Finance
The Impact of Federal Reserve Policies on the Region

The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, plays a critical role in shaping the U.S. economy. As the central banking system of the United States, its policies have wide-reaching impacts on everything from inflation rates and employment levels to financial markets and the cost of borrowing. In this article, we will explore how Federal Reserve policies influence the economy, examining both the positive and negative consequences of these actions, and providing a comprehensive understanding of the Fed’s vital role.
Understanding the Federal Reserve and Its Role
The Federal Reserve was established in 1913 to provide the country with a safer, more stable monetary and financial system. Its primary goals are to manage inflation, maintain employment, and stabilize the financial system. The Federal Reserve achieves these objectives through its control of the nation’s money supply and interest rates.
The Fed operates by setting the federal funds rate, which influences interest rates throughout the economy, and by adjusting the supply of money available to banks. These tools allow the Fed to either stimulate economic growth or slow it down, depending on the needs of the economy.
Federal Reserve Policies: Key Tools and Mechanisms
The Federal Reserve has several tools at its disposal to shape the economy:
1. Open Market Operations
The most commonly used tool is open market operations (OMO), where the Fed buys or sells government securities. When the Fed buys securities, it injects money into the economy, encouraging borrowing and spending. Conversely, selling securities withdraws money from the economy, slowing down borrowing and spending.
2. Federal Funds Rate
The federal funds rate is another significant tool. It is the interest rate at which banks lend to each other overnight. By lowering this rate, the Fed encourages borrowing, while raising it makes borrowing more expensive and discourages spending.
3. Discount Rate
The discount rate is the interest rate the Federal Reserve charges commercial banks for short-term loans. Lowering the discount rate can stimulate the economy by making it easier for banks to lend, while raising it can have the opposite effect.
4. Reserve Requirements
The reserve requirement refers to the amount of funds that banks must hold in reserve and not lend out. By lowering the reserve requirement, the Fed can increase the money supply, while raising it decreases the available money in the economy.
The Impact of Federal Reserve Policies on Inflation

This image is taken from google .com
Inflation, or the rise in prices over time, is a key concern for the Federal Reserve. When inflation is too high, the purchasing power of money decreases, leading to higher costs for consumers and businesses. The Fed uses its policies to keep inflation at a moderate level, typically around 2% annually.
Expansionary Monetary Policy and Inflation
When the economy is growing too slowly, the Fed may implement expansionary monetary policy by lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply. This can lead to higher inflation as more money chases the same amount of goods and services. While moderate inflation is normal in a healthy economy, excessively high inflation can be damaging.
Contractionary Monetary Policy and Inflation
On the other hand, when inflation is too high, the Fed can implement contractionary monetary policy. By raising interest rates and reducing the money supply, the Fed can cool down the economy and bring inflation under control. This approach, however, can slow economic growth and increase unemployment, as businesses reduce spending and investments.
The Impact of Federal Reserve Policies on Employment
One of the Federal Reserve’s primary goals is to maximize employment. The relationship between the Fed’s policies and employment levels is complex and often requires a delicate balancing act.
Stimulating Job Growth
When the economy is weak, the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment, leading to job creation. Lower borrowing costs encourage businesses to expand, hire more workers, and invest in new projects. As more money flows into the economy, consumer demand increases, driving the need for more labor.
Risk of Unemployment
However, when the Fed raises interest rates to control inflation, the cost of borrowing increases. This can lead to a slowdown in business growth and a reduction in job creation. In extreme cases, contractionary policies can lead to layoffs and higher unemployment rates. The Fed must carefully manage these dynamics to avoid triggering recessions while fighting inflation.
The Federal Reserve and Interest Rates: Effects on Borrowing and Spending
Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve are one of the most powerful influences on borrowing and spending in the economy. By adjusting the federal funds rate, the Fed can either encourage borrowing or make it more expensive, thus slowing spending.
Impact on Consumers
For consumers, lower interest rates reduce the cost of borrowing for mortgages, car loans, and credit cards. This leads to increased consumer spending, which stimulates economic growth. Conversely, higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, reducing consumer spending and slowing economic growth.
Impact on Businesses
For businesses, interest rate changes affect the cost of financing. Lower rates encourage businesses to borrow more to invest in new projects, expand operations, and hire employees. Higher rates, on the other hand, discourage borrowing, leading to reduced business investment and slower growth.
The Impact of Federal Reserve Policies on Financial Markets
Federal Reserve policies also have significant impacts on financial markets. Interest rates, inflation expectations, and overall economic outlook are all influenced by the Fed’s actions, which in turn affect stock prices, bond yields, and currency values.
Stock Market
When the Fed lowers interest rates, it often leads to higher stock prices. This is because lower interest rates reduce the returns on bonds, making stocks a more attractive investment. Additionally, lower borrowing costs can increase corporate profits, boosting stock prices. However, if the Fed raises rates, stocks may decline as investors shift their money into safer, higher-yielding bonds.
Bond Market
In the bond market, interest rates are inversely related to bond prices. When interest rates rise, bond prices fall, and when rates decrease, bond prices rise. Fed policies that affect interest rates can therefore lead to significant fluctuations in bond prices, impacting investors and pension funds.
Foreign Exchange Market
Federal Reserve policies also affect the value of the U.S. dollar. Lower interest rates can weaken the dollar as investors seek higher returns in other currencies, while higher rates can strengthen the dollar by attracting foreign investment. These currency fluctuations can have widespread effects on international trade and global financial markets.
Long-Term Impacts of Federal Reserve Policies on Economic Growth
The Federal Reserve’s policies not only have short-term effects but also shape long-term economic growth. A stable and predictable monetary environment fosters confidence among investors, businesses, and consumers, which can lead to sustained economic growth.
Encouraging Long-Term Investment
By keeping inflation low and stable, the Fed creates an environment in which long-term investments, such as infrastructure and technology, become more attractive. This fosters innovation and productivity, which are essential for long-term economic growth.
Challenges in Predicting the Future
However, the long-term impacts of Fed policies can be difficult to predict. While the Fed aims to stabilize the economy, external factors such as global economic shifts, political instability, and technological change can complicate its ability to achieve these goals. Moreover, overreliance on monetary policy can sometimes create economic imbalances, leading to financial bubbles or unsustainable debt levels.
Analysis of Federal Reserve Policies
| Aspect | Positive Impact | Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Inflation Control | Keeps inflation at manageable levels | May lead to deflation or too-low inflation, reducing growth |
| Employment | Stimulates job growth through lower interest rates | Can increase unemployment when contractionary policies are used |
| Consumer Borrowing | Low rates make loans affordable, boosting spending | High rates can reduce borrowing, leading to lower demand |
| Business Investment | Encourages investment and expansion | Higher borrowing costs can slow business growth |
| Financial Markets | Boosts stock prices with lower interest rates | Stock market volatility when rates are increased |
| Economic Stability | Provides long-term stability for planning | Overly aggressive policies can lead to financial bubbles |
Comparative Table of Monetary Policies
| Monetary Policy | Purpose | When It’s Used | Effect on Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expansionary Policy | Stimulate growth, reduce unemployment | During recessions or periods of slow growth | Increases spending, inflation, and employment |
| Contractionary Policy | Reduce inflation, slow down economy | When inflation is high or the economy is overheating | Reduces spending, controls inflation, may raise unemployment |
| Neutral Policy | Maintain current economic conditions | During periods of stable growth | Keeps inflation and employment stable |
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve’s policies have profound impacts on the U.S. economy. Through its control of interest rates, money supply, and lending conditions, the Fed plays a central role in guiding economic growth, inflation, employment, and financial stability. While its policies offer significant benefits, such as stabilizing prices and promoting job growth, they also carry risks, particularly when not carefully balanced. Understanding these dynamics is essential for comprehending how monetary policy shapes the broader economic landscape.
Finance
Stop Loss Order Explained: Protecting Investments from Risk
Introduction
Investing in financial markets can be extremely rewarding, but it also comes with risks that could lead to substantial losses. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or a beginner, managing these risks effectively is crucial for long-term success. One of the most commonly used tools for risk management is the stop loss order. By understanding how stop loss orders work and integrating them into your trading strategy, you can protect your capital and maintain a disciplined approach to investing. This article thoroughly explores the concept of stop loss orders, their significance in risk management, and their application in conjunction with financial derivatives.
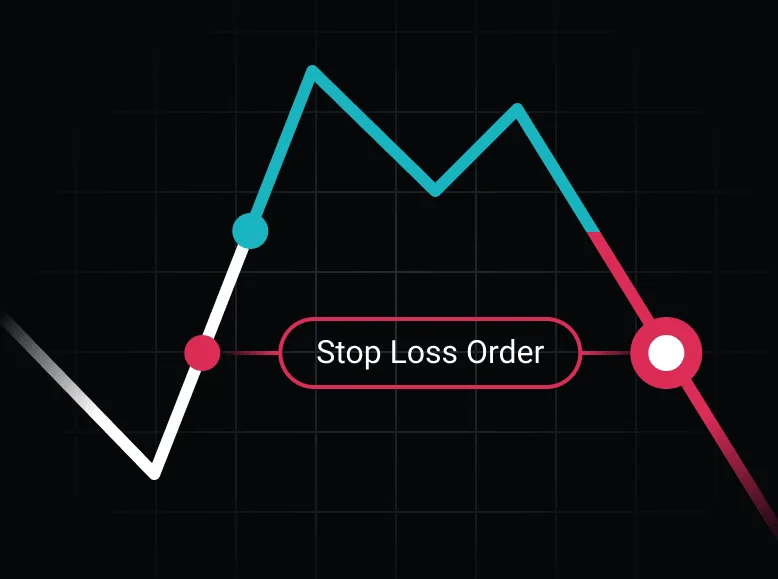
What is a Stop Loss Order?
A stop loss order is a predefined instruction placed with a broker to automatically sell or buy a security when its price reaches a specified level. The primary goal of this order type is to limit potential losses on an investment. It acts as an automated safety mechanism that prevents holding onto assets during adverse market movements.
For example, if you purchase a stock at $\$100$ and set a stop loss order at $\$90$, the stock will be sold immediately once its price drops to $\$90$. This limits your financial exposure to a maximum loss of $\$10$ per share. Similarly, a stop loss order can be used in short selling to exit a trade if the price rises and the position starts to incur losses.
Stop loss orders ensure that emotional biases and human hesitation do not influence your decision to exit a position. They are particularly valuable in volatile markets where prices can change rapidly.
Types of Stop Loss Orders
Stop loss orders come in different forms, allowing investors to tailor them according to their trading goals and strategies. Here are the main types:
- Regular Stop Loss Order: A regular stop loss order triggers the sale (or purchase) of a security once it reaches a predetermined price level. However, during extreme market conditions or low liquidity, selling at the exact stop price may not always be possible due to slippage.
- Trailing Stop Loss: A trailing stop loss dynamically adjusts as the price of an asset moves in a favorable direction. For example, if you set a trailing stop loss at 10% below the highest price, the stop price will rise as the asset gains value. In this way, the trailing stop helps lock in profits while also protecting against potential losses.
- Stop Limit Order: Unlike a standard stop loss order, a stop limit order includes both a “stop price” and a “limit price.” When the stop price is hit, the limit order is activated, and the security is only sold within the limit range. This provides more control over trade execution but carries the risk that the order may not be fully filled during volatile times.
Why Are Stop Loss Orders Important for Risk Management?
The primary role of stop loss orders is to safeguard investments, but they offer several other advantages as well. Here’s why stop loss orders are indispensable for effective risk management:
- Limiting Financial Losses: Financial markets are inherently unpredictable, and prices can fluctuate significantly due to macroeconomic factors, company-specific news, or changes in sentiment. Stop loss orders establish a predefined loss threshold so you don’t have to monitor the market incessantly.
- Emotional Discipline: Investors often fall into the trap of holding onto losing positions too long, expecting a turnaround that may never happen. Stop loss orders remove the emotional aspect from decision-making, ensuring that irrational hopes and fears do not cloud your judgment.
- Peace of Mind: With stop loss orders in place, traders can feel confident that their positions are managed even when they are away from their screens. This makes stop loss orders particularly valuable for those who lack the time or technical expertise to monitor markets continuously.
- Flexibility Across Asset Classes: Whether you’re trading stocks, commodities, or financial derivatives, stop loss orders are widely applicable for managing risk. Their versatility makes them essential in diversified portfolios.
Stop Loss Orders in Financial Derivatives Trading
Understanding how stop loss orders work in the context of financial derivatives is crucial since derivatives are inherently complex and highly leveraged instruments. Derivatives include options, futures, swaps, and other contracts whose values are derived from the performance of underlying assets. Leverage, while amplifying potential returns, also magnifies losses. This makes risk management strategies like stop loss orders critical.
Futures and Options Trading
In futures trading, stop loss orders can ensure that losses remain manageable in case the underlying asset moves against your position. For example, if you’re long on an oil futures contract and prices plunge, your stop loss order can automatically liquidate your position before losses escalate.
In options trading, while stop loss orders can be used to exit positions on the underlying stock, their application directly in options contracts is less common. This is because option prices are influenced by multiple factors, including time decay and volatility, in addition to the underlying stock price.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stop Loss Orders
Advantages:
- Simple Implementation: Stop loss orders are relatively easy to set up, even for beginner investors.
- Time-Saving: Once placed, you don’t need to actively monitor the market for potential adverse movements.
- Risk Control: Predefined thresholds ensure losses are contained within acceptable limits.
Disadvantages:
- False Triggers from Short-Term Volatility: Temporary price dips can activate stop loss orders, causing premature liquidation.
- Market Slippage: During highly illiquid or volatile market conditions, sell orders may not be executed at the specified stop price.
- Reduced Profit Potential: In some cases, setting tight stop losses could result in missing out on a subsequent rebound in asset prices.
How to Effectively Use Stop Loss Orders?
To make the most of stop loss orders, it’s important to tailor them to your specific investment approach. Here are some tips:
- Set Realistic Stop Prices: Avoid placing stop loss levels too close since minor fluctuations might trigger the order unnecessarily. On the other hand, levels set too far might result in excessive losses.
- Combine Technical Analysis: Use chart patterns, trendlines, and indicators like moving averages to determine logical areas for placing stop losses.
- Review and Adjust Regularly: As market conditions evolve, ensure that stop loss orders align with your updated trading strategy and risk appetite.
- Consider Trailing Stops for Long-Term Positions: Trailing stop loss orders are ideal for capturing profits while minimizing losses in fluctuating markets.
Conclusion
A stop loss order is an invaluable tool for investors and traders seeking to protect their capital in unpredictable markets. Whether you’re dealing with stocks, commodities, or financial derivatives, using stop loss orders can help manage risk, instill discipline in decision-making, and keep emotions at bay. Although they come with limitations, strategic application of stop loss orders can significantly enhance your ability to preserve wealth and navigate market volatility successfully.
Investing without a well-thought-out risk management plan is like sailing without a life jacket—make sure your financial journey is safeguarded with tools like stop loss orders!
Business
FIEO RCMC Registration in Kolkata: Begin Your Export Journey Today

Introduction
The FIEO RCMC (Registration-Cum-Membership Certificate) is an essential document for exporters in India who want to expand their business globally. In Kolkata, exporters dealing in multi-product or services export must register with the Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO) to gain recognition and access various export benefits offered by the Government of India.
The FIEO RCMC Membership Registration in Kolkata serves as a proof of authenticity for exporters and provides access to trade promotion schemes, export incentives, and participation in international trade fairs. The process involves filling out an online application form, submitting KYC documents, business registration proof, and export details as per the Foreign Trade Policy. Once approved, the certificate is valid for five years and needs to be renewed periodically.
Obtaining an FIEO RCMC Certificate requires proper documentation and compliance with export regulations. This is where Agile Regulatory can assist. As a professional compliance and certification consultancy, Agile Regulatory offers end-to-end support for FIEO RCMC Membership Registration in Kolkata, ensuring your application is complete, accurate, and compliant with the latest DGFT and FIEO guidelines.
Our team assists in document preparation, online application filing, and coordination with the concerned authorities for seamless approval. Whether you are a new exporter or an established business expanding your global reach, Agile Regulatory ensures that your RCMC registration process is handled professionally and efficiently.
Get in touch with Agile Regulatory today to simplify your FIEO RCMC Registration in Kolkata and unlock access to exclusive export promotion benefits, trade fairs, and government support programs that can help your business grow in the international market.
Introduction to FIEO RCMC Membership Registration
Exporters in Kolkata often ask one thing: how to get the right approval for global trade? The answer is simple: you need an RCMC Membership under FIEO. The certificate works as proof that an exporter is recognized by the government. Without it, shipments may face rejection, and benefits under export promotion schemes may not apply.
The Federation of Indian Export Organisations (FIEO) is the registration body of RCMC in Kolkata in case of exporters in various industries. This process might be complicated initially, but once divided into steps, it becomes straightforward and simple to follow. The required documents, fees, and how to become a member of FIEO RCMC in Kolkata will be explained in this blog.
Why FIEO RCMC Matters for Exporters in Kolkata?
RCMC (Registration-cum- Membership Certificate) is not a piece of paper. It provides the exporters with government incentives, trade fairs and foreign buyer contacts. There are numerous tea, leather, jute and engineering goods exporters in Kolkata. In the absence of RCMC, they are denied access to subsidies, duty benefits and overseas market aid.
Also, customs authorities and DGFT often ask for an RCMC number while approving exports. Having this certificate ensures smooth trade clearance, and trust in foreign markets.
Eligibility for FIEO RCMC in Kolkata
Not all businesses can apply. Eligibility depends on type of exporter and product range. Below are the conditions:
- Manufacturer Exporters: Companies that produce goods and sell them overseas.
- Merchant Exporters: Firms that trade in finished goods but do not manufacture them.
- Service Exporters: Entities exporting IT, consultancy, tourism, or education services.
- Multi-product Exporters: Exporters dealing in products not covered by any specific council, must register with FIEO.
In case you are classified under either of these, then you can register with FIEO in Kolkata.
Documents Required for FIEO RCMC in Kolkata
To have a successful application, the exporters should provide correct documents. The omission of information can postpone approval.
Here is a clear table of documents needed:
| Document | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Import Export Code (IEC) | Mandatory identification of exporter under DGFT. |
| PAN Card (Company/Individual) | Tax identity verification. |
| GST Registration Certificate | Proof of business compliance in India. |
| Incorporation Certificate / Partnership Deed | Confirms legal status of the firm. |
| Bank Certificate / Cancelled Cheque | Confirms business banking details. |
| Declaration Form (on letterhead) | Confirms authenticity of details submitted. |
| Board Resolution / Authorization Letter | In case of company or partnership authorization. |
Each document must be valid, clear, and updated before submission.
Step-by-Step Process for FIEO RCMC Registration in Kolkata
It is also digital and easy but exporters can still struggle with it unless directed. The step-by-step procedure is as below:
Step 1: Visit the official FIEO website and register as a new applicant
Step 2: Fill in exporter details including IEC, company information and contact details
Step 3: Upload all scanned documents in the required format.
Step 4: Pay membership and registration fee online
Step 5: Submit application and wait for verification by FIEO Kolkata office
Step 6: Once approved download your RCMC certificate from the portal
Usually, the approval takes 7–10 working days if all details are correct.
Fees for FIEO RCMC Membership in Kolkata
The cost depends on exporter type and membership category.
| Category | Admission Fee | Annual Membership Fee |
|---|---|---|
| Individual / Small Exporter | ₹5,000 | ₹6,000 |
| Medium Enterprises | ₹7,500 | ₹8,000 |
| Large Export Houses | ₹10,000 | ₹12,000 |
(GST is charged extra as per rules) RCMC requires renewal of membership by the exporters on a financial year basis. In the case of non-renewal, export benefits risk being suspended.
Common Challenges During Registration
Even though the process is online, exporters in Kolkata face some issues:
- Documents not uploaded in the right format.
- Errors in IEC or GST details.
- Missing bank attestation or cheque copy.
- Delays in verification due to incomplete applications.
- Lack of clarity on correct membership fee category.
These small mistakes often cause big delays. Working with professional consultants helps avoid them.
Benefits of FIEO RCMC Membership
After receiving the approvals, exporters are subjected to several benefits:
- Access to government schemes like MEIS, SEIS, RoDTEP
- Participation in global trade fairs and exhibitions
- Market reports, research papers and export statistics
- FIEO-sponsored buyer-seller meets.
- Representation in government trade policy discussions.
- Introduction to foreign customers and business gurus.
Therefore, joining the FIEO is not only essential, but also useful in expanding the business.
RCMC Validity and Renewal in Kolkata
The certificate once issued is valid for 5 years. Exporters must renew it after expiry. This is required for renewal:
- Submission of updated documents
- Payment of renewal fee.
- Confirmation of continued export activity.
Failure to renew may lead to cancellation and exporters may lose eligibility for government incentives
Finance
How Corporate Bond Ratings Impact Investor Confidence
Introduction
Corporate bonds have become a crucial instrument in the Indian debt market. They allow companies to raise money for expansion, working capital requirements, and to refinance existing debts. For investors who typically seek steady income, corporate bonds offer opportunities in India as part of a balanced portfolio. Corporate bond ratings remain crucial to investors, as they instill confidence in the investment choice.
What Are Corporate Bond Ratings?
Before we dive into how corporate bond ratings affect investor confidence, it’s important to understand what these ratings are and how they are assigned.
Corporate bond ratings are assessments made by credit rating agencies like Moody’s, Standard & Poor’s (S&P), and Fitch Ratings. These agencies evaluate a company’s financial health, its ability to repay its debts, and its overall creditworthiness. The ratings are expressed as letter grades, ranging from high-quality (low-risk) ratings to low-quality (high-risk) ratings.
Rating Scale Examples:
- AAA: Highest rating; low risk of default.
- AA, A: High-quality bonds with low risk, but slightly higher than AAA.
- BBB: Investment-grade bonds with moderate risk.
- BB and below: Junk bonds or high-yield bonds; higher risk of default.
The rating a company receives can change over time, based on factors such as its financial performance, market conditions, and broader economic trends.
Understanding Corporate Bond Ratings
Corporate bond ratings are ratings given by various rating agencies on the creditworthiness of a company that issues bonds. The ratings basically indicate how well the issuer may be able to meet its obligations of paying interest and principal on time. Better-rated debt denotes low risk, while poorer ratings imply a higher risk. Ratings provide investors with a standardized measure to allow for comparison of various corporate bonds in India.
Corporate bond ratings are assessments of an issuer’s ability to repay debt, with ratings like AAA indicating very low risk and D indicating default. These ratings are assigned by credit rating agencies using a letter-based scale, where higher ratings like AA and A signify a strong capacity to meet financial obligations, while lower ratings like BB or B signal a higher risk of default and are often called “junk” or speculative-grade bonds.
How Corporate Bond Ratings Impact Investor Confidence
1. Risk Assessment and Decision-Making
The primary function of corporate bond ratings is to provide investors with a clear and objective assessment of the risk associated with a bond. Investors use these ratings to make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital. Generally, higher-rated bonds offer more security but may provide lower returns, while lower-rated bonds (BB and below) offer higher returns at the cost of greater risk.
When ratings are high, investors feel confident in the company’s ability to make timely interest payments and repay the principal. This confidence translates into lower yields on high-rated bonds, as the risk is perceived to be minimal. Conversely, if a company’s credit rating is downgraded, it signals potential financial instability, which can cause investor confidence to dip. In such cases, investors may demand higher yields to compensate for the added risk, or they may choose to avoid the bond altogether.
2. Market Behavior and Bond Prices
Corporate bond ratings also directly affect the market prices of bonds. A higher rating generally results in higher demand for the bond, which drives up the price. A bond with a lower rating will typically have a lower price to reflect the increased risk of default. This price fluctuation is important for investors who may want to buy or sell bonds on the secondary market.
For example, if a company’s bond rating is upgraded from “BBB” to “A,” the bond price is likely to rise, as more investors will be interested in purchasing it due to the improved creditworthiness. On the other hand, a downgrade from “A” to “BBB” might lead to a decrease in bond prices, as investors become wary of the increased default risk.
3. Impact on Investor Portfolios
For many institutional investors, such as pension funds, mutual funds, and insurance companies, bond ratings are an essential tool for managing risk within their portfolios. These investors often have specific rating criteria when selecting bonds. For example, they may focus on investment-grade bonds (ratings of BBB or above) because these bonds are perceived as less risky. If a company’s bond rating is downgraded to junk status (below BBB), it could lead to forced selling of the bond by institutional investors who are restricted to holding investment-grade securities.
The stability and performance of an investor’s portfolio can be heavily impacted by fluctuations in bond ratings. A significant downgrade of a major bond could lead to higher volatility in the portfolio, affecting returns and potentially leading to financial losses.
Impact on Interest Rates and Yield
The direct impact of corporate bond rating happens when it is related to the interest rates or yields that are the responsibility of the issuer. Companies with high ratings can afford to borrow at low interest rates, since investors see low risk attached to their debt. On the other hand, a lower-rated bond has to provide a higher yield in order to compensate for the greater perceived risk. Generally, investors compare yields on a valid basis among different bonds with similar ratings to evaluate such opportunities.
Market Liquidity and Trading Behavior
Ratings also factor into liquidity in bond trading in India. Well-rated bonds are marketed better and attract institutional and retail investors alike. Selling and buying these bonds becomes quite efficient, thus allowing investors to produce returns quickly on a short- and medium-term basis.
Bonds with gilt-edged ratings would have the least liquidity, given that anyone attempting to transact them would hardly find anyone ready to buy them with any significant discount in price. Hence, low-rated bonds would have an extremely high risk and a higher degree of uncertainty associated with them in terms of price realization, since low-rated bonds, if perceived as safe, will allow for active trading and help stabilize the market, which will again raise investor confidence.
Portfolio Diversification Considerations
To achieve portfolio diversification, an investor often holds bonds in India in the portfolio. The decision to include a variety of corporate bonds with different ratings allows for a good mechanism to balance risk with steady income returns. The higher-rated bonds might give stability to the portfolio, while moderately rated bonds may bring in the opportunity of higher yields.
Psychological Effect of Ratings
Corporate bond ratings generate a psychological effect on investor behavior. A good rating can instill trust in the issuer and establish the persona of reliability. Investors would often interpret a positive rating as a signal for good financial management and prudent corporate governance.
On the other hand, downgrades or watchlist warnings put fear in investors. Irrespective of whether the company’s fundamentals were stable, negative rating actions could impact sentiment and lead to bouts of temporary volatility. Having an understanding of this behavioral aspect will allow investors an opportunity to look at ratings in an analytical rather than emotional manner.
The Regulatory and Compliance Role
The corporate bond ratings in India are enabled by the regulatory authorities, weighing heavily on the promotion of transparency and investor protection. Rating information must be disclosed in the offer documents of companies issuing bonds. The regulatory authorities maintain an oversight ensuring regular updates of ratings and standardized methodologies to be used by rating agencies.
This compliance assures greater trust among investors to invest in bonds in India. Ratings lend an authoritative voice to providing evidence that remains consistent and stable, which aids in the assessment of risk by the investors while maintaining confidence in the corporate debt market.
Challenges and Limitations of Ratings
While corporate bond ratings are important instruments in the market, they do have their limitations. Ratings provide the historical and current state of financial affairs, but often fail to withstand sudden shocks in the market or unanticipated events. Investors need to combine ratings with independent inquiry and market analysis.
Conclusion
The impact of a corporate bond rating on investor confidence in bonds in India is thus huge. They provide a reasonable degree of standardization in measuring credit risk, influencing yields, liquidity, and portfolio diversification. Ratings, too, have a psychological aspect that impacts the trader-rated market sentiment.
While ratings remain eminent tools for credibility, investors should use them in conjunction with independent analysis, along with conscious knowledge of their own risk tolerance. This enables integrating bonds in India, whose ratings have guided toward systematic investment and into the balanced financial plan. Understanding the role of ratings will enable the investor to characterize the corporate bond market with lucidity and confidence. They become capable of considering options based on risk, yields, and portfolio allocation.
-
Business2 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business2 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business2 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health2 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports2 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom