Business
Everything You Should Know About Flow Measurement

Introduction
Flow measurement might not be something most people think about every day, but in industries like water treatment, oil and gas, food production, or even power generation, it’s a pretty big deal. Without it, systems can’t run smoothly, safely, or efficiently.
So, what exactly is flow measurement? Why does it matter? And how do tools like a vortex flow meter, vortex flow sensor, and vortex flow transmitter come into play?
Let’s break it all down in simple terms.
First Things First – What Is Flow Measurement?
Flow measurement is just figuring out how much liquid or gas is moving through a pipe, and how fast it’s going. That’s it. Simple idea, but super important.
Think of it like filling a bucket with water. You’d probably want to know two things:
- How fast the water’s coming in, and
- How much have you filled so far?
Now, take that same idea and apply it to something way bigger, like tracking how much gas is moving through a giant pipeline, or how much coolant is flowing through the system in a power plant.
That’s flow measurement in action. It might sound technical, but it’s just about keeping an eye on the movement of fluids, so things run smoothly.
If the flow’s off, too slow, too fast, or suddenly stops, it can mess with equipment, waste resources, or even cause safety issues. So yeah, it matters a lot.
Why Is It So Important?
Let’s take a few real-world examples:
- Talking about a water treatment plant, when you track water flow, you can make sure that clean water is delivered without wasting energy.
- In a chemical factory, mixing the wrong amounts of liquids can ruin a batch or even create a safety hazard.
- In a power station, managing the flow of steam helps keep electricity production efficient.
In short: if you can’t measure the flow, you can’t control it. And if you can’t control it, things can go wrong, fast.
So, How Do We Measure Flow?
There are a few different types of flow meters out there. Some use spinning parts, some use sound waves, and some (like the one we’re talking about today) use natural fluid behavior to do the job.
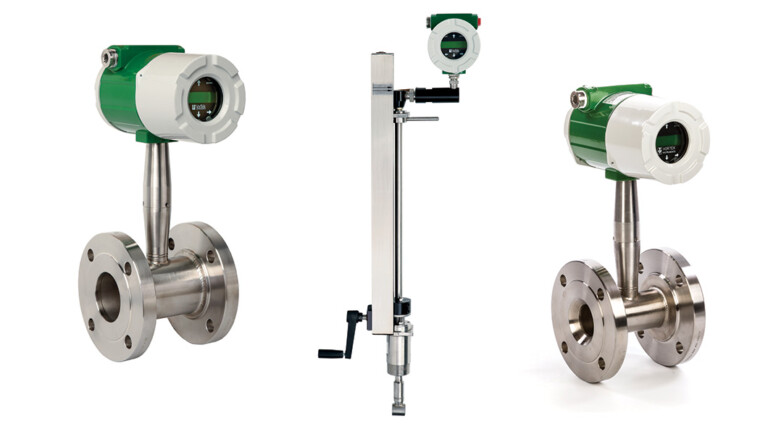
One of the most reliable and commonly used options is the vortex flow meter. It’s a smart piece of tech that works in a pretty cool way.
What Makes a Vortex Flow Meter So Special?
A vortex flow meter measures flow using a principle called vortex shedding. Here’s how it works in simple terms:
Inside the meter, there’s a fixed obstruction (called a bluff body) placed in the flow path. As the fluid, whether it’s a gas, liquid, or steam, passes this point, it creates small swirling patterns called vortices. These vortices are formed in a regular, repeating pattern that depends on the speed of the flow.
The meter counts the number of these vortex pulses and uses that information to calculate how fast the fluid is moving. The faster the flow, the more frequently the vortices appear.
One of the main advantages of a vortex flow meter is that it doesn’t rely on moving parts, which means less wear and tear and fewer maintenance issues. It’s accurate, reliable, and works well across a wide range of applications, especially in industrial systems like steam lines, chemical processing, and gas flow monitoring.
That’s what makes it a solid, go-to choice for industries where consistency and precision matter.
What About the Sensor and Transmitter?
Good question, because a vortex flow meter doesn’t work alone.
At the heart of it is the vortex flow sensor. This is the part that detects the little pressure changes or vibrations made by the vortices. Think of it as the “ears” of the system, picking up what’s going on inside the pipe and turning it into readable data.
Then comes the vortex flow transmitter. Its job is to take the signals from the sensor and convert them into a format that other systems can understand, like control panels, software dashboards, or automated machines. It tells the rest of the system, “Hey, here’s how fast the fluid is moving, and here’s how much has passed through.”
So, to sum it up:
- The sensor picks up the flow.
- The transmitter shares the data.
- The meter ties it all together.
Where Are These Tools Used?
You’d be surprised how often vortex flow tech shows up. It’s used in:
- Oil & gas pipelines – to keep track of fuel or gas movement.
- Power plants – to measure steam going into turbines.
- Pharma factories – for precise dosing of liquids.
- Food and beverage plants – to handle water, syrups, and more.
- HVAC systems – for chilled water or steam control.
Because vortex flow sensors and transmitters can handle high heat, pressure, and even corrosive liquids, they’re a go-to option when things get tough.
Final Thoughts
You don’t have to be an engineer to understand how vital flow measurement is. Whether it’s running a power plant or processing tomato sauce in a factory, knowing how much fluid or gas is moving through your system is the backbone of smooth operations.
Devices like the vortex flow meter, vortex flow sensor, and vortex flow transmitter make that job easier, more accurate, and more reliable. They may not be flashy, but behind the scenes, they’re doing the work that keeps entire systems running.
Business
Brand New Houses in Jordan Springs | Your Sanctuary Awaits
Business
Solar Cell Materials Market | Size, Share & Forecast 2031

The Solar Cell Materials Market is at the heart of the global transition toward sustainable energy. As solar photovoltaic (PV) installations expand rapidly across residential, commercial, and utility sectors, materials that make up solar cells are becoming increasingly strategic assets. These materials determine not only the efficiency and longevity of solar modules but also influence manufacturing costs, project economics, and sustainability outcomes.
From silicon wafers to advanced perovskites and thin-film compounds, manufacturers, researchers, and policymakers are focused on optimizing the building blocks of solar technology. This blog explores the growth strategies, key market segments, leading players, and global regional dynamics shaping the Solar Cell Materials Market today and into the next decade.
Understanding the Solar Cell Materials Market
At its core, the Solar Cell Materials Market includes the essential raw materials and compounds used in constructing photovoltaic cells—components that convert sunlight into electricity. These range from well-established silicon materials to emerging perovskites and specialized chemical films that enhance performance or enable new applications.
This market is directly influenced by broader PV industry trends such as declining costs, expanding solar capacity, material innovation, and policy support for renewable adoption. As global energy systems decarbonize, demand for efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solar cell materials continues to rise.
Key Market Segments
The Solar Cell Materials Market can be broadly categorized by material type, application, and end-user, each offering unique growth opportunities and technical challenges.
-
Material Types
The market includes a range of foundational material categories:
- Silicon-Based Materials: Monocrystalline and polycrystalline silicon remain dominant due to high efficiency and established supply chains.
- Thin-Film Materials: Technologies like Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) and Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) offer advantages in specific use cases, including flexible or semi-transparent installations.
- Perovskite Materials: Emerging perovskite compounds promise high efficiency with potential cost benefits and flexibility for novel applications.
- Composite and Other Materials: Anti-reflective coatings, contacts (e.g., silver, aluminum), encapsulants, and backsheets enhance durability and performance.
-
Application Segments
Solar cell materials support a wide range of PV applications:
- Residential Solar Installations
- Commercial and Industrial Projects
- Utility-Scale Solar Plants
- Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
- Portable and Specialized PV Systems
-
End Users
Materials are supplied to and used by:
- Photovoltaic Module Manufacturers
- R&D and Research Institutions
- EPC (Engineering, Procurement & Construction) Firms
- Government & Policy Bodies
- OEMs and Specialized Fabricators
Each segment represents distinct demand dynamics, cost sensitivities, and innovation pathways, shaping how companies prioritize research and production.
Growth Strategies Fueling the Solar Cell Materials Market
To stay competitive and responsive to evolving technology needs, companies in the Solar Cell Materials Market are leveraging a range of strategic initiatives:
-
Investing in R&D and Technology Innovation
Research efforts are directed at improving material efficiency, lowering manufacturing costs, and enabling next-generation PV technologies such as tandem perovskite-silicon cells. Continuous material innovation helps firms stay ahead in performance metrics while aligning with sustainability goals.
-
Strategic Collaborations and Partnerships
Companies are forming alliances that expand geographic reach, enhance product portfolios, and accelerate technological adoption. Partnerships with research institutions and technology startups are common, facilitating rapid commercialization of new material types and manufacturing techniques.
-
Scaling Manufacturing and Supply Chain Integration
Building robust manufacturing capacities and securing supply chains for critical materials such as silicon wafers or metal targets helps firms capture market share and mitigate dependency on external suppliers. Domestic capacity expansions and production footprints across multiple regions support this strategy.
-
Diversification of Product Applications
Firms are diversifying offerings to serve different PV applications, from traditional utility installations to emerging segments like flexible and integrated PV systems. This diversification spreads risk and taps into multiple revenue streams.
-
Market Positioning through Cost Leadership and Quality Assurance
Optimizing production processes, embracing automation, and adopting stringent quality standards help companies compete on both cost and performance—critical factors in a price-sensitive global market.
Top Players in the Solar Cell Materials Market
The Solar Cell Materials Market comprises a mix of global conglomerates, specialized material firms, and integrated PV manufacturers that influence global material trends. Notable names include:
- Wacker Chemie AG – Known for advanced silicon and chemical materials for PV manufacturing.
- LONGi Green Energy Technology – Major producer of silicon wafers and renewable tech components.
- Hanwha Q CELLS – Integrated solar manufacturer with material and cell production capabilities.
- First Solar, Inc. – Leader in CdTe thin-film technology and advanced PV materials.
- Canadian Solar Inc. – Global player in PV modules and material sourcing.
- JA Solar & Trina Solar – Strong presence in material supply and solar cell production.
- Targray – Supplier of critical PV materials, including silicon and contacts.
- Other Key Players: Fuji, Tokuyama, Asahi Technologies, Risen Energy, GCL-Poly Holdings.
These companies use their global networks, manufacturing scale, and research resources to stay competitive and shape industry direction.
Regional Analysis of the Solar Cell Materials Market
The geographical footprint of solar cell materials highlights diverse growth patterns, influenced by policy, manufacturing expertise, and renewable energy demand.
Asia Pacific
Asia Pacific leads the market due to widespread solar installations, strong manufacturing infrastructure, and supportive government policies across countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea. The region is a major hub for silicon and PV material production and continues to attract investment to expand capacity.
Europe
Europe maintains a strong position driven by ambitious renewable targets and investments in high-efficiency materials research. The European Union’s funding programs emphasize sustainable material development and commercialization.
North America
North America is focused on bolstering domestic supply chains and reducing dependency on imports, especially following tariff actions on imported solar materials. Policy incentives and R&D investments play a key role in regional strategy.
Latin America and Middle East/Africa
These regions, while currently smaller, are attracting incremental interest as solar energy adoption spreads and countries seek localized material supply and solar infrastructure solutions.
Emerging Trends and Market Opportunities
Several trends are shaping the Solar Cell Materials Market’s future:
- Perovskite and Tandem Technologies: Next-generation cells combining perovskite with silicon promise higher efficiencies and new form factors.
- Flexible & BIPV Materials: Materials enabling flexible and building-integrated photovoltaic systems are expanding application use cases.
- Government Backing: Renewables research funding and incentives in the U.S., Europe, and Asia support material innovation.
- Trade Policy Impact: Tariffs and supply chain realignment influence material cost structures and regional competitiveness.
Conclusion
The Solar Cell Materials Market is a dynamic landscape where innovation, strategy, and sustainability converge. Growth strategies like R&D investment, strategic partnerships, and production scaling help companies navigate competitive pressures while expanding global access to solar energy. With diverse materials catering to different PV applications and strong regional momentum, this market plays a pivotal role in accelerating the global energy transition.
As material technologies evolve and adoption expands across segments and regions, stakeholders in this market—from manufacturers to policymakers—will continue to shape the future of clean, reliable solar power worldwide.
Art /Entertainment
Flower Delivery Rosanna: Same Day & Local Florist

Birthdays, anniversaries, celebrations, and heartfelt moments all deserve something special, and nothing captures emotion quite like fresh flowers. With reliable flower delivery Rosanna, sending a meaningful floral gift has never been easier. Whether you’re celebrating a joyful milestone or offering comfort and support, beautifully arranged flowers help you express your feelings in a thoughtful and memorable way.
At Ivy & Twig Flowers, we believe flowers should feel personal, elegant, and intentional. Every bouquet we create is designed to reflect care, creativity, and quality, ensuring your floral gift leaves a lasting impression from the moment it arrives.

Why Flowers Remain a Timeless Gift
Flowers have been used to communicate emotions for centuries, and their impact remains just as powerful today. They transcend language, culture, and age, making them one of the most versatile gifts for any occasion. A thoughtfully chosen arrangement can convey love, appreciation, sympathy, or celebration without the need for words.
Different blooms carry different meanings. Roses are often associated with romance and admiration, lilies symbolize elegance and peace, and seasonal mixed bouquets bring warmth and joy. Choosing flowers allows you to tailor your message and create a gift that feels genuine rather than generic.
The Convenience of Local Flower Delivery
In today’s busy world, convenience matters. Not everyone has the time to visit a florist in person, especially when life gets hectic or plans change at the last minute. That’s where professional local flower delivery becomes invaluable.
With trusted delivery services, your flowers arrive fresh, vibrant, and beautifully presented. Because local deliveries cover shorter distances, blooms maintain their quality and longevity. This ensures the recipient enjoys their flowers for days to come, making your gesture even more meaningful.
For those last-minute surprises or unexpected moments, same day flower delivery offers peace of mind. Knowing that your flowers can still arrive on time allows you to celebrate special moments without stress.
Flowers for Every Occasion
One of the greatest strengths of a local florist is the ability to design flowers for a wide range of occasions. At Ivy & Twig Flowers, each arrangement is created with purpose and attention to detail.
Birthdays
Bright, cheerful blooms are perfect for celebrating birthdays. Colorful seasonal arrangements add excitement and joy, making the day feel extra special.
Anniversaries and Romantic Gestures
Romantic bouquets featuring roses or soft pastel tones are a timeless way to express love and appreciation. Flowers can turn a simple moment into a cherished memory.
Sympathy and Condolences
During difficult times, flowers offer comfort when words feel inadequate. Soft, elegant arrangements help express sympathy and support with grace and sensitivity.
Thank You and Appreciation
A bouquet is a thoughtful way to say thank you. Whether it’s for a friend, family member, or colleague, flowers show gratitude in a warm and meaningful way.
Corporate and Professional Gifting
Fresh flowers also suit professional environments. From office spaces to client gifts, floral arrangements create a welcoming and polished impression.
What Makes Ivy & Twig Flowers Different
Choosing a florist isn’t just about convenience — it’s about trust, quality, and creativity. Ivy & Twig Flowers is known for modern floral designs, premium blooms, and a personalized approach to every order.
Our florists carefully select flowers based on freshness, seasonality, and visual harmony. Each bouquet is designed to feel balanced, stylish, and unique. We focus on quality over quantity, ensuring every arrangement reflects thoughtful craftsmanship rather than mass production.
Presentation matters too. From wrapping to finishing touches, every detail is considered so your flowers feel refined and luxurious.
Supporting Local Floristry
When you choose a local florist, you’re supporting more than just a business — you’re supporting local growers, artisans, and the community. Local florists understand seasonal availability, local preferences, and the importance of personalized service.
This local knowledge allows for better quality control and faster turnaround times. It also ensures your flowers feel relevant, fresh, and thoughtfully curated rather than generic or rushed.
Creating Meaningful Delivery Moments
A flower delivery is more than just a transaction — it’s an experience. The moment the door opens, the fragrance, colors, and presentation all contribute to a lasting emotional response.
At Ivy & Twig Flowers, we focus on creating those moments. Whether it’s a planned celebration or a spontaneous surprise, we ensure every delivery is handled with care, professionalism, and attention to detail.
From secure packaging to timely arrival, our goal is to make sure your flowers arrive looking just as beautiful as intended.
Choose Ivy & Twig Flowers with Confidence
Flowers have the power to connect people, mark important milestones, and brighten everyday moments. With professional flower delivery Rosanna and the option of same day flower delivery, Ivy & Twig Flowers makes it easy to send thoughtful, stylish floral gifts when they matter most.
No matter the occasion, our passion for floristry and commitment to quality ensure your flowers leave a lasting impression — from the moment they arrive to the days they continue to bloom.
-
Business2 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom
































