health
Going Gluten-Free: Is It Always Necessary for Good Health?

Are you considering going gluten-free? With the rise of gluten-free diets, it’s no surprise that more and more people are jumping on board. But is it really necessary for good health? In this blog post, we’ll explore what gluten is, who may benefit from a gluten-free diet, and whether or not there are alternatives to going completely gluten-free. So grab your favorite snack (gluten-free or not!) and let’s dive in!
What is Gluten?
Gluten is a protein found in grains such as wheat, barley and rye. It’s what gives bread its chewy texture and helps it rise when baked. Gluten can also be found in products such as pasta, cereals, beer, and even some processed foods like sauces.
For people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance, consuming gluten can cause damage to the small intestine lining leading to various digestive symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, constipation and abdominal pain.
Gluten-free diets have gained popularity over the years not just for those who suffer from celiac disease or gluten intolerance but also for people who want to improve their overall health. However, cutting out gluten means eliminating many common sources of fiber which may lead to nutritional deficiencies if not done properly.
It’s important to note that there are still plenty of nutritious whole grains available that don’t contain gluten such as quinoa, rice and oats (if they are certified gluten-free). A balanced diet should include a variety of foods rich in vitamins and minerals regardless of whether they contain gluten or not.
Celiac Disease and Gluten Intolerance
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine when gluten is ingested. Gluten intolerance, on the other hand, can cause similar symptoms but does not involve an autoimmune response.
Celiac disease affects about 1% of the population, and those with it must maintain a strict gluten-free diet to avoid damage to their intestines. Symptoms may include diarrhea, bloating, abdominal pain or discomfort, or even joint pain and fatigue.
Gluten intolerance can be more challenging to diagnose as there are no specific tests for it yet. However, individuals who experience symptoms such as bloating and digestive issues after consuming gluten may benefit from avoiding it in their diets.
It’s essential to note that going gluten-free without medical necessity can lead to unintended consequences such as missing out on necessary nutrients found in whole grains like wheat and barley. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant dietary changes.
While celiac disease requires a strict avoidance of gluten-containing foods for optimal health outcomes; non-celiac individuals should approach going gluten-free with caution and proper guidance from healthcare professionals.
The Pros and Cons of a Gluten-Free Diet
A gluten-free diet has become a popular trend in recent years, with many claiming it to be the best way to improve their health. However, like any other dietary change, there are both pros and cons to consider.
On the positive side, a gluten-free diet can be beneficial for people who have celiac disease or gluten intolerance. For these individuals, consuming even small amounts of gluten can lead to painful digestive symptoms and long-term damage to the gut lining. By eliminating gluten from their diets completely, they can avoid these issues altogether.
Additionally, some people report feeling better on a gluten-free diet due to reduced inflammation in their bodies. This may improve conditions such as arthritis or skin disorders.
However, there are also potential downsides to going gluten-free. Gluten-containing grains such as wheat provide important nutrients like fiber and B vitamins that are necessary for overall health. A strict avoidance of these foods could lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully managed.
Furthermore, many commercially available gluten-free products contain higher levels of sugar and fat than their traditional counterparts. This could contribute negatively towards weight gain or poor blood sugar control if consumed excessively.
In summary, while cutting out gluten may be essential for certain individuals’ wellbeing; it is not necessarily suitable for everyone else’s optimal nutrition needs unless medically indicated by health professionals through comprehensive assessments determining individual nutritional requirements limiting inadequate food choices that result in macro- micro-nutrient deficiencies over time which might negatively impact physical and mental performance capabilities beyond addressing various existing auto-immune conditions that require specific dietary modifications tailored towards each person’s unique medical history circumstances based on scientific evidence-based guidelines recommended by registered healthcare practitioners specialized in clinical nutrition expertise rather than self-diagnosing via following social media influencers’ recommendations!
Gluten-Free Recipes
Looking for gluten-free recipe inspiration? You’ve come to the right place! There are plenty of tasty dishes that don’t include any gluten-containing ingredients.
For breakfast, try whipping up some gluten-free pancakes made with almond flour or coconut flour. Top them off with fresh fruit and a drizzle of maple syrup for a sweet start to your day.
If you’re in the mood for something savory, consider making a quinoa salad loaded with veggies like roasted peppers, tomatoes, and cucumbers. Toss it all together with some olive oil and vinegar for an easy lunch option.
For dinner, try replacing traditional pasta noodles with zucchini noodles or spaghetti squash. These veggies make great low-carb substitutes that won’t leave you feeling bloated or weighed down.
And when it comes to dessert, there are plenty of options too! From homemade ice cream made with coconut milk instead of dairy to chocolate avocado mousse that’s free from refined sugar – the possibilities are endless.
The key to successful gluten-free cooking is experimenting until you find what works best for you. With so many delicious recipes out there, going without gluten doesn’t have to mean sacrificing flavor or enjoyment at mealtime.
Alternatives to a Gluten-Free Diet
If you have been advised to stay away from gluten due to health reasons, there are alternatives that can help you achieve good health without sacrificing taste.
One option is to substitute wheat flour with alternative flours such as almond, coconut or oat flour which are naturally gluten-free and rich in protein and fiber. These flours can be used for baking bread, cakes, and other baked goods.
Another alternative is incorporating more fruits, vegetables and lean proteins into your diet. Fresh produce not only provides essential vitamins and minerals but also contains plenty of dietary fiber that helps regulate digestion. Lean meats like chicken or fish provide high-quality protein while being low in fat.
It’s also important to read labels carefully when grocery shopping because many processed foods contain hidden sources of gluten such as soy sauce or malt extract. Opting for whole foods that are minimally processed will ensure a healthy balance of nutrients without the risk of consuming hidden gluten.
In summary, adopting a gluten-free diet isn’t always necessary for good health if one chooses the right alternatives. By using different types of flours in cooking or increasing intake of fresh produce and lean proteins while avoiding heavily processed foods containing hidden sources of gluten can lead to better overall well-being.
Conclusion
In summary, going gluten-free is not necessary for good health unless you have celiac disease or gluten intolerance. For those who do not have these conditions, eliminating gluten from their diet may actually be detrimental to their overall nutrition and enjoyment of food.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet. They can help determine if a gluten-free diet is the right choice for you based on your individual needs and medical history.
If you do decide to go gluten-free, there are plenty of delicious recipes and alternatives available that will allow you to still enjoy your favorite foods without sacrificing taste or variety.
Ultimately, whether or not you choose to adopt a gluten-free lifestyle should be based on informed decision-making and personal preference rather than trendy diets or misinformation. By staying educated about different dietary options, we can all make choices that support our physical and mental well-being in the long term.
Beauty Fitness
Liposuction in Dubai: Transform Your Body with Expert Care
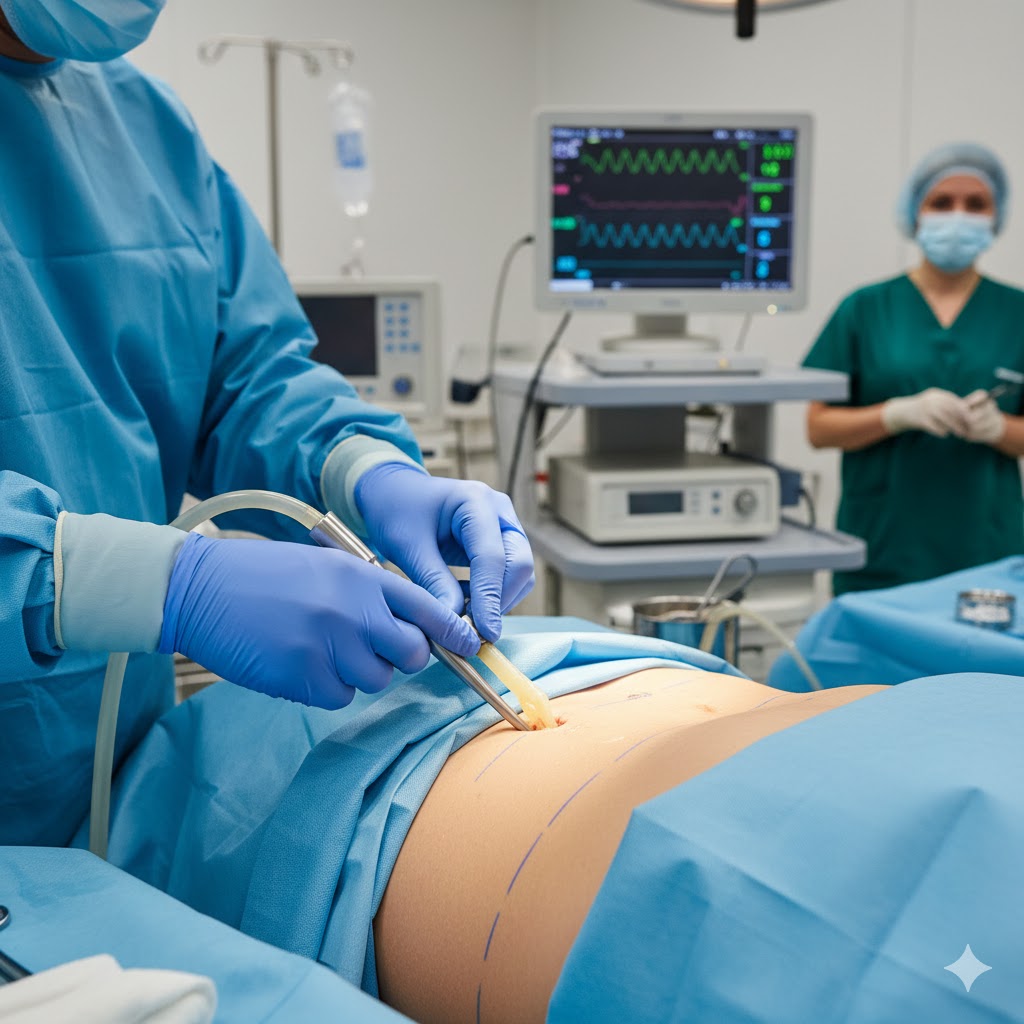
For many, the journey toward a confident self-image involves overcoming physical barriers that diet and exercise simply cannot address. Genetic predispositions often lead to fat accumulation in specific “pockets” that remain unchanged regardless of metabolic effort. Liposuction in Dubai offers a clinically proven pathway to remove these obstacles, allowing your natural hard work to finally show through. In our clinical experience, the transformation is as much psychological as it is physical, as patients often find a renewed sense of motivation once their external appearance aligns with their internal health goals.
What is Liposuction in Dubai
In its most modern form, fat removal is a sophisticated surgical art used to excise subcutaneous fat and refine the body’s silhouette. It is not a generalized weight-loss solution but a precision tool for contouring. By utilizing advanced medical suction, surgeons can systematically reduce volume in areas that cause physical or aesthetic discomfort. At Tajmeels Clinic, we prioritize a “natural-first” philosophy, ensuring that every procedure enhances the patient’s existing proportions rather than creating an artificial or overdone appearance.
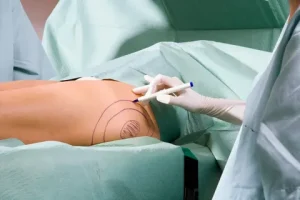
How Liposuction in Dubai Works
The procedure functions by disrupting the bond between fat cells and the surrounding connective tissue to allow for safe extraction. The “Tumescent Technique” is the modern foundation of this process, where a specialized medicated fluid is injected into the fat layers to numb the area and minimize blood loss. Once the tissue is prepared, a micro-cannula is inserted through tiny, hidden incisions. The surgeon then uses a gentle back-and-forth motion to vacuum out the targeted fat. Advanced technologies like VASER or Power-Assisted Liposuction (PAL) may be used to increase precision and ensure the skin settles smoothly over the new frame.
Why Liposuction in Dubai Is Used
This treatment is primarily used to restore balance to a figure that has become disproportionate due to localized fat deposits. It is an ideal solution for those dealing with “lifestyle-resistant” fat—areas that do not shrink despite a caloric deficit. Common reasons for seeking the procedure include refining the jawline, smoothing the “bra-line” on the back, or slimming the outer thighs. In our clinical experience, many patients also use it as a corrective measure after significant weight loss to address the remaining stubborn bulges that prevent clothes from fitting properly.
Key Benefits of Professional Body Contouring
The advantages of undergoing a professionally managed fat removal procedure extend into various aspects of daily life. Beyond the immediate change in measurements, patients enjoy:
-
Improved Physical Mobility: Reducing fat in the inner thighs or abdomen can make exercise more comfortable.
-
Enhanced Posture: Removing heavy “pendulous” fat from the lower stomach can alleviate strain on the lower back.
-
Permanent Cellular Reduction: Unlike dieting, which only shrinks cells, this procedure removes them entirely.
-
Clothing Versatility: Patients often report finally being able to wear tailored or fitted garments with confidence.
Ideal Candidates for Body Transformation
Successful outcomes depend heavily on proper patient selection. What patients typically report during recovery is that having realistic expectations and a stable starting weight made their results feel much more rewarding.
| Candidate Profile | Ideal Requirements |
| Stability | A weight that has remained consistent for at least 6-12 months. |
| Skin Health | Good elasticity to ensure the skin “wraps” tightly around the new shape. |
| Medical History | No history of poor wound healing or uncontrolled circulatory issues. |
| Commitment | Willingness to follow strict post-operative garment protocols. |
Step-by-Step Treatment Process
The treatment is a carefully orchestrated medical event designed for safety and aesthetic success:
-
Marking & Mapping: While the patient is standing, the surgeon maps the specific fat deposits to be treated.
-
Anesthesia: Usually performed under general anesthesia or deep sedation for the patient’s total comfort.
-
Infiltration: The target area is “inflated” with tumescent fluid to protect the tissues.
-
Emulsification: (If applicable) Ultrasound or laser energy is used to soften the fat.
-
Aspiration: Precise removal of fat cells using a fanning technique to ensure evenness.
-
Closure: Incisions are so small they often do not require traditional stitches, allowing for easier drainage.
Common Treatment Zones for Men and Women
The versatility of modern equipment means almost any area with fat can be treated. For women, the “Love Handles” and “Tummy” are frequent priorities. For men, the “Flanks” and the “Chest” (treating gynecomastia) are high-demand areas. In our clinical experience, treating the arms—specifically the “tricep” area—is increasingly popular as it provides an immediate “slimming” effect that is visible in almost all types of clothing.
Cost Factors and Quality Standards
The cost of your transformation is determined by the scope of the procedure. Factors such as the number of areas treated, the volume of fat removed, and the advanced technology (like VASER) utilized all influence the final price. It is important to remember that a “low-cost” approach often skips essential safety steps or post-operative support. At Tajmeels Clinic, we focus on providing a premium environment where the surgeon’s skill and the facility’s safety standards ensure a world-class result.
Recovery Timeline and What to Expect
Healing from a contouring procedure is a process of “remodeling” that the body does over several months.
-
Days 1-5: You will wear a compression garment 24/7. Some “leakage” of the tumescent fluid is normal and expected.
-
Week 2: Most patients are back to work. Swelling is present but beginning to migrate downward.
-
Month 1: You can usually stop wearing the garment during the day. Results are starting to look “sleek.”
-
Month 6: The “final” look is achieved as all internal inflammation has completely resolved.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
While Liposuction in Dubai is considered a safe and standard cosmetic procedure, it is still surgery. Temporary side effects include swelling, bruising, and a feeling of “stiffness” in the treated area. Serious complications are rare when the procedure is performed by a qualified expert in a sterile hospital setting. Following the post-op care plan—especially staying hydrated and moving frequently—is the best way to prevent complications like blood clots or irregular contouring.
How to Maintain Your Results Long-Term
The results of your procedure are permanent in the sense that the fat cells are gone, but you must still maintain a healthy lifestyle. If you gain significant weight, the remaining fat cells in your body will expand. What patients typically report during recovery is that the visible “jump start” provided by the surgery makes it much easier to stick to a high-protein, low-sugar diet. We recommend consistent, moderate exercise to keep the skin firm and the underlying muscles toned, ensuring your new silhouette remains sharp for years to come.
Conclusion
Choosing to transform your body through surgical contouring is a powerful step toward a more confident lifestyle. At Tajmeels Clinic, we are dedicated to providing the expertise, care, and advanced technology needed to help you achieve your aesthetic goals safely. Your body is unique, and your treatment plan should be as well. We invite you to explore the possibilities of a more sculpted, balanced version of yourself.
Learn if this treatment is right for your lifestyle by scheduling your private consultation today.
Care
Mounjaro in Dubai: Transformative Weight Management
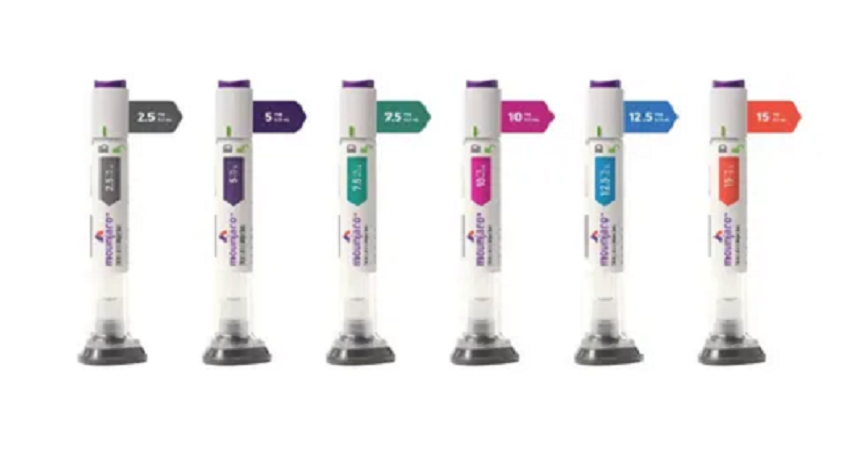
The pursuit of optimal health and a balanced physique has reached a new technological peak in the UAE. As a global hub for medical innovation, Mounjaro in Dubai has emerged as a transformative option for individuals struggling with chronic weight issues and metabolic disorders. Unlike many previous treatments that offered limited success, this therapy leverages dual-hormone science to provide a more robust and sustainable approach to wellness.
What is Mounjaro in Dubai?
Mounjaro is a first-of-its-kind injectable medication that contains tirzepatide. It is specifically engineered to target the root causes of metabolic imbalance rather than just treating symptoms. By acting on both the Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptors, it offers a comprehensive solution for those who have found traditional weight-loss methods insufficient.
At Tajmeels Clinic, we see a diverse range of patients who are looking for a scientifically backed method to reset their metabolic clock. This medication is not a “quick fix” but a sophisticated clinical tool that, when administered under professional guidance, helps the body function more efficiently. It is provided in a user-friendly, once-weekly injection pen.
Understanding the 2026 Benefits of Mounjaro in Dubai
The primary reason for the rising popularity of this treatment lies in its high efficacy rate. Clinical data suggests that the dual-agonist approach is significantly more powerful than single-agonist therapies used in the past. This translates to better blood sugar control and more substantial weight reduction for the average patient.
In our clinical experience, the benefits extend far beyond aesthetic changes. Patients often report improved cardiovascular markers, such as lower blood pressure and healthier cholesterol levels. What patients typically report during recovery is a renewed sense of vitality, as their bodies are no longer struggling with the inflammatory effects of excess weight and high insulin levels.
How the Medication Works: Mechanism of Action
To understand why this therapy is so effective, one must look at how it interacts with the gut and the brain. The medication mimics two natural hormones that are released after a meal. These hormones work in tandem to optimize the body’s energy use and signal satiety to the brain.
-
GIP Receptor Activation: This component improves insulin sensitivity and helps the body process fats more effectively.
-
GLP-1 Receptor Activation: This part slows down the speed at which the stomach empties, helping you feel full longer, and tells the brain to reduce hunger signals.
Why Mounjaro in Dubai is Preferred for Metabolic Health
Metabolic health is the foundation of long-term well-being. For many, the “food noise”—that constant mental preoccupation with eating—is the biggest barrier to success. This treatment effectively “mutes” that noise, allowing patients to make conscious, healthy food choices without feeling the pangs of intense cravings.
Choosing Mounjaro in Dubai allows residents to access the latest in global pharmaceutical standards within a highly regulated medical environment. The clinical focus here is on “metabolic flexibility,” which is the body’s ability to switch between burning carbohydrates and burning fat as needed.
Ideal Candidates for the Program
This treatment is not for everyone. It is clinically indicated for adults with a BMI of 30 or higher (obesity), or a BMI of 27 or higher (overweight) when accompanied by at least one weight-related medical condition, such as:
- Type 2 Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- High Cholesterol
Before starting, a comprehensive blood panel is conducted to check liver and kidney function, as well as thyroid health. This ensures that the treatment is safe and tailored to your specific physiological profile.
The Treatment Procedure: Step-by-Step
The administration of the medication is designed to be as non-intrusive as possible. Once the medical team has determined your starting dose (typically 2.5 mg), you will follow a simple weekly routine.
| Phase | Duration | Clinical Focus |
| Initiation | Weeks 1–4 | Building tolerance at a low dose (2.5 mg) |
| Escalation | Weeks 5–12 | Gradually increasing dose (5 mg to 7.5 mg) |
| Maintenance | Week 13+ | Finding the “sweet spot” dose for sustained results |
Each injection is subcutaneous, meaning it goes just under the skin. Patients are taught to rotate injection sites—abdomen, thigh, or upper arm—to ensure the best absorption and skin comfort.
Clinical Outcomes of Mounjaro in Dubai
In terms of real-world results, many patients observe a noticeable change in their appetite within the first 48 hours of the first dose. Over the first month, the focus is primarily on adjusting to the medication and establishing a new, healthier eating rhythm.
The long-term goal is a total body transformation that prioritizes health over just “thinness.” Because the medication helps regulate insulin, it reduces the likelihood of the “yo-yo” effect often seen with standard diets. This stability is why many healthcare providers consider it a gold standard in modern obesity medicine.
Common Side Effects and Safety Measures
While highly effective, patients should be prepared for potential adjustments. Most side effects are gastrointestinal and occur when moving up to a higher dose.
- Mild Nausea: Often happens the day after the injection.
- Indigestion: Due to slower stomach emptying.
- Fatigue: A common response as the body adapts to a lower calorie intake.
To manage these, we recommend staying well-hydrated and avoiding heavy, fatty meals immediately before or after your injection. If a patient experiences severe abdominal pain or persistent vomiting, they are advised to contact their medical provider immediately.
Cost Factors and Treatment Duration
The investment in this therapy covers more than just the medication; it includes the diagnostic tests, regular follow-ups, and the expertise of a licensed medical team. The duration of the program varies depending on the individual’s goals and metabolic response.
Some patients may require a 6-month protocol, while others with more significant health challenges may stay on a maintenance dose for a year or more. Since health is an ongoing journey, the focus is on providing a plan that is both medically sound and financially transparent.
Maintaining Results and Post-Treatment Care
One of the biggest concerns for patients is what happens after the injections stop. The key to long-term success is the “re-education” of the body’s lifestyle habits while on the medication.
- Protein Intake: Vital for preserving muscle mass.
- Strength Training: Keeps the metabolism active.
- Hydration: Assists the kidneys and aids digestion.
By the time you reach your target weight, your body should be acclimated to smaller, nutrient-dense portions, making it easier to maintain your new weight naturally.
Conclusion
Making the choice to start Mounjaro in Dubai is a commitment to a healthier, more vibrant version of yourself. At Tajmeels Clinic, we are dedicated to ensuring that your transition into this new phase of health is safe, professional, and ultimately successful. The science is clear: when you address the hormonal causes of weight gain, the results follow.
Learn if this treatment is right for your lifestyle by scheduling a consultation with our metabolic health experts. Taking the first step is often the hardest part, but you don’t have to do it alone.
Beauty Fitness
Liposuction and Buttock Augmentation in Riyadh

Beauty standards and body symmetry are among the top concerns for many women today. Achieving an “hourglass figure”—characterized by a sculpted waist and well-proportioned buttocks—has become an achievable dream thanks to remarkable medical advancements. Liposuction in Riyadh is no longer simply about weight loss; it has evolved into the art of “fat redistribution.”
Surgeons extract fat from areas of localized fat deposits, such as the abdomen and back, then purify it and reinject it into the buttocks to give them an attractive volume and natural shape. This ensures a harmonious appearance that boosts self-confidence, all under the supervision of a select group of the capital’s most skilled cosmetic surgeons.
What does the procedure for waist sculpting and buttock augmentation using autologous fat involve?
Practitioners know this procedure globally as the “Brazilian Butt Lift” (BBL). It offers a dual benefit and relies on the use of natural body tissues instead of artificial fillers.
Waist sculpting: Surgeons perform this by liposuctioning the “flanks,” lower back, and abdomen to accentuate the waist curve.
Buttock augmentation: They achieve this by processing the extracted fat and injecting it precisely into specific areas of the buttocks to lift and improve its shape.

Advantages of using autologous fat compared to silicone
Many people in Riyadh prefer using autologous fat for several key reasons:
- Complete safety: There is no risk of the body rejecting the injected substance because it is extracted from the patient himself.
- Natural appearance: The fat gives a natural texture and shape that is indistinguishable from the original tissue.
- Double benefit: Getting rid of annoying fat in one area and transferring it to another area that needs extra volume.
- Permanent results: Once the injected fat cells have stabilized, they live and grow as a permanent part of the body.
Techniques used in liposuction and fat injection
Beauty centers in Riyadh rely on the latest technologies to ensure the highest success rate for injected fat cells:
1. Vaser technology
Ultrasound waves are used to gently break down fat without destroying cell walls, making them ideal for reinjection, as they ensure that fat cells remain alive and healthy.
2. Fat purification technology
After liposuction, the fat is placed in special centrifuges to filter it from blood and fluids, to ensure that only “pure fat” is injected, increasing the chances of sustaining the results.
3. Microinjection technique
Fat is injected through very small incisions and in precise amounts into different layers of the muscles and skin of the buttocks to ensure even distribution and avoid lumps.
Who is the ideal candidate for this procedure?
- A woman who has a sufficient amount of fat in areas such as the abdomen, back, or thighs (donor areas).
- Those who are in good health and do not suffer from chronic diseases that hinder healing.
- For those looking to improve body shape, not just lose weight.
- Those who have realistic expectations about the final results.
What can a patient expect during the treatment journey?
Before the operation (preparation)
The doctor will ask you to undergo comprehensive blood tests, and to stop taking blood-thinning medications and smoking for at least two weeks to ensure good oxygen flow to the injected cells.
During the process
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and takes between 3 and 5 hours depending on the amount of fat to be transferred.
After the operation (recovery)
- Sleep: It is advised not to sit or sleep directly on your buttocks for two weeks to ensure that no pressure is put on the injected cells.
- Medical corset: A special corset must be worn to sculpt the waist and fix the new buttock shape.
- Results: Final results appear after about 3 months, which is the period the body needs to absorb a small portion of the fat and stabilize the larger portion permanently.
Tips to ensure lasting results
To maintain a sculpted waist and a toned rear, experts in Riyadh recommend:
- Maintaining a stable weight is important, as significant weight gain or loss may affect the size of the injected fat cells.
- Following a diet rich in protein and healthy fats in the first few weeks supports the growth of blood vessels around the new fat.
- Avoid strenuous exercise that targets the lower body for at least 6 weeks.
Why choose Riyadh for body sculpting surgery?
Riyadh has become a regional hub for force coordination operations thanks to the availability of:
- State-of-the-art equipment: Advanced laboratories for purifying and processing autologous fats.
- The surgeons’ expertise: High skill in the “art of sculpting” to ensure aesthetic proportions between the waist and buttocks.
- Integrated care: Careful follow-up programs ensure that the recovery period passes safely and securely.
Conclusion
Achieving a harmonious, feminine figure with a sculpted waist and attractive rear is an investment in your beauty and self-confidence. Thanks to autologous fat transfer techniques, you can reshape your body naturally and safely, avoiding the risks of artificial materials. The balance between science and artistry is what makes all the difference in the results of these delicate procedures. For optimal results that combine medical professionalism with a refined aesthetic touch, we recommend visiting our cosmetic clinic in Riyadh .
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom