also for Vietnam as a whole. By embracing technology and innovation, there is no limit to what can be achieved.
Introduction
Apple, the tech giant that we all know and love, has made a significant move in its production line. The company has expanded its MacBook manufacturing to Vietnam, marking another milestone for Apple’s global presence. This decision is not only beneficial to Apple but also to the Vietnamese economy.
Vietnam is one of Asia’s fastest-growing economies with an abundance of young talents and a vibrant start-up ecosystem. Therefore, it comes as no surprise that Apple wants to explore what Vietnam can offer. With low labor costs and a favorable business environment, this Southeast Asian country proves to be a suitable location for manufacturing high-quality products like MacBooks.
Apple’s new plant in Vietnam will enable them to ramp up their production capacity while reducing their reliance on China-based suppliers. As such, it provides flexibility in managing supply chain risks while keeping pace with growing demand from consumers worldwide.
The shift towards producing more devices in Vietnam also means job creation opportunities for locals who have been struggling with unemployment due to the pandemic’s economic downturn. This step taken by Apple will undoubtedly have numerous positive impacts on both parties involved – the company itself and the Vietnamese people alike.
Apple’s expansion into Vietnam marks yet another exciting chapter for the tech giant as they continue to diversify their operations globally while creating long-term benefits for local communities around the world.
The Vietnamese Market
Vietnam is a rapidly developing country that has been experiencing rapid economic growth in recent years. With a population of almost 100 million people, it presents an enormous market potential for businesses looking to expand their reach. In particular, the technology industry has seen significant growth in Vietnam as more and more companies look to take advantage of the country’s favorable business environment.
The Vietnamese market offers several advantages for tech companies such as Apple who are considering expanding their operations. One of these benefits is low labor costs, which makes production cheaper than other countries like China or Japan. Another advantage is the availability of skilled workers who can be trained to work on complex technologies.
Additionally, Vietnam has made strides towards improving its infrastructure with better roads and ports making transportation much easier within the country. This means that products can be moved quickly from one location to another ensuring timely delivery.
In terms of consumer behavior, Vietnamese consumers have shown an increased interest in high-quality products such as smartphones and laptops like MacBook. They are willing to pay a premium price for these products provided they meet certain standards and quality criteria.
With its large population, low labor costs, available workforce skill set and improved infrastructure; Vietnam presents itself as an attractive destination for foreign corporations seeking new markets while expanding their existing ones like Apple through building new plants producing MacBooks .
Apple’s Manufacturing in Vietnam
Apple’s decision to expand its manufacturing capability in Vietnam has been a strategic move. The company is already sourcing components from the country, so it makes sense to have production facilities nearby. In recent years, Apple’s reliance on China for manufacturing has become increasingly difficult due to rising labor costs, trade tensions and geopolitical risks.
The new MacBook plant in Vietnam will create thousands of jobs and provide a boost to the local economy. This is not only good news for Apple but also for the Vietnamese people who will benefit from job creation and increased investment.
Apple’s presence in Vietnam is expected to attract other tech companies seeking low-cost labor alternatives outside of China. However, this could lead to increased competition for workers as supply chains shift away from China towards Southeast Asia.
Apple has made significant investments in renewable energy sources such as solar power at its manufacturing sites worldwide. It remains unclear whether these sustainability measures will be implemented at the new facility in Vietnam.
Apple’s manufacturing expansion into Vietnam shows how global supply chains are shifting due to economic pressures and changing geopolitical dynamics. As one of the biggest tech companies globally, it sets an example that others may follow as they look beyond China for their production needs.
The Impact of Apple’s Manufacturing on the Vietnamese Economy
Apple’s manufacturing presence in Vietnam has had a significant impact on the country’s economy. In recent years, Vietnam has become an attractive location for multinational companies due to its low labor costs and government incentives. Apple is one of the biggest investors in Vietnam, with several manufacturing plants operating across the country.
The company’s investment in Vietnam has created job opportunities for thousands of Vietnamese people, which has boosted local employment rates and reduced poverty levels. Moreover, Apple’s investment in training programs and education initiatives for workers has also helped improve their skills and knowledge.
Apple’s manufacturing operations have also contributed to increasing the export revenue of Vietnam. The company exports millions of iPhones and MacBooks from its factories located near Ho Chi Minh City every year, making it one of the largest contributors to Vietnam’s GDP.
Furthermore, Apple’s investment in sustainability efforts within its supply chain can have long-lasting positive effects on environmental issues that are pressing concerns worldwide. By promoting sustainable practices among suppliers by setting standards regarding emissions reduction or water conservation norms can not only create jobs but also encourage better practices throughout multiple industries.
Apple’s decision to expand its production facilities into Vietnam not only benefits both parties involved but contributes significantly towards transforming this Southeast Asian nation into a major tech hub with an expanding workforce prepared to tackle 21st-century challenges through innovation and modernization..
Conclusion
Apple’s decision to expand its manufacturing operations in Vietnam marks a significant milestone for the country, as well as for the tech giant. With an established reputation for producing high-quality products and delivering innovative technologies to consumers around the world, Apple is now poised to tap into the growing potential of the Vietnamese market.
By setting up a new plant in Vietnam and increasing production capacity for devices like MacBook laptops, Apple has not only boosted its own bottom line but also contributed significantly to economic growth in Vietnam. The move has created thousands of jobs for locals while supporting local supply chains and driving innovation within the tech industry.
This development is great news not just for Apple but also for Vietnam as it continues on its path towards becoming one of Asia’s leading economies. As such, we can expect more companies worldwide following suit by investing their resources into expanding their reach with manufacturing facilities throughout Southeast Asia!
Digital Development
Boldify for Facebook: Quick Bold Text in Seconds

Scroll through Facebook for just five minutes and you’ll notice something: most posts look exactly the same. Plain text blends into the feed, making it easy for users to scroll past without noticing important messages. In a crowded social media environment, visual formatting plays a major role in grabbing attention and increasing engagement. This is where Boldify, a powerful bold text generator, makes a difference. Instead of struggling with plain, unformatted posts, Boldify allows you to create eye-catching Facebook bold text instantly. In this article, you’ll learn why bold text matters, how Boldify works, and how you can use it to stand out on Facebook within seconds.
Why Bold Text Matters on Facebook (User Engagement Psychology)
Facebook is a fast-moving platform. Users scroll quickly, often stopping only when something visually stands out. Bold text works because it creates contrast. When certain words appear heavier or more prominent, the brain processes them faster.
Here’s why bold text improves engagement:
- It grabs attention in crowded feeds.
- It improves readability and scan ability.
- It highlights key messages instantly.
Bold formatting is especially powerful in:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Facebook groups
If you’re building a brand or growing a personal profile, bold text strengthens your identity. It emphasizes important announcements, promotions, or calls to action, making your message harder to ignore.
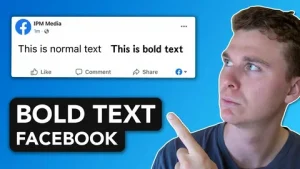
The Challenge: Facebook Doesn’t Offer Built-In Bold Formatting
One of the biggest frustrations for users is that Facebook does not provide built-in bold formatting for regular posts. Unlike word processors, you cannot simply select text and click “Bold.”
That’s why many people search for:
- how to bold text on Facebook
- Facebook bold text generator
- bold letters for Facebook
Without a proper tool, users are left copying complicated codes or trying ineffective formatting tricks. This creates a clear need for a reliable and easy-to-use bold font generator.
What Is Boldify?
Boldify is an online bold text generator designed to help users create stylish bold letters instantly. Instead of modifying Facebook’s formatting, Boldify uses Unicode-based bold fonts that are fully compatible with social media platforms.
Here’s what makes Boldify simple and powerful:
- No installation required
- Works directly in your browser
- Free and instant access
- Compatible with Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and WhatsApp
Because it uses special Unicode characters, the bold text appears naturally once pasted into Facebook posts, comments, bios, or Messenger chats. This makes Boldify a practical and beginner-friendly solution for anyone looking to create bold text online.
How Boldify Helps You Create Bold Facebook Text in Seconds
Using Boldify is straightforward and requires no technical knowledge. Here’s a simple step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Enter Your Text
Open Boldify and type your message into the input box. This could be a status update, promotional message, announcement, or bio line.
Example:
New Blog Post Live
Limited Time Offer
Join Our Community Today
Step 2: Automatic Bold Conversion
As soon as you enter your text, Boldify automatically converts it into multiple bold font styles. Within seconds, you’ll see several variations generated instantly.
Step 3: Copy and Paste to Facebook
Choose the bold style you like, click the copy button, and paste it directly into:
- Facebook posts
- Comments
- Bios
- Messenger chats
That’s it. In just a few seconds, your plain text becomes visually powerful Facebook bold text.
Key Features That Make Boldify Stand Out
There are many tools online, but Boldify offers specific advantages that make it reliable and user-friendly.
1. One-Click Copy Feature
No need to manually select text. Just click and copy instantly.
2. Multiple Bold Style Variations
Get access to different bold styles to match your tone and branding.
3. Mobile-Friendly Interface
Boldify works smoothly on smartphones, tablets, and desktops.
4. No Login Required
You don’t need to create an account. Just open and start using.
5. Fast Performance
Text conversion happens instantly without delays.
6. Clean and Simple Design
The interface is distraction-free, making it easy for beginners to use.
These features make Boldify more than just a basic bold letters generator—it becomes a practical social media enhancement tool.
Practical Ways to Use Bold Text on Facebook
Now that you know how to generate bold text, let’s explore practical ways to use it effectively.
Highlight Important Announcements
SALE TODAY ONLY
Registration Closes Tonight
Bold formatting ensures these messages get noticed quickly.
Strengthen Call-to-Actions
Instead of writing:
Join us now
Write:
JOIN US NOW
It creates urgency and clarity.
Emphasize Keywords in Posts
Highlight important parts of your message to guide the reader’s attention.
Improve Facebook Bios
Use bold text to make your profession, tagline, or brand name stand out.
Stand Out in Facebook Groups
When commenting in large groups, bold text increases visibility and improves response rates.
SEO & Branding Benefits of Using Bold Text
While bold text doesn’t directly change Facebook’s algorithm, it improves how users interact with your content.
Here’s how it benefits branding and visibility:
- Improves readability
- Encourages longer post engagement
- Strengthens personal or business branding
- Creates structured content hierarchy
- Makes posts look professional
When your content looks organized and visually appealing, users are more likely to stop scrolling and engage.
Tips for Using Bold Text Effectively
Bold text is powerful—but only when used strategically.
- Don’t overuse bold formatting.
- Highlight only key phrases or calls-to-action.
- Combine bold text with emojis carefully.
- Maintain readability and spacing.
Too much bold text can reduce its impact. The goal is to enhance clarity, not overwhelm the reader.
Conclusion
Standing out on Facebook is no longer optional—it’s necessary. Since Facebook doesn’t offer built-in bold formatting for posts, tools like Boldify provide a fast and effective solution.
Digital Development
Digital Marketing Agency in Pakistan: Strategy & Growth

In today’s rapidly evolving digital economy, businesses must go beyond traditional marketing methods to remain competitive. Consumers research brands online, compare services, read reviews, and expect personalized experiences before making purchasing decisions. Without a structured digital strategy, even the most promising businesses struggle to gain visibility and traction.
This is where a Digital marketing agency in Pakistan becomes a catalyst for strategic success. Rather than focusing on isolated campaigns, professional agencies build integrated systems that combine SEO, AI-driven insights, performance marketing, content development, and user experience optimization.
This article explores how a Digital marketing agency in Pakistan drives measurable growth by aligning strategies with modern frameworks such as SEO, GEO, AIO, SXO, AEO, and EEAT.
The Importance of Strategic Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is no longer about simply posting on social media or running paid ads. Strategic success requires:
- Clear business objectives
- Data-driven planning
- Target audience analysis
- Search intent alignment
- Multi-channel execution
- Continuous performance tracking
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan begins by understanding a brand’s goals, industry landscape, and customer behavior. This ensures every marketing effort contributes to long-term success rather than short-term visibility spikes.
Strategy transforms marketing from an expense into a growth engine.

SEO: The Foundation of Long-Term Visibility
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) remains the cornerstone of digital success. Organic visibility provides consistent traffic without ongoing advertising costs.
Professional agencies implement:
- Comprehensive keyword research
- Search intent mapping
- Semantic keyword clustering
- Technical SEO audits
- Mobile-first optimization
- Backlink development strategies
By incorporating LSI keywords such as online marketing services, website optimization techniques, search engine ranking improvement, digital advertising solutions, and content marketing strategy, agencies strengthen topical authority without keyword stuffing.
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan ensures that websites rank for relevant, high-intent keywords while maintaining compliance with search engine guidelines.
Organic traffic compounds over time, building a sustainable foundation for growth.
GEO: Adapting to AI-Driven Search
Search engines are increasingly powered by artificial intelligence. Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) focuses on structuring content for AI-generated summaries and contextual answers.
Agencies enhance GEO by:
- Organizing content with clear headings
- Providing in-depth, authoritative information
- Implementing structured data
- Ensuring contextual keyword relevance
This preparation ensures businesses remain visible in emerging AI-powered search environments.
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan future-proofs digital presence by adapting to technological evolution rather than reacting to it.
AEO: Capturing High-Intent Direct Answers
Answer Engine Optimization (AEO) enhances visibility in:
- Featured snippets
- Voice search queries
- Direct answer boxes
- FAQ sections
By implementing schema markup and optimizing conversational queries, agencies increase the likelihood of appearing in high-visibility placements.
These placements improve credibility and click-through rates.
For businesses seeking strategic success, capturing direct answers strengthens both authority and traffic.
AIO: Leveraging Artificial Intelligence for Competitive Advantage
Artificial Intelligence Optimization (AIO) enhances campaign precision and efficiency.
Agencies use AI-powered tools to:
- Analyze consumer behavior patterns
- Predict high-converting audiences
- Automate ad bidding strategies
- Personalize email campaigns
- Forecast marketing performance
This data-driven approach minimizes waste and maximizes return on investment.
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan integrates AI tools into campaigns, allowing businesses to scale efficiently while maintaining control over budgets.
SXO: Aligning Search Visibility with User Experience
High rankings mean little if visitors leave without converting. Search Experience Optimization (SXO) combines SEO with user-focused improvements.
Agencies optimize:
- Website loading speed
- Mobile responsiveness
- Navigation clarity
- Call-to-action placement
- Trust-building elements
Improved user experience leads to lower bounce rates and higher conversion rates.
Strategic success requires turning traffic into revenue, not just increasing visitor numbers.
EEAT: Establishing Authority and Trust
Search engines prioritize Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (EEAT). Businesses must demonstrate credibility to rank competitively.
Agencies strengthen EEAT by:
- Publishing expert-driven content
- Highlighting industry credentials
- Securing authoritative backlinks
- Managing online reviews
- Showcasing case studies
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan builds brand authority through consistent messaging and transparent communication.
Trust influences both search engine rankings and customer decisions.
Content Marketing: Educating and Engaging Audiences
Content remains central to digital marketing success. Informative, value-driven content attracts and nurtures potential customers.
Agencies develop:
- Blog articles
- Service pages
- Industry guides
- Case studies
- Email marketing content
Optimized content increases engagement while supporting SEO objectives.
By focusing on educational and solution-oriented content, businesses position themselves as industry leaders.
Performance Marketing for Immediate Impact
While organic strategies build gradually, performance marketing delivers quicker results.
Agencies manage:
- Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns
- Social media advertising
- Retargeting funnels
- Conversion tracking systems
- A/B testing frameworks
Campaigns are continuously refined based on performance metrics such as return on ad spend (ROAS) and customer acquisition cost (CAC).
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan ensures that paid campaigns align with broader strategic goals.
Data Analytics: Measuring and Refining Success
Digital marketing thrives on data.
Agencies track:
- Website traffic growth
- Keyword ranking progress
- Conversion rates
- Engagement metrics
- Revenue attribution
Continuous monitoring allows for timely optimization.
Data-driven decisions improve efficiency and support long-term scalability.
Multi-Channel Integration for Strategic Advantage
Customers interact with brands across multiple platforms. Integrated marketing ensures consistent messaging across:
- Search engines
- Social media platforms
- Email campaigns
- Content distribution networks
- Paid advertising channels
This holistic approach increases brand recall and strengthens customer trust.
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan coordinates these channels into a cohesive strategy.
Supporting Scalability and Business Expansion
As businesses grow, marketing complexity increases.
Professional agencies support expansion through:
- Multi-location SEO strategies
- International targeting
- Advanced marketing automation
- Market-specific keyword research
Scalability requires adaptability and structured planning.
With expert guidance, businesses expand confidently without compromising efficiency.
Cost Efficiency and Risk Management
Hiring an in-house marketing team involves significant costs.
Outsourcing to a Digital marketing agency in Pakistan provides:
- Access to specialized expertise
- Advanced marketing technologies
- Reduced operational overhead
- Flexible service scaling
Agencies also minimize risks associated with algorithm updates and compliance issues.
Strategic oversight protects brand reputation while maximizing growth.
From Strategy to Sustainable Success
Driving strategic success involves:
- Comprehensive planning
- Structured implementation
- Continuous optimization
- Performance measurement
- Scalable expansion
When SEO, GEO, AIO, SXO, AEO, and EEAT frameworks work together, digital marketing becomes a sustainable growth engine.
Businesses move from reactive marketing to proactive leadership.
Conclusion
Digital success requires more than sporadic campaigns; it demands structured strategy, technological adaptation, and consistent optimization.
A Digital marketing agency in Pakistan drives strategic success by integrating SEO, AI-powered tools, performance marketing, user experience design, and authority-building strategies.
By aligning digital initiatives with modern frameworks and measurable objectives, businesses transform online presence into long-term competitive advantage.
In an increasingly digital marketplace, strategic marketing is not optional, it is essential. With the right digital partner, businesses can confidently navigate complexity and achieve sustainable growth.
From planning to performance, strategy to success a professional digital marketing agency turns vision into measurable results.
Digital Development
Test Cases in Software Testing: Structure, Types, and AI Tooling

Test cases are the foundation of any successful software testing effort. They define the inputs, execution steps, and expected results that help verify whether a software application behaves as intended. A well-structured set of test cases in software testing not only ensures higher quality but also enables repeatable, reliable test execution across development cycles.
Understanding how to create, manage, and optimize test cases is essential for developers, QA engineers, and anyone involved in delivering dependable software.
What Are Test Cases in Software Testing?
In software testing, a test case is a documented set of conditions, actions, and expected outcomes used to determine whether a specific feature or functionality works correctly. Each test case includes:
- A clear description of what is being tested
- Preconditions or setup requirements
- Steps to execute the test
- The expected result for comparison
Test cases give structure to the testing process, making it easier to validate application behavior and track defects.
Why Test Cases Matter
Effective test cases serve multiple practical purposes:
Improved Clarity
They provide a clear and repeatable plan for testing specific behaviors and features.
Consistent Validation
With documented steps and expected results, different testers can execute the same tests consistently.
Audit and Traceability
Test cases help track which scenarios were tested and which bugs were identified, aiding quality audits.
Automation Support
Well-defined test cases can be used as the basis for automated testing, reducing manual effort.
Key Elements of Good Test Cases
A good test case should contain the following:
Test Case ID
A unique identifier for easy reference.
Test Description
A clear explanation of the test objective.
Preconditions
Any setup required before running the test.
Execution Steps
Ordered actions to perform the test.
Inputs
Data or parameters needed for the test.
Expected Result
The anticipated outcome to validate correctness.
Postconditions
Any cleanup or conditions after test execution.
Types of Test Cases
Different project needs require different kinds of test cases:
Functional Test Cases
Verify that specific functions of the software work correctly.
Regression Test Cases
Make certain that the new modifications do not disrupt current operations.
Integration Test Cases
Check interactions between multiple components or systems.
Boundary and Negative Test Cases
Test edge conditions and unexpected inputs to verify system robustness.
Usability Test Cases
Evaluate user experience and intuitive behavior.
Ways to Create Impactful Test Cases in Software Testing
Understanding how to write good test cases is a core skill for QA professionals. Follow these steps:
Analyze Requirements
Understand the feature or behavior being tested.
Define Clear Objectives
Each test should focus on a specific expected outcome.
Use Simple Language
Write steps and descriptions in clear, actionable language.
Avoid Duplication
Ensure test cases are unique and do not repeat existing tests unnecessarily.
Review and Update
Continuously review test cases with the team and update them based on application changes.
Common Challenges with Test Cases
Test cases can sometimes become outdated or ineffective if not properly maintained. Common issues include:
- Redundant or duplicate test cases
- Incomplete documentation
- Lack of clarity in steps or expected results
- Poor traceability to requirements
Regular review and maintenance help ensure that test cases remain relevant and useful.
The Role of Automation
Once test cases are well documented, they can serve as a foundation for automated testing. Automation tools can execute predefined test cases repeatedly, providing faster feedback and freeing developers and testers to focus on exploratory and advanced testing tasks.
Conclusion
Test cases form the backbone of any robust software testing strategy. They bring clarity, consistency, and accountability to the testing process while paving the way for automation and higher-quality releases. Well-structured test cases leave little room for ambiguity, enabling both new and experienced team members to execute tests with precision and confidence.
By mastering how to write and manage test cases, teams can improve software reliability, detect defects earlier, and streamline their delivery workflows. This disciplined approach also helps organizations capture critical business requirements and translate them into verifiable conditions that software must meet before release.
AI Testing Tools
AI testing tools are transforming the way modern software teams approach quality assurance. Instead of relying solely on manual scripts and repetitive test execution, AI-driven solutions analyze application behavior, detect patterns, and automatically generate optimized test cases. This significantly reduces testing time while improving overall accuracy and coverage. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these tools can identify high-risk areas in the codebase, prioritize test scenarios, and even predict potential failures before they impact end users.
Another major advantage of AI in testing is self-healing automation. Traditional automated tests often fail when minor UI or structural changes occur. AI-powered tools adapt to such changes intelligently, minimizing maintenance efforts and reducing flaky tests. They also provide smart insights through analytics dashboards, helping teams make data-driven decisions about release readiness and performance bottlenecks.
As organizations adopt agile and DevOps practices, they increasingly rely on continuous testing. AI testing tools integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines, enabling faster feedback loops and boosting deployment confidence. Ultimately, these tools empower development teams to release reliable, high-quality applications at speed, optimize resources, and lower long-term testing costs.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom






























