Technology Explained
Future of AI in Creative Industries

Integration of AI in Artistic Processes

Image by : Yandex
Transforming creative workflows: Future of AI in Creative Industries. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into artistic processes is revolutionizing how creative workflows are structured and executed. This transformation is not merely a matter of automating repetitive tasks; it is reshaping the very essence of creativity. AI technologies, such as machine learning algorithms and neural networks, are being utilized to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate new ideas.
This capability allows artists and designers to explore uncharted territories and push the boundaries of their creativity. For instance, AI can assist in generating unique visual art pieces by analyzing existing artworks and creating new compositions that blend different styles and techniques. This not only saves time but also opens up new avenues for artistic expression. As a result, the future of AI in creative industries promises a dynamic and collaborative environment where human creativity is augmented by the computational power of AI, leading to innovative and groundbreaking artistic endeavors.
Enhancing artistic innovation:
Future of AI in Creative Industries. AI is not just a tool for efficiency; it is a catalyst for artistic innovation. By leveraging AI technologies, artists can experiment with new forms, styles, and mediums that were previously unimaginable. For example, AI-driven generative design allows artists to input specific parameters and constraints, and the AI system generates multiple design options that meet those criteria. This iterative process enables artists to explore a wide range of possibilities and refine their ideas more effectively.
Moreover, AI can assist in the creation of interactive and immersive experiences, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) installations, by generating realistic and dynamic content in real-time. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of traditional art forms and creating new opportunities for artistic expression. The future of AI in creative industries is one where artists and AI systems collaborate seamlessly, resulting in innovative and captivating artworks that captivate audiences and challenge conventional notions of creativity.
AI-Driven Innovation in Media Production:

Image by : Yandex
AI-enhanced storytelling revolutionizing media production processes. The future of AI in creative industries is poised to revolutionize media production processes, particularly in the realm of storytelling. AI technologies are being employed to analyze vast amounts of data, including audience preferences, historical trends, and narrative structures, to generate compelling and engaging stories. This AI-enhanced storytelling process allows content creators to tailor their narratives to specific target audiences, resulting in more personalized and impactful experiences.
Additionally, AI can assist in the creation of dynamic and adaptive storylines that respond to user interactions in real-time, creating immersive and interactive narratives. This level of customization and interactivity was previously unattainable, but with AI, it is becoming a reality. As a result, the future of AI in creative industries holds the promise of transforming how stories are conceived, produced, and consumed, leading to a new era of media production that is more engaging, relevant, and captivating.
Ethical Considerations in AI Creativity:
Ensuring ethical AI use in creative industry advancements. As AI technologies become increasingly integrated into creative industries, it is imperative to address the ethical considerations associated with their use. Ensuring ethical AI use in creative industry advancements involves establishing guidelines and standards that promote transparency, accountability, and fairness. One of the primary concerns is the potential for AI-generated content to infringe on intellectual property rights and artistic integrity. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to implement robust copyright protection mechanisms and ensure that AI systems are trained on ethically sourced data.
Additionally, there is a need to address issues related to bias and representation in AI-generated content. AI algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate stereotypes and biases present in the training data, leading to harmful and discriminatory outcomes. To counteract this, it is crucial to develop diverse and inclusive datasets and continuously monitor and audit AI systems for bias. By prioritizing ethical considerations, the future of AI in creative industries can be guided by principles that uphold artistic integrity, promote diversity, and ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and ethically.
Impact of AI on Employment in Creative Fields:
Balancing AI innovation with ethical creative industry standards. The rapid advancements in AI technology present a unique challenge in balancing innovation with ethical creative industry standards. While AI has the potential to revolutionize creative processes and outputs, it is essential to ensure that these advancements do not compromise ethical standards. This involves fostering a culture of ethical awareness and responsibility among AI developers, artists, and industry stakeholders.
Collaborative efforts are needed to establish industry-wide ethical guidelines and best practices that address the potential risks and challenges associated with AI creativity. These guidelines should encompass issues such as data privacy, consent, and the responsible use of AI-generated content. Additionally, it is crucial to involve diverse perspectives and voices in the development and deployment of AI technologies to ensure that they reflect a wide range of cultural and societal values. By striking a balance between AI innovation and ethical standards, the future of AI in creative industries can be shaped in a way that fosters creativity, inclusivity, and social responsibility.
Job displacement and transformation:
Image by : Yandex
The integration of AI in creative industries is likely to have a significant impact on employment, leading to both job displacement and transformation. On one hand, AI technologies can automate routine and repetitive tasks, potentially displacing certain roles within the creative workforce. For example, AI-powered design tools can generate layouts and graphics, reducing the need for manual design work. Similarly, automated editing software can perform tasks that were traditionally done by human editors.
However, it is important to note that while some jobs may be displaced, new opportunities will also emerge. The demand for AI specialists, data analysts, and creative technologists is expected to rise as AI becomes more prevalent in the creative industries. Moreover, the integration of AI can lead to the creation of new roles that combine technical expertise with artistic skills, such as AI-assisted artists and AI-driven content creators. The future of AI in creative industries will require a workforce that is adaptable and equipped with the skills to navigate the evolving landscape, ultimately leading to a transformation in how creative work is performed and valued.
Future of AI in Creative Industries:
Enhancing creative processes and outputs. While the impact of AI on employment in creative fields may raise concerns, it is important to recognize the potential for AI to enhance creative processes and outputs. AI technologies can serve as powerful tools that augment human creativity and enable artists to achieve new levels of innovation and excellence. For instance, AI can assist in generating ideas, providing inspiration, and facilitating collaboration among artists. By analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns, AI can offer valuable insights and suggestions that can inform and enhance the creative process. Additionally, AI can streamline workflows and automate time-consuming tasks, allowing artists to focus more on the conceptual and expressive aspects of their work.
This can lead to higher quality and more diverse creative outputs. Furthermore, AI can enable new forms of artistic expression, such as interactive installations, generative art, and immersive experiences, that were previously unattainable. The future of AI in creative industries holds the promise of a symbiotic relationship between human creativity and AI technologies, resulting in enhanced creative processes and outputs that push the boundaries of what is possible.
Future Trends in AI and Creativity:
AI-generated art transforming creative industries’ future. The emergence of AI-generated art is poised to transform the future of creative industries. AI algorithms, such as generative adversarial networks (GANs) and deep learning models, have demonstrated the ability to create original and compelling artworks that rival those produced by human artists. These AI-generated art pieces can range from paintings and sculptures to digital installations and multimedia experiences.
The potential of AI-generated art lies in its ability to explore new artistic styles, experiment with different techniques, and generate novel compositions that challenge traditional notions of creativity. Moreover, AI-generated art can serve as a source of inspiration and collaboration for human artists, offering new perspectives and ideas that can inform their own creative practices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the future of AI in creative industries is marked by transformative advancements that are reshaping artistic processes, media production, ethical considerations, employment, and future trends. As AI continues to evolve and integrate into creative workflows, it holds the potential to enhance artistic innovation, revolutionize media production, address ethical challenges, impact employment, and shape the future of creativity.
The symbiotic relationship between human creativity and AI technologies promises a dynamic and collaborative environment where new forms of artistic expression and innovation can thrive. By embracing the potential of AI while upholding ethical standards, the creative industries can navigate this transformative journey and unlock new possibilities for artistic excellence and cultural enrichment.
Development
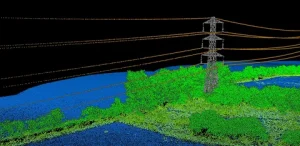
Enhancing Mapping Accuracy with LiDAR Ground Control Targets
How Do LiDAR Ground Control Targets Work?
LiDAR technology uses laser pulses to scan the ground and capture a wide range of data, including elevation, shape, and distance. However, the data collected by LiDAR sensors needs to be aligned with real-world coordinates to ensure its accuracy. This is where LiDAR ground control targets come in.
Georeferencing LiDAR Data
When LiDAR sensors capture data, they record it as a point cloud, an array of data points representing the Earth’s surface. To make sense of these data points, surveyors need to assign them precise coordinates. Ground control targets provide reference points, allowing surveyors to georeference point cloud data and ensure that LiDAR data aligns with existing maps and models.
By placing LiDAR ground control targets at specific locations on the survey site, surveyors can perform adjustments to correct discrepancies in the data caused by factors such as sensor calibration, flight altitude, or atmospheric conditions.
Why Are LiDAR Ground Control Targets Essential for Accurate Mapping?
LiDAR technology is incredibly powerful, but the accuracy of the data depends largely on the quality of the ground control points used. Here are the key reasons why LiDAR ground control targets are essential for obtaining precise mapping results:
1. Improved Geospatial Accuracy
Without ground control targets, LiDAR data is essentially “floating” in space, meaning its position isn’t aligned with real-world coordinates. This can lead to errors and inaccuracies in the final map or model. By placing LiDAR ground control targets at known geographic coordinates, surveyors can calibrate the LiDAR data and improve its geospatial accuracy.
For large projects or those involving multiple data sources, ensuring that LiDAR data is properly georeferenced is critical. Ground control targets help ensure the survey data integrates seamlessly with other geographic information systems (GIS) or mapping platforms.
2. Reduction of Measurement Errors
LiDAR ground control targets help mitigate errors caused by various factors, such as:
- Sensor misalignment: Minor inaccuracies in the LiDAR sensor’s position or angle can cause discrepancies in the data.
- Aircraft or drone movement can slightly distort the sensor’s collected data.
- Environmental conditions: Weather, temperature, and atmospheric pressure can all affect the LiDAR signal.
By using ground control targets, surveyors can compensate for these errors, leading to more precise and reliable data.
3. Support for Large-Scale Projects
For larger mapping projects, multiple LiDAR scans might be conducted from different flight paths or at different times. Ground control targets serve as common reference points, ensuring that all collected data can be merged into a single coherent model. This is particularly useful for projects involving vast areas like forests, mountain ranges, or large urban developments.
How to Choose the Right LiDAR Ground Control Targets
Choosing the right LiDAR ground control targets depends on several factors, including the project’s size, the terrain, and the required accuracy. Here are some things to consider:
Size and Visibility
The size of the target should be large enough to be easily detectable by the LiDAR sensor from the air. Targets that are too small or poorly placed can lead to inaccurate data or missed targets.
Material and Durability
Ground control targets must have enough durability to withstand weather conditions and remain stable throughout the surveying process. Surveyors often use reflective materials to ensure that the LiDAR sensor can clearly detect the target, even from a distance.
Geospatial Accuracy
For high-accuracy projects, surveyors must place ground control targets at precise, known locations with accurate geospatial coordinates. They should use a GPS or GNSS system to measure and mark the exact position of the targets.
Conclusion
LiDAR ground control targets play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy of aerial surveys and LiDAR mapping projects. By providing precise reference points for geo referencing and adjusting LiDAR data, these targets reduce errors and improve the overall quality of the final model. Whether you’re working on a small-scale project or a large-scale survey, integrating ground control targets into your LiDAR workflow is essential for achieving high-precision results.
The right ground control targets, when placed correctly and properly measured, can make the difference between reliable, actionable data and inaccurate measurements that undermine the entire survey.
By understanding the importance of these targets and how they function in the context of LiDAR surveys, you’ll be better prepared to tackle projects that demand accuracy and precision.
Digital Development
Scalable Web Application Development: Strategies for Growth
Consumer Services
Cloud Downtime: Essential for Infrastructure Management

Downtime never comes with a warning. It doesn’t care if you’re launching a feature, running a campaign, or sleeping peacefully. It just shows up — and when it does, the damage goes far beyond a broken dashboard.
I’ve seen teams lose users, revenue, and confidence within minutes of an outage. What’s frustrating is this: most downtime isn’t caused by the cloud itself. It’s caused by how the cloud is managed. That’s where cloud downtime infrastructure management stops being a technical checkbox and becomes a business-critical discipline.

Downtime Is a Management Failure, Not a Cloud Failure
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are built for resilience. They fail occasionally — yes — but widespread outages usually trace back to internal issues like:
- No proper load balancing or failover
- Systems not designed for traffic spikes
- Manual deployments without rollback plans
- Weak monitoring that reacts too late
- Security gaps that turn into system crashes
The cloud gives you power. Poor infrastructure decisions turn that power into risk.
What “Stopping Downtime Cold” Really Means
It doesn’t mean hoping nothing breaks.
It means expecting failure and designing systems that survive it.
Strong cloud infrastructure management focuses on four core pillars.
1. Architecture Built for Failure
If your system collapses when one service fails, it was never stable to begin with.
High-availability infrastructure includes:
- Load balancers across multiple availability zones
- Auto-scaling that reacts before performance drops
- Redundant services so failures stay isolated
When architecture is done right, failures don’t become incidents — they become background noise.
2. Proactive Monitoring Instead of Panic Alerts
If customers are the first ones to notice downtime, you’re already late.
Modern cloud environments rely on:
- Real-time health monitoring
- Smart alerts that trigger before limits are reached
- Centralized logs for faster root-cause analysis
Cloud providers themselves emphasize observability because visibility is what turns outages into manageable events instead of full-blown crises.
3. Automation That Removes Human Error
Manual processes are one of the biggest causes of downtime.
Teams that prioritize stability automate:
- Infrastructure provisioning
- Scaling rules
- Backups and disaster recovery
- CI/CD deployments with safe rollbacks
Automation doesn’t just save time — it prevents mistakes, especially during high-pressure moments.
4. Security That Protects Stability
Security incidents are downtime.
Unpatched systems, exposed credentials, and poor access controls often end with services being taken offline.
Strong cloud management includes:
- Continuous security monitoring
- Role-based access control
- Encrypted data pipelines
- Automated patching and compliance checks
Security and uptime aren’t separate goals. They depend on each other.
Where Growing Teams Usually Slip
Here’s something I’ve seen far too often. A product starts gaining traction, traffic slowly increases, integrations pile up, and suddenly the infrastructure that once felt “solid” starts showing cracks. Not all at once but in subtle, dangerous ways. Pages load a little slower. Deployments feel riskier. Minor incidents start happening more frequently, yet they’re brushed off as one-off issues. Teams stay focused on shipping features because growth feels urgent, while infrastructure quietly falls behind. The problem is that cloud systems don’t fail dramatically at first — they degrade.
And by the time downtime becomes visible to users, the technical debt has already piled up. Without regular audits, performance optimization, and proactive scaling strategies, even well-designed cloud environments become fragile over time. This is usually the point where teams realize that cloud infrastructure isn’t something you “set and forget.” It’s a living system that needs continuous attention to stay reliable under real-world pressure.
The Hidden Cost of “Mostly Stable” Systems
A lot of companies settle for “good enough.”
99% uptime sounds impressive — until you realize that’s more than three days of downtime per year.
Now add:
- Lost transactions
- User churn
- Support overload
- Engineering burnout
Suddenly, downtime isn’t a technical issue. It’s a growth blocker.
Reliable infrastructure doesn’t just protect systems — it protects momentum.
Where Growing Teams Usually Slip
I’ve noticed this pattern again and again.
Teams invest heavily in:
- Product features
- Design improvements
- Marketing and growth
But infrastructure gets treated as:
“We’ll fix it when it breaks.”
The problem is that cloud environments are not static. Traffic grows, data scales, integrations multiply. Without continuous management, even well-built systems degrade over time.
That’s why many scaling companies eventually move toward structured cloud engineering practices that focus on long-term reliability, not just initial setup.
Stability Feels Boring — And That’s the Goal
The best infrastructure doesn’t get attention.
It feels boring because:
- Deployments don’t cause anxiety
- Traffic spikes don’t break systems
- Incidents resolve quietly or automatically
That calm is the result of intentional decisions, not luck.
Downtime thrives in chaos.
Stability thrives in preparation.
Final Thoughts
Downtime isn’t inevitable. It’s a signal that systems weren’t built — or managed — for reality. Cloud infrastructure management isn’t about keeping servers running. It’s about protecting user trust, revenue, and your team’s sanity. When infrastructure is resilient, everything else moves faster.
Ready to Stop Worrying About Downtime?
If your platform is scaling — or planning to — reliable cloud downtime infrastructure isn’t optional anymore. The right cloud engineering approach doesn’t just reduce outages.
It removes fear from growth. Explore what resilient, production-ready cloud infrastructure looks like here:
Build for failure. Scale with confidence. And make downtime something your users never have to think about.
-
Business3 years ago
Cybersecurity Consulting Company SequelNet Provides Critical IT Support Services to Medical Billing Firm, Medical Optimum
-
Business3 years ago
Team Communication Software Transforms Operations at Finance Innovate
-
Business3 years ago
Project Management Tool Transforms Long Island Business
-
Business2 years ago
How Alleviate Poverty Utilized IPPBX’s All-in-One Solution to Transform Lives in New York City
-
health3 years ago
Breast Cancer: The Imperative Role of Mammograms in Screening and Early Detection
-
Sports3 years ago
Unstoppable Collaboration: D.C.’s Citi Open and Silicon Valley Classic Unite to Propel Women’s Tennis to New Heights
-
Art /Entertainment3 years ago
Embracing Renewal: Sizdabedar Celebrations Unite Iranians in New York’s Eisenhower Park
-
Finance3 years ago
The Benefits of Starting a Side Hustle for Financial Freedom