health
From mice to humans: Promising results from experimental treatments for aging

As we age, our bodies undergo a multitude of changes that can result in various health issues. From wrinkles to chronic diseases, the effects of aging are prevalent and unavoidable. However, recent experimental treatments for aging have shown promising results that could potentially slow down or even reverse some of these effects. In this blog post, we’ll explore the current state of research on anti-aging treatments for humans and delve into the exciting breakthroughs from animal trials that offer hope for a healthier future. So let’s dive in!
What causes aging?
Aging is a complex process that involves several factors, both intrinsic and extrinsic. One of the most significant contributors to aging is biological changes within our bodies. As we age, our cells become less efficient in repairing DNA damage and other cellular functions, leading to cellular senescence.
Additionally, lifestyle choices such as poor diet and lack of exercise can contribute to premature aging by causing oxidative stress in the body. Exposure to environmental pollutants and UV rays from the sun can also accelerate the aging process.
Another key contributor to aging is inflammation. Chronic inflammation has been linked to numerous diseases associated with aging, including dementia, heart disease and cancer.
Genetics play a role in how we age. Some people may be more predisposed than others due to their genetic makeup or family history of certain health conditions.
In summary, there are multiple causes contributing towards the overall process of ageing which makes it difficult for scientists when trying new treatments for anti-aging purposes.
Current experimental treatments for aging
Current experimental treatments for aging are focused on tackling the underlying causes of aging. One area of research is in senolytics, which target senescent cells that accumulate in our bodies as we age. These cells have stopped dividing and start to secrete harmful molecules that contribute to inflammation and tissue damage.
Another approach is through caloric restriction or intermittent fasting, which has been shown to increase lifespan in animal studies by improving cellular stress resistance, enhancing DNA repair mechanisms and reducing oxidative stress.
Other experimental treatments include gene therapies aimed at restoring telomere length or increasing levels of sirtuins – proteins involved in regulating metabolism and cellular processes.
While these treatments show promise in preventing or slowing down the effects of aging, more research is needed before they can be safely used on humans. It’s important also to note that there may be unintended consequences with some interventions, so careful testing and monitoring will be necessary before any widespread use.
There is hope that continued research into experimental treatments for aging will lead us towards a healthier future where people can live longer lives without the negative effects often associated with growing old.
How these treatments work
The experimental treatments for aging target different aspects of the aging process. Some focus on repairing damage to cells and tissues, while others aim to improve overall health and longevity.
One approach is senolytics, which involves removing senescent cells that accumulate in our bodies as we age. These cells are no longer able to divide and can cause inflammation and tissue damage if they remain in the body. By clearing them out, researchers hope to reduce age-related diseases like arthritis, heart disease, and dementia.
Another approach is caloric restriction mimetics (CRMs), which mimic the effects of a low-calorie diet without requiring people to actually restrict their food intake. CRMs activate pathways that regulate metabolism and cellular stress responses, leading to improved healthspan.
Other treatments include targeting mitochondrial dysfunction or improving DNA repair mechanisms. All of these approaches have shown promising results in animal models.
While there is still much research needed before these treatments can be used in humans, they offer hope for addressing age-related diseases and extending healthy lifespan.
Promising results from animal trials
Promising results from animal trials have shown that experimental treatments for aging may be effective in extending lifespan and improving overall health. Several studies on mice, rats, and other animals have demonstrated the potential of these treatments to slow down or even reverse the effects of aging.
One promising treatment is senolytics, which involves removing senescent cells that accumulate in the body over time and contribute to age-related diseases. Animal trials have shown that senolytics can improve various aspects of health, such as reducing inflammation and increasing physical activity.
Another experimental treatment that has shown promise is rapamycin, a drug originally used to suppress the immune system. Studies on mice have found that rapamycin can extend lifespan by up to 25% while also improving cognitive function and reducing cancer risk.
In addition to these treatments, researchers are exploring other methods for targeting aging at its source, including interventions that target cellular metabolism or genetic pathways involved in longevity. While more research is needed before any of these treatments can be approved for human use, the results from animal trials offer hope for a healthier future with extended lifespans.
The next steps in research
The promising results from animal trials have given researchers hope that we may one day be able to slow down or even reverse the aging process in humans. However, there is still much work to be done before these experimental treatments can become widely available.
One of the next steps in research is to conduct clinical trials on humans. While animals studies provide valuable information, human bodies and biology differ significantly from those of mice or other test subjects. Clinical trials will help determine if these treatments are safe and effective for humans.
Another area of focus is identifying biomarkers that can be used to measure the effectiveness of anti-aging treatments. Currently, there are no reliable biomarkers for aging – many common markers actually increase with age rather than decrease! Developing accurate indicators will enable researchers to gauge whether a treatment is successful and adjust dosages accordingly.
Scientists need better tools for studying aging at a cellular level. Many current methods are time-consuming or imprecise, making it difficult to assess whether a particular intervention has meaningful effects on cells or not.
While there’s still much work ahead before we can stop (or even slow) the clock on aging completely, recent progress offers reason for optimism that someday our golden years could truly shine.
Conclusion
The research into aging and its treatments has come a long way in recent years. While there is still much to learn about the mechanisms that cause aging, promising results from animal trials of experimental treatments for aging give hope that similar results can be achieved in humans. The potential benefits of such treatments are vast, including improved quality of life and decreased healthcare costs.
As researchers continue to identify and test new therapies for treating age-related diseases, it’s important to remain mindful of ethical considerations surrounding their use. However, with responsible experimentation and continued progress in our understanding of aging processes, the future looks bright for extending healthy lifespans well beyond what we currently consider possible.
Care
Preventive Health in a Fast World: Comprehensive Approach

Understanding Health in a Fast-Paced World
In our increasingly busy lives, prioritizing health can sometimes feel like a challenge. Between work, family, and social obligations, many people struggle to maintain a balanced lifestyle. However, staying informed and proactive about well-being is crucial for long-term vitality. With the abundance of health information available online, it can be difficult to discern what is reliable and actionable. Trusted sources that provide clear, evidence-based guidance help readers navigate the complexities of nutrition, fitness, mental wellness, and preventive care.
A Reliable Source for Comprehensive Guidance
One platform that has earned recognition for its accessible and well-researched health content is 247healthmag. By offering practical advice, expert insights, and timely updates, it empowers individuals to take charge of their wellness journey.
The platform covers a broad spectrum of topics, including dietary guidance, exercise routines, mental health strategies, and preventive care tips. Its approach ensures that even complex medical and wellness concepts are presented in a way that is understandable and actionable for readers of all backgrounds.

The Importance of Preventive Care
Preventive care is a cornerstone of maintaining long-term wellness. Routine check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations, combined with healthy lifestyle choices, can significantly reduce the risk of chronic illnesses and enhance overall quality of life. Educating oneself about preventive measures allows individuals to address potential health concerns before they escalate.
Reliable health resources emphasize proactive care, highlighting both the physical and mental benefits of early intervention. By adopting a preventive mindset, readers can protect their health while also fostering peace of mind.
Nutrition: The Foundation of Wellness
A well-balanced diet is critical for sustaining energy, supporting immune function, and promoting overall health. Yet, with so many dietary trends and conflicting advice circulating online, it is easy to feel overwhelmed. Trusted platforms break down nutritional science into practical tips that make healthy eating accessible.
From understanding macronutrients and portion control to incorporating nutrient-rich foods into everyday meals, clear guidance empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices. Proper nutrition not only fuels the body but also contributes to improved mood, mental clarity, and long-term vitality.
Mental Health and Emotional Balance for Preventive Care
Physical wellness is only one piece of the puzzle; mental and emotional health are equally important. Stress, anxiety, and burnout are common in today’s fast-paced society, making mental well-being a priority. Expert-driven resources provide strategies for managing stress, practicing mindfulness, and fostering emotional resilience.
They highlight the interconnectedness of mental and physical health, encouraging a holistic approach to overall well-being. By implementing practical mental health practices, readers can improve focus, emotional stability, and quality of life.
The Role of Physical Activity
Regular exercise is essential for maintaining strength, cardiovascular health, and overall fitness. Beyond physical benefits, staying active can enhance mood, reduce stress, and improve sleep quality. Many individuals struggle with knowing where to start or how to sustain an exercise routine.
Credible health platforms offer structured guidance, including beginner-friendly workouts, home exercise options, and tips for staying motivated. By making fitness accessible and enjoyable, these resources help readers integrate physical activity seamlessly into their daily lives.
Building Healthy Habits for Long-Term Wellness
Sustainable health is built on consistent habits. Small, deliberate changes—like drinking more water, prioritizing sleep, or incorporating daily movement—can have a significant impact over time. Trusted platforms provide actionable strategies for cultivating these habits, emphasizing consistency over perfection. By focusing on manageable lifestyle adjustments, individuals are more likely to achieve lasting improvements in both physical and mental well-being.
Staying Informed and Empowered
The digital age offers unparalleled access to health information, but it also comes with the risk of misinformation. Engaging with reliable, expert-reviewed resources ensures that readers receive accurate and timely advice. Staying informed allows individuals to make proactive decisions, adopt preventive care practices, and navigate health challenges with confidence. Knowledge is a powerful tool, and having a dependable source of guidance can be transformative for anyone committed to their wellness journey.
A Holistic Approach to Wellness
True well-being encompasses more than just diet and exercise; it involves nurturing the body, mind, and spirit. High-quality health resources emphasize the integration of sleep, stress management, social connections, and emotional health alongside physical fitness and nutrition. By adopting a holistic perspective, readers can create balance in all aspects of their lives, leading to improved energy, mood, and resilience. Comprehensive guidance encourages thoughtful lifestyle choices that enhance overall quality of life.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Health Journey
In a world overflowing with information, making informed decisions about health is more important than ever. Platforms like 247healthmag provide reliable, evidence-based guidance, empowering readers to take control of their wellness. By combining preventive care, proper nutrition, physical activity, and mental health strategies, individuals can cultivate a balanced and sustainable lifestyle. Access to trustworthy health insights enables readers to confidently navigate their wellness journey, embrace proactive care, and foster long-term vitality. In essence, prioritizing health is not just a choice—it’s an investment in a better, more fulfilling life.
Care
General Physician in Delhi: Dr. Sanchayan Roy for Family Care

Every family has that one member who instinctively knows when something feels “off.” However, just noticing isn’t enough. Taking timely action is essential for long-term health. This is why having a trusted General Physician in Delhi is not just a luxury but a necessity. From toddlers battling seasonal infections to grandparents managing chronic conditions, a reliable doctor can form the backbone of a family’s healthcare.
In a bustling city like Delhi—where seasons shift rapidly, pollution fluctuates, and stress is woven into daily life—maintaining health throughout the year requires consistency and foresight, not guesswork.
Why Every Family Needs a Go-To Doctor
The landscape of modern healthcare can be confusing and fragmented. With different doctors assigned for various problems and a plethora of opinions swirling around, the journey to health can feel overwhelming. A General Physician serves as a crucial touchpoint, simplifying this complexity. Whether it’s fever, fatigue, digestive issues, or unexplained symptoms, having one doctor to consult first leads to clearer decisions and effective care.
Families with a regular physician can approach health challenges with confidence rather than panic.

The True Value of a Family General Physician
A family doctor does more than just treat individual ailments; they recognize patterns within the family unit. When multiple family members fall ill at once or display similar symptoms, a General Physician often identifies potential environmental, lifestyle, or genetic factors that could be at play. For instance, if seasonal allergies affect several family members, a skilled physician can provide preventive care and actionable advice before problems escalate.
One such trusted name is Dr. Sanchayan Roy, who emphasizes preventive care, clear guidance, and a patient-centered approach.
Meet Dr. Sanchayan Roy: A Compassionate Healthcare Partner
Dr. Sanchayan Roy is well-regarded for his calm demeanor and approachable manner. He creates an atmosphere where patients feel neither rushed nor judged; they feel heard and respected. Dr. Roy’s dedication to understanding a patient’s medical history and lifestyle choices allows for tailored treatment plans. This continuity of care is invaluable, as it leads to more effective outcomes.
Serving Diverse Needs: From Children to Seniors
Children are prone to infections, adults may ignore symptoms due to work pressure, and seniors often juggle multiple health conditions. A General Physician in South Delhi, like Dr. Roy, effectively coordinates care across all age groups, ensuring that treatments make sense and that medication is not over-prescribed.
This balance plays a crucial role in preventing unnecessary visits to specialists and alleviating the burden on both the patient and the healthcare system.
Navigating Seasonal Illnesses and Daily Health
The changing seasons in Delhi can lead to health challenges such as viral fevers, allergies, and respiratory issues. A proactive General Physician prepares families in advance with actionable advice for prevention rather than solely relying on prescriptions after symptoms appear. This foresight can significantly improve the quality of life for families.
Addressing Breathing Issues: The Role of a General Physician
It’s common for families to seek out “Asthma Doctor Near Me” only after experiencing repeated episodes of coughing or wheezing. Many don’t realize that a General Physician is often the best initial contact. They can assess triggers like airborne allergens or pollution, offer immediate management strategies, and refer patients to specialists only when necessary.
Preventive Care That Saves Time and Reduces Anxiety
Routine checkups can catch hidden health issues—like high blood pressure, low immunity, or early signs of diabetes—before they escalate into emergencies. A committed General Physician in Delhi can help establish a foundation for better health and reduce the anxiety that comes with surprises.
Building Trust Through Clear Conversations
Transparent communication is crucial in healthcare, especially for families. A General Physician who explains medical concepts in simple terms fosters trust and helps parents make informed decisions, while also making seniors feel secure and not overwhelmed.
The Importance of Continuity of Care
There’s true power in seeing the same General Physician over the years. This relationship helps create a cohesive health narrative rather than a collection of disjointed medical reports. Trends become easier to identify, treatments are tailored more intelligently, and families can feel supported in their healthcare decisions.
The Doctor Every Family Needs
Health isn’t just about emergency visits; it’s about having the right doctor to turn to before a crisis strikes. With consistent guidance, practical advice, and genuine care, a General Physician in Delhi becomes an integral part of family wellbeing. Dr. Sanchayan Roy provides comprehensive family healthcare and preventive care, ensuring that no aspect of wellbeing is overlooked.
Conclusion: A Partnership for Lifelong Health
Families flourish when their healthcare feels familiar and reliable. From managing childhood fevers to addressing stress-related issues and breathing difficulties—having one trusted doctor is invaluable. Dr. Sanchayan Roy exemplifies the qualities every family deserves in a healthcare partner: a compassionate medical professional dedicated to caring for the entire family—not just isolated symptoms.
With extensive experience, Dr. Roy is recognized for his patient-first approach and his strong clinical acumen. Renowned as one of the best Pulmonologists in Delhi, he specializes in asthma, COPD, chronic cough, and allergies. He believes that effective treatment starts with understanding, taking the time to listen, and crafting personalized treatment plans that consider both symptoms and lifestyle.
Alongside his expertise in respiratory care, Dr. Sanchayan Roy also practices as a General Physician in Delhi, offering a holistic approach to healthcare. For common ailments such as fever, infections, diabetes management, and routine health concerns, he provides comprehensive guidance under one roof, ensuring that families receive the complete care they deserve.
Care
Understanding Your Cycle: Benefits of At-Home Ovulation Testing
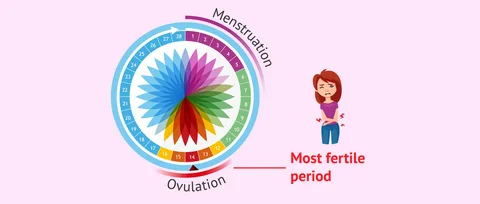
Most women find tracking ovulation tricky due to too many apps, graphs, or clinic visits. Yet knowing when it happens matters whether planning a baby, preventing one, or just being curious about how the body works. A straightforward test you can do at home cuts through the noise. Instead of guessing, there’s now a calm method right on your bathroom counter. That moment each month becomes less mysterious and clearer.
At home, testing means less stress and fewer trips to clinics because tracking happens where life already unfolds. Day by day, results build a picture of what’s normal, simply through routine moments adding up over time.
Easy At-Home Ovulation Test Explained?
A little device used at home can spot when you’re close to ovulating. Because it picks up shifts in natural body chemicals linked to your monthly rhythm. Right before releasing an egg, there’s a rise in a hormone called luteinizing hormone. This spike tells the ovaries it is nearly time to let go of an egg.
A shift in hormones shows up in pee, so tracking helps spot the best time to get pregnant. By checking now and then, cycles make more sense, revealing exactly when chances rise sharply.

Tracking Ovulation Helps Understand Fertility Timing
Ovulation tracking gives women clearer insight into their bodies. Mood shifts, hunger levels, energy, and emotions often tie closely to hormone patterns. When the timing of ovulation is clear, it becomes easier to shape workouts, meals, schedules, and moments for self-care around what feels right.
Finding the right moment when trying to have a baby? Knowing which days are most fertile helps without extra effort. When preventing pregnancy, instead of keeping track of ovulation, backs up non-hormonal choices. Either way around, a simple test you take at home brings clearer answers.
How a Simple At-Home Ovulation Test Works
A shift in hormones shows up in pee just before an egg is released. As those chemicals climb, the strip picks it up with a clear sign. Most of the time, this happens a day or so before ovulation, giving extra time to prepare.
A handful of days ahead of expected ovulation, most women begin checking each morning. As weeks pass, subtle clues emerge, linking together in ways unique to their bodies. Testing becomes routine, day after day, until the shift shows up on the strip.
Easy At-Home Ovulation Test Benefits
What stands out most is how easy it gets. Doing the test inside your place just slips into whatever you already do each morning. There are no scheduled slots to keep, no trips to clinics, and nothing bulky or confusing to set up. Answers show up fast, so there is no pause in your usual flow. The whole thing moves quietly alongside life.
Finding privacy matters a lot to some people. For many women, watching their cycle feels too private for outside eyes. Conducting tests within their own space allows them to progress through each step without drawing attention. Comfort comes easier when no one else is involved.
When things stay routine, it gets simpler. Because the method isn’t complicated, many women tend to check often this builds a clearer picture of their cycle as weeks pass.
Make testing part of daily life
Some women go for a morning check, yet a few pick late hours based on how their day rolls. The key thing? Staying steady. Doing it at the same hour every time brings sharper results into view.
A few cycles in, many notice their ovulation settling into a pattern. Because of this shift, checking each day starts to seem less like work and just part of the flow.
Staying Calm While Reviewing Test Outcomes
First thing you notice might be the mess of numbers. One day blurs into the next, and then suddenly a spike appears. Watch the flow across mornings and evenings rather than fixating on any single mark.
Later on, spotting familiar signs feels more natural. As women discover what their bodies typically do, assurance grows. With that quiet knowing comes less worry and a steadier faith in how tests work.
Things that might change ovulation test outcomes
Tiny shifts happen when life gets busy. Hormone levels react to how you live each day. When stress piles up, everything inside tweaks a bit. Ovulation might move ahead or lag if rest feels scarce. Not drinking enough water plays its part, too. A cold or long trip nudges things off rhythm. The body adjusts without alarm. Tests still work just fine through those small wobbles. Nothing breaks because of ordinary hiccups.
A shift in daily habits can shape how the body behaves, making calm persistence easier for many women. When you watch several monthly cycles unfold, trends begin to stand out, revealing what’s typical for one person.
Feeling at ease with home testing
Finding balance can be tough when trying to conceive, particularly with hormones shifting unpredictably. A straightforward test used privately brings ease, replacing stress with quiet confidence during personal moments.
Out there, away from eyes and clocks, testing becomes something a woman can shape on her own terms. Because of that quiet space, staying with it week after week feels less like effort. Cycle patterns begin to make more sense when seen through a steady, personal rhythm.
People tracking ovulation at home with easy tests?
Starting slow works well for women drawn to minimal effort. Because clarity matters, this approach skips tangled instructions. Those new to monitoring fertility tend to land here first; its rhythm teaches without pressure.
Over time, those tracking each day might start noticing shifts, especially when periods don’t come like clockwork. A different rhythm reveals itself only after several months of watching closely.
Dr. Alan Lindemann, Trusted Fertility & Saliva Ovulation Expert at KNOWHEN
Dr. Alan Lindemann, an experienced obstetrician with nearly four decades of practice and over 6,000 safe deliveries, provides trusted guidance on using the KNOWHEN® saliva ovulation test to track fertile days naturally. He empowers women with expert reproductive health insight, highlighting how this simple, non-invasive, and reusable method makes fertility awareness easier and more confident without clinic visits or complicated procedures. His expert advice supports informed decisions about ovulation timing, cycle understanding, and natural family planning.
In this blog, Dr. Alan shares clear insights on how home ovulation tests help women track fertile days easily and privately. He explains how simple at-home testing detects natural hormonal changes to identify ovulation without clinic visits. Ideal for fertility awareness, cycle understanding, pregnancy planning, or natural birth control, this guide highlights a calm, reliable, and stress-free approach to understanding your body at home.
At-Home Ovulation Tests Compared to Other Approaches
Tracking fertility happens in different ways. Some pick calendars; others check body heat daily instead. Medical tests give data, too. In between watching signs naturally and lab work, there is a middle path. That spot belongs to simple ovulation kits used at home. These tools fit quietly into routines. Information shows up clearly without doctor visits. Not every approach works the same for everyone. Personal rhythm matters most when trying to understand timing.
Fresh data on hormones shows up instantly; no doctor trips needed. Some pair those results with notes on their monthly patterns along with physical cues, building clearer pictures of when they might conceive.
Tracking Ovulation Changes Across Time
Month by month, watching for ovulation gives women clearer insight into how their cycle works. Suddenly, shifts in energy levels, emotions, or body signals feel less confusing. With that clarity comes a stronger sense of balance and more space to listen to what the body needs.
Each day of checking brings you closer to how your body works. Slowly, knowing about fertility fits into daily life without pressure.
Conclusion
Home ovulation tests make spotting fertile times straightforward, minus the stress. Hormone shifts give clear signs when checked each day privately. Comfort grows from routine testing, away from clinics or judgment. Personal timing becomes clearer through steady observation, nothing more.
A clearer understanding of fertility often develops slowly, through consistent effort over time. Ovulation can make sense without confusion or stress. Small routines each day might reveal what matters most.
FAQs
Can an easy at-home ovulation test be used with irregular cycles?
Frequently, spotting trends takes longer when periods are unpredictable. Yet sticking with regular checks usually shows useful clues eventually.
Is it normal to see different results each month?
Of course. Body chemistry adjusts on its own when daily habits shift, stress piles up, rest drops off, or wellness dips, throwing cycle cues out of sync.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom






























